How to Calculate Value at Risk (VaR) for a Trading Strategy
Understanding how to accurately calculate Value at Risk (VaR) is essential for traders and risk managers aiming to quantify potential losses in their portfolios. This article provides a comprehensive guide on the process, methods, and considerations involved in calculating VaR for trading strategies, ensuring you have the knowledge needed to implement effective risk management practices.
What Is Value at Risk (VaR)?
Value at Risk (VaR) is a statistical measure that estimates the maximum expected loss of a portfolio over a specified time horizon with a given confidence level. For example, if your portfolio has a 1-day VaR of $1 million at 95% confidence, it implies there’s only a 5% chance that losses will exceed this amount within one day. Traders use VaR as an essential tool to understand potential downside risks and allocate capital accordingly.
Why Is Calculating VaR Important in Trading?
In trading environments, where market volatility can be unpredictable, quantifying potential losses helps traders make informed decisions about position sizing and risk exposure. Accurate VaR calculations enable traders to set stop-loss levels, determine appropriate leverage limits, and comply with regulatory requirements such as Basel Accords. Moreover, understanding the limitations of VaR ensures that traders do not rely solely on this metric but incorporate additional risk measures like Expected Shortfall or stress testing.
Key Steps in Calculating VaR for Your Trading Strategy
Calculating VaR involves several systematic steps designed to analyze historical data or simulate future scenarios:
1. Define Your Time Horizon
The first step is selecting an appropriate time frame over which you want to estimate potential losses—commonly one day for intraday trading or longer periods like one month depending on your strategy. The choice depends on your trading frequency and investment horizon; shorter horizons are typical for active traders while longer ones suit institutional investors.
2. Select Confidence Level
Next is choosing the confidence level—usually set at 95% or 99%. This percentage indicates how confident you are that actual losses will not exceed your calculated VaR during the specified period. Higher confidence levels provide more conservative estimates but may also lead to larger capital reserves being set aside.
3. Gather Historical Data
Historical data forms the backbone of most VaR calculations. You need sufficient past price movements or returns relevant to your assets or portfolio components—such as stocks, commodities, currencies—to model future risks accurately.
4. Estimate Return Distribution
Using historical data points collected over your chosen period—for example: daily returns over six months—you estimate how asset prices have historically behaved by modeling their return distribution. This can involve calculating mean returns and standard deviations if assuming normality or fitting other distributions based on empirical data.
5. Calculate Portfolio Returns
For portfolios containing multiple assets with different weights, compute combined returns considering correlations among assets:
- Weighted Returns: Multiply each asset's return by its proportion in the portfolio.
- Covariance Matrix: Use historical covariance between assets' returns for more precise modeling.This step ensures you capture diversification effects when estimating overall portfolio risk.
6. Determine Quantiles Based on Distribution
Depending on your chosen method:
- For Historical VaR, identify percentile thresholds directly from historical return data.
- For Parametric Methods, calculate quantiles assuming specific distributions like normal distribution.
- For Monte Carlo Simulation, generate numerous simulated paths based on estimated parameters (mean/variance/covariance), then analyze these simulations’ outcomes.
7. Compute Final VaR Estimate
Finally:
- In Historical methods: select the loss value corresponding to your confidence percentile.
- In Parametric approaches: use statistical formulas involving mean return minus z-score times standard deviation.
- In Monte Carlo simulations: determine percentile loss across all simulated outcomes.This result represents your estimated maximum expected loss within the defined parameters.
Common Methods Used in Calculating VaRs
Different techniques exist depending upon complexity needs and available data:
Historical Simulation:
Uses actual past market movements without assuming any specific distribution; straightforward but relies heavily on recent history which may not predict future extremes effectively.
Parametric Method:
Assumes asset returns follow known distributions such as normal distribution; computationally simple but may underestimate tail risks during volatile periods when assumptions break down.
Monte Carlo Simulation:
Generates thousands of possible future scenarios based on stochastic models; highly flexible allowing incorporation of complex features like non-normality but computationally intensive requiring robust models and high-quality input data.
Considerations When Applying These Methods
While calculating VaRs provides valuable insights into potential risks faced by trading strategies, it’s crucial also recognize its limitations:
Model Assumptions: Many methods assume stable market conditions which might not hold during crises leading to underestimation of extreme events.
Data Quality: Reliable historic price data is vital; missing information can distort results significantly.
Time Horizon & Confidence Level: Longer horizons increase uncertainty; higher confidence levels produce more conservative estimates but require larger capital buffers.
By understanding these factors upfront—and supplementing quantitative analysis with qualitative judgment—you enhance overall risk management robustness.
Incorporating Stress Testing & Complementary Measures
Given some limitations inherent in traditional VAR models—especially during extraordinary market events—it’s advisable also employ stress testing alongside VAR calculations:
- Simulate extreme scenarios beyond historical experience
- Assess impact under hypothetical shocks
- Combine results with other metrics such as Expected Shortfall
These practices help ensure comprehensive coverage against unforeseen risks affecting trading positions.
Practical Tips for Traders Using Variance-Based Models
To optimize VA R calculation accuracy:
– Regularly update input data reflecting current market conditions
– Adjust model parameters when significant shifts occur
– Use multiple methods concurrently—for instance combining Historical simulation with Monte Carlo approaches
– Maintain awareness of model assumptions versus real-world dynamics
Implementing these best practices enhances decision-making precision while aligning with regulatory standards.
How Regulatory Frameworks Influence Your Calculation Approach
Regulatory bodies like Basel Accords mandate financial institutions maintain sufficient capital reserves based partly upon their calculated VA R figures—a process emphasizing transparency and robustness in measurement techniques:
– Ensure compliance through documented methodologies – Validate models periodically – Incorporate stress testing results into overall risk assessments
Adhering strictly helps avoid penalties while fostering trust among stakeholders.
Calculating Value at Risk effectively requires understanding both statistical techniques and practical considerations unique to each trading strategy's context — including asset types involved , time horizons ,and desired confidence levels . By following structured steps—from gathering reliable historic data through sophisticated simulation—and recognizing inherent limitations,you can develop robust measures that support prudent decision-making amid volatile markets . Remember always complement quantitative analysis with qualitative judgment,and stay updated regarding evolving best practices within financial risk management frameworks .


kai
2025-05-09 22:08
How do you calculate Value at Risk (VaR) for a trading strategy?
How to Calculate Value at Risk (VaR) for a Trading Strategy
Understanding how to accurately calculate Value at Risk (VaR) is essential for traders and risk managers aiming to quantify potential losses in their portfolios. This article provides a comprehensive guide on the process, methods, and considerations involved in calculating VaR for trading strategies, ensuring you have the knowledge needed to implement effective risk management practices.
What Is Value at Risk (VaR)?
Value at Risk (VaR) is a statistical measure that estimates the maximum expected loss of a portfolio over a specified time horizon with a given confidence level. For example, if your portfolio has a 1-day VaR of $1 million at 95% confidence, it implies there’s only a 5% chance that losses will exceed this amount within one day. Traders use VaR as an essential tool to understand potential downside risks and allocate capital accordingly.
Why Is Calculating VaR Important in Trading?
In trading environments, where market volatility can be unpredictable, quantifying potential losses helps traders make informed decisions about position sizing and risk exposure. Accurate VaR calculations enable traders to set stop-loss levels, determine appropriate leverage limits, and comply with regulatory requirements such as Basel Accords. Moreover, understanding the limitations of VaR ensures that traders do not rely solely on this metric but incorporate additional risk measures like Expected Shortfall or stress testing.
Key Steps in Calculating VaR for Your Trading Strategy
Calculating VaR involves several systematic steps designed to analyze historical data or simulate future scenarios:
1. Define Your Time Horizon
The first step is selecting an appropriate time frame over which you want to estimate potential losses—commonly one day for intraday trading or longer periods like one month depending on your strategy. The choice depends on your trading frequency and investment horizon; shorter horizons are typical for active traders while longer ones suit institutional investors.
2. Select Confidence Level
Next is choosing the confidence level—usually set at 95% or 99%. This percentage indicates how confident you are that actual losses will not exceed your calculated VaR during the specified period. Higher confidence levels provide more conservative estimates but may also lead to larger capital reserves being set aside.
3. Gather Historical Data
Historical data forms the backbone of most VaR calculations. You need sufficient past price movements or returns relevant to your assets or portfolio components—such as stocks, commodities, currencies—to model future risks accurately.
4. Estimate Return Distribution
Using historical data points collected over your chosen period—for example: daily returns over six months—you estimate how asset prices have historically behaved by modeling their return distribution. This can involve calculating mean returns and standard deviations if assuming normality or fitting other distributions based on empirical data.
5. Calculate Portfolio Returns
For portfolios containing multiple assets with different weights, compute combined returns considering correlations among assets:
- Weighted Returns: Multiply each asset's return by its proportion in the portfolio.
- Covariance Matrix: Use historical covariance between assets' returns for more precise modeling.This step ensures you capture diversification effects when estimating overall portfolio risk.
6. Determine Quantiles Based on Distribution
Depending on your chosen method:
- For Historical VaR, identify percentile thresholds directly from historical return data.
- For Parametric Methods, calculate quantiles assuming specific distributions like normal distribution.
- For Monte Carlo Simulation, generate numerous simulated paths based on estimated parameters (mean/variance/covariance), then analyze these simulations’ outcomes.
7. Compute Final VaR Estimate
Finally:
- In Historical methods: select the loss value corresponding to your confidence percentile.
- In Parametric approaches: use statistical formulas involving mean return minus z-score times standard deviation.
- In Monte Carlo simulations: determine percentile loss across all simulated outcomes.This result represents your estimated maximum expected loss within the defined parameters.
Common Methods Used in Calculating VaRs
Different techniques exist depending upon complexity needs and available data:
Historical Simulation:
Uses actual past market movements without assuming any specific distribution; straightforward but relies heavily on recent history which may not predict future extremes effectively.
Parametric Method:
Assumes asset returns follow known distributions such as normal distribution; computationally simple but may underestimate tail risks during volatile periods when assumptions break down.
Monte Carlo Simulation:
Generates thousands of possible future scenarios based on stochastic models; highly flexible allowing incorporation of complex features like non-normality but computationally intensive requiring robust models and high-quality input data.
Considerations When Applying These Methods
While calculating VaRs provides valuable insights into potential risks faced by trading strategies, it’s crucial also recognize its limitations:
Model Assumptions: Many methods assume stable market conditions which might not hold during crises leading to underestimation of extreme events.
Data Quality: Reliable historic price data is vital; missing information can distort results significantly.
Time Horizon & Confidence Level: Longer horizons increase uncertainty; higher confidence levels produce more conservative estimates but require larger capital buffers.
By understanding these factors upfront—and supplementing quantitative analysis with qualitative judgment—you enhance overall risk management robustness.
Incorporating Stress Testing & Complementary Measures
Given some limitations inherent in traditional VAR models—especially during extraordinary market events—it’s advisable also employ stress testing alongside VAR calculations:
- Simulate extreme scenarios beyond historical experience
- Assess impact under hypothetical shocks
- Combine results with other metrics such as Expected Shortfall
These practices help ensure comprehensive coverage against unforeseen risks affecting trading positions.
Practical Tips for Traders Using Variance-Based Models
To optimize VA R calculation accuracy:
– Regularly update input data reflecting current market conditions
– Adjust model parameters when significant shifts occur
– Use multiple methods concurrently—for instance combining Historical simulation with Monte Carlo approaches
– Maintain awareness of model assumptions versus real-world dynamics
Implementing these best practices enhances decision-making precision while aligning with regulatory standards.
How Regulatory Frameworks Influence Your Calculation Approach
Regulatory bodies like Basel Accords mandate financial institutions maintain sufficient capital reserves based partly upon their calculated VA R figures—a process emphasizing transparency and robustness in measurement techniques:
– Ensure compliance through documented methodologies – Validate models periodically – Incorporate stress testing results into overall risk assessments
Adhering strictly helps avoid penalties while fostering trust among stakeholders.
Calculating Value at Risk effectively requires understanding both statistical techniques and practical considerations unique to each trading strategy's context — including asset types involved , time horizons ,and desired confidence levels . By following structured steps—from gathering reliable historic data through sophisticated simulation—and recognizing inherent limitations,you can develop robust measures that support prudent decision-making amid volatile markets . Remember always complement quantitative analysis with qualitative judgment,and stay updated regarding evolving best practices within financial risk management frameworks .
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Subzero Labs completed a $20 million seed round led by Pantera Capital to build Rialo—the first full-stack blockchain network for real-world applications, bridging Web2 usability with Web3 capabilities. Here are the project's core highlights:
💰 Project Features:
-
Native Real-World Connectivity: Direct integration with web services, no complex middleware needed
Event-Driven Transactions: Automatic execution based on real-world triggers like package delivery, weather insurance
Real-World Data Access: Built-in FICO scores, weather data, market information, and other off-chain data
RISC-V & Solana VM Compatibility: Developers can reuse existing tools and code
🎯 Technical Advantages: 1️⃣ Invisible Infrastructure: Simplified development workflow, letting developers focus on product innovation 2️⃣ Privacy Protection: Suitable for regulated industries like healthcare and finance 3️⃣ Cross-Platform Compatibility: Seamlessly integrate existing systems with blockchain technology 4️⃣ Developer-Centric: Eliminates complex oracle, cross-chain bridge integrations
🏆 Funding Lineup:
-
Lead: Pantera Capital
Participants: Coinbase Ventures, Hashed, Susquehanna Crypto, Mysten Labs, Fabric Ventures, etc.
Investor Quote: "The only full-stack network for real-world applications"
💡 Team Background:
-
Founders: Ade Adepoju (former Netflix distributed systems, AMD microchips) & Lu Zhang (former Meta Diem project, large-scale AI/ML infrastructure)
Team from: Meta, Apple, Amazon, Netflix, Google, Solana, Coinbase, and other top-tier companies
Early engineers from Mysten Labs who contributed to Sui network development
🔐 Use Cases:
-
Asset Tokenization: Real estate, commodities, private equity
Prediction Markets: Event-driven automatic settlement
Global Trading: Cross-border payment and settlement systems
AI Agent Orchestration & Supply Chain Management
IoT-integrated tracking and verification
🌟 Market Positioning:
-
Solving Developer Retention Crisis: Simplifying blockchain development complexity
Serving trillion-dollar real-world asset tokenization market
Different from throughput-focused Layer-1s, emphasizing practicality and real applications
📱 Development Progress:
-
Private devnet now live
Early development partner testing underway
Public launch timeline in preparation (specific dates TBD)
Developers can join waitlist for early access
🔮 Core Philosophy: "Rialo isn't a Layer 1"—By making blockchain infrastructure "invisible," developers can build truly real-world connected decentralized applications, rather than just pursuing transaction speed metrics.
Rialo, with strong funding support, top-tier team background, and revolutionary technical architecture, is positioned to drive blockchain technology's transition from experimental protocols to production-ready applications as key infrastructure.
Read the complete technical architecture analysis: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/rialo-blockchain-guide/?utm_source=blog
#Rialo #SubzeroLabs #Blockchain #RealWorldAssets



JU Blog
2025-08-05 10:30
🚀 Rialo Blockchain: $20M Seed Round Building Revolutionary Web3 Infrastructure!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
3 Days Left! The JuCoin Million Airdrop is going wild! 🎉
👉 RT and lock in your Hashrate airdrop:
✅ KYC
✅ Activate JU Node
🎰 100% win rate Lucky Wheel — win up to 1,000U in a single spin 👉 https://bit.ly/4eDheON
#Jucoin #JucoinVietnam #Airdrop


Lee Jucoin
2025-08-14 03:26
The JuCoin Million Airdrop
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🔍About #Xpayra:
🔹Xpayra is a next-generation crypto-financial infrastructure that combines PayFi concepts with Web3 technology, committed to reshaping diversified on-chain financial services such as stablecoin settlement, virtual card payments, and decentralized lending.
🔹The project adopts a modular smart contract framework, zero-knowledge technology, and a high-performance asset aggregation engine to achieve secure interoperability and aggregation of funds, data, and rights across multiple chains.
👉 More Detail:https://bit.ly/45efKr5
#Jucoin #JucoinVietnam#Xpayra #Airdrop


Lee Jucoin
2025-08-14 03:24
📣Xpayra Officially Joins the JuCoin Ecosystem
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Engle-Granger Two-Step Method for Cointegration Analysis?
The Engle-Granger two-step method is a foundational statistical approach used in econometrics to identify and analyze long-term relationships between non-stationary time series data. This technique helps economists, financial analysts, and policymakers understand whether variables such as interest rates, exchange rates, or commodity prices move together over time in a stable manner. Recognizing these relationships is essential for making informed decisions based on economic theories and market behaviors.
Understanding Cointegration in Time Series Data
Before diving into the specifics of the Engle-Granger method, it’s important to grasp what cointegration entails. In simple terms, cointegration occurs when two or more non-stationary time series are linked by a long-term equilibrium relationship. Although each individual series may exhibit trends or cycles—making them non-stationary—their linear combination results in a stationary process that fluctuates around a constant mean.
For example, consider the prices of two related commodities like oil and gasoline. While their individual prices might trend upward over years due to inflation or market dynamics, their price difference could remain relatively stable if they are economically linked. Detecting such relationships allows analysts to model these variables more accurately and forecast future movements effectively.
The Two Main Steps of the Engle-Granger Method
The Engle-Granger approach simplifies cointegration testing into two sequential steps:
Step 1: Testing for Unit Roots (Stationarity) in Individual Series
Initially, each time series under consideration must be tested for stationarity using unit root tests such as the Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) test. Non-stationary data typically show persistent trends or cycles that violate many classical statistical assumptions.
If both series are found to be non-stationary—meaning they possess unit roots—the next step involves examining whether they share a cointegrated relationship. Conversely, if either series is stationary from the outset, traditional regression analysis might suffice without further cointegration testing.
Step 2: Estimating Long-Run Relationship and Testing Residuals
Once confirmed that both variables are integrated of order one (I(1)), meaning they become stationary after differencing once, researchers regress one variable on another using ordinary least squares (OLS). This regression produces residuals representing deviations from this estimated long-term equilibrium relationship.
The critical part here is testing whether these residuals are stationary through another ADF test or similar methods. If residuals turn out to be stationary—that is they fluctuate around zero without trending—then it indicates that the original variables are indeed cointegrated; they move together over time despite being individually non-stationary.
Significance of Cointegration Analysis
Identifying cointegrated relationships has profound implications across economics and finance:
- Long-Term Forecasting: Recognizing stable relationships enables better prediction models.
- Policy Formulation: Governments can design policies knowing certain economic indicators tend to move together.
- Risk Management: Investors can hedge positions based on predictable co-movements between assets.
For instance, if exchange rates and interest rates are found to be cointegrated within an economy's context, monetary authorities might adjust policies with confidence about their long-term effects on currency stability.
Limitations and Critiques of the Engle-Granger Method
Despite its widespread use since its inception in 1987 by Clive Granger and Robert Engle—a Nobel laureate—the method does have notable limitations:
Linearity Assumption: It presumes linear relationships between variables; real-world economic interactions often involve nonlinearities.
Sensitivity to Outliers: Extreme values can distort regression estimates leading to incorrect conclusions about stationarity.
Single Cointegrating Vector: The method tests only for one possible long-run relationship at a time; complex systems with multiple equilibria require more advanced techniques like Johansen’s test.
Structural Breaks Impact: Changes such as policy shifts or economic crises can break existing relationships temporarily or permanently but may not be detected properly by this approach unless explicitly modeled.
Understanding these limitations ensures users interpret results cautiously while considering supplementary analyses where necessary.
Recent Developments Enhancing Cointegration Testing
Since its introduction during the late 20th century, researchers have developed advanced tools building upon or complementing the Engle-Granger framework:
Johansen Test: An extension capable of identifying multiple co-integrating vectors simultaneously within multivariate systems.
Vector Error Correction Models (VECM): These models incorporate short-term dynamics while maintaining insights into long-term equilibrium relations identified through cointegration analysis.
These developments improve robustness especially when analyzing complex datasets involving several interconnected economic indicators simultaneously—a common scenario in modern econometrics research.
Practical Applications Across Economics & Finance
Economists frequently employ engel-granger-based analyses when exploring topics like:
- Long-run purchasing power parity between currencies
- Relationship between stock indices across markets
- Linkages between macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth rate versus inflation
Financial institutions also utilize this methodology for arbitrage strategies where understanding asset price co-movements enhances investment decisions while managing risks effectively.
Summary Table: Key Aspects of Engel–Granger Two-Step Method
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects stable long-term relations among non-stationary variables |
| Main Components | Unit root testing + residual stationarity testing |
| Data Requirements | Variables should be integrated of order one (I(1)) |
| Limitations | Assumes linearity; sensitive to outliers & structural breaks |
By applying this structured approach thoughtfully—and recognizing its strengths alongside limitations—researchers gain valuable insights into how different economic factors interact over extended periods.
In essence, understanding how economies evolve requires tools capable of capturing enduring linkages amidst volatile short-term fluctuations. The Engle-Granger two-step method remains an essential component within this analytical toolkit—helping decode complex temporal interdependencies fundamental for sound econometric modeling and policy formulation.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 22:52
What is the Engle-Granger two-step method for cointegration analysis?
What Is the Engle-Granger Two-Step Method for Cointegration Analysis?
The Engle-Granger two-step method is a foundational statistical approach used in econometrics to identify and analyze long-term relationships between non-stationary time series data. This technique helps economists, financial analysts, and policymakers understand whether variables such as interest rates, exchange rates, or commodity prices move together over time in a stable manner. Recognizing these relationships is essential for making informed decisions based on economic theories and market behaviors.
Understanding Cointegration in Time Series Data
Before diving into the specifics of the Engle-Granger method, it’s important to grasp what cointegration entails. In simple terms, cointegration occurs when two or more non-stationary time series are linked by a long-term equilibrium relationship. Although each individual series may exhibit trends or cycles—making them non-stationary—their linear combination results in a stationary process that fluctuates around a constant mean.
For example, consider the prices of two related commodities like oil and gasoline. While their individual prices might trend upward over years due to inflation or market dynamics, their price difference could remain relatively stable if they are economically linked. Detecting such relationships allows analysts to model these variables more accurately and forecast future movements effectively.
The Two Main Steps of the Engle-Granger Method
The Engle-Granger approach simplifies cointegration testing into two sequential steps:
Step 1: Testing for Unit Roots (Stationarity) in Individual Series
Initially, each time series under consideration must be tested for stationarity using unit root tests such as the Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) test. Non-stationary data typically show persistent trends or cycles that violate many classical statistical assumptions.
If both series are found to be non-stationary—meaning they possess unit roots—the next step involves examining whether they share a cointegrated relationship. Conversely, if either series is stationary from the outset, traditional regression analysis might suffice without further cointegration testing.
Step 2: Estimating Long-Run Relationship and Testing Residuals
Once confirmed that both variables are integrated of order one (I(1)), meaning they become stationary after differencing once, researchers regress one variable on another using ordinary least squares (OLS). This regression produces residuals representing deviations from this estimated long-term equilibrium relationship.
The critical part here is testing whether these residuals are stationary through another ADF test or similar methods. If residuals turn out to be stationary—that is they fluctuate around zero without trending—then it indicates that the original variables are indeed cointegrated; they move together over time despite being individually non-stationary.
Significance of Cointegration Analysis
Identifying cointegrated relationships has profound implications across economics and finance:
- Long-Term Forecasting: Recognizing stable relationships enables better prediction models.
- Policy Formulation: Governments can design policies knowing certain economic indicators tend to move together.
- Risk Management: Investors can hedge positions based on predictable co-movements between assets.
For instance, if exchange rates and interest rates are found to be cointegrated within an economy's context, monetary authorities might adjust policies with confidence about their long-term effects on currency stability.
Limitations and Critiques of the Engle-Granger Method
Despite its widespread use since its inception in 1987 by Clive Granger and Robert Engle—a Nobel laureate—the method does have notable limitations:
Linearity Assumption: It presumes linear relationships between variables; real-world economic interactions often involve nonlinearities.
Sensitivity to Outliers: Extreme values can distort regression estimates leading to incorrect conclusions about stationarity.
Single Cointegrating Vector: The method tests only for one possible long-run relationship at a time; complex systems with multiple equilibria require more advanced techniques like Johansen’s test.
Structural Breaks Impact: Changes such as policy shifts or economic crises can break existing relationships temporarily or permanently but may not be detected properly by this approach unless explicitly modeled.
Understanding these limitations ensures users interpret results cautiously while considering supplementary analyses where necessary.
Recent Developments Enhancing Cointegration Testing
Since its introduction during the late 20th century, researchers have developed advanced tools building upon or complementing the Engle-Granger framework:
Johansen Test: An extension capable of identifying multiple co-integrating vectors simultaneously within multivariate systems.
Vector Error Correction Models (VECM): These models incorporate short-term dynamics while maintaining insights into long-term equilibrium relations identified through cointegration analysis.
These developments improve robustness especially when analyzing complex datasets involving several interconnected economic indicators simultaneously—a common scenario in modern econometrics research.
Practical Applications Across Economics & Finance
Economists frequently employ engel-granger-based analyses when exploring topics like:
- Long-run purchasing power parity between currencies
- Relationship between stock indices across markets
- Linkages between macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth rate versus inflation
Financial institutions also utilize this methodology for arbitrage strategies where understanding asset price co-movements enhances investment decisions while managing risks effectively.
Summary Table: Key Aspects of Engel–Granger Two-Step Method
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects stable long-term relations among non-stationary variables |
| Main Components | Unit root testing + residual stationarity testing |
| Data Requirements | Variables should be integrated of order one (I(1)) |
| Limitations | Assumes linearity; sensitive to outliers & structural breaks |
By applying this structured approach thoughtfully—and recognizing its strengths alongside limitations—researchers gain valuable insights into how different economic factors interact over extended periods.
In essence, understanding how economies evolve requires tools capable of capturing enduring linkages amidst volatile short-term fluctuations. The Engle-Granger two-step method remains an essential component within this analytical toolkit—helping decode complex temporal interdependencies fundamental for sound econometric modeling and policy formulation.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Mais sous cette surface calme, les zones se dessinent…
🟥 Zone rouge : le support a tenu, mais reste un terrain miné
🟨 Zone jaune : entre neutralité et pivot psychologique
🟦 Zone bleue: un champ de bataille à fort volume. Et si le $BTC/USDT l’atteint… cela pourrait enclencher un nouveau momentum.
🔍 Ce type de configuration est souvent le théâtre de mouvements violents — et imprévisibles.
🧠 Ce n’est pas le moment de FOMO, mais d’observer... stratégiquement.
💬 Tu es team breakout ou team range ? Dis-moi ce que tu vois dans le graphe.
#BTC #PriceAction #CryptoMarket
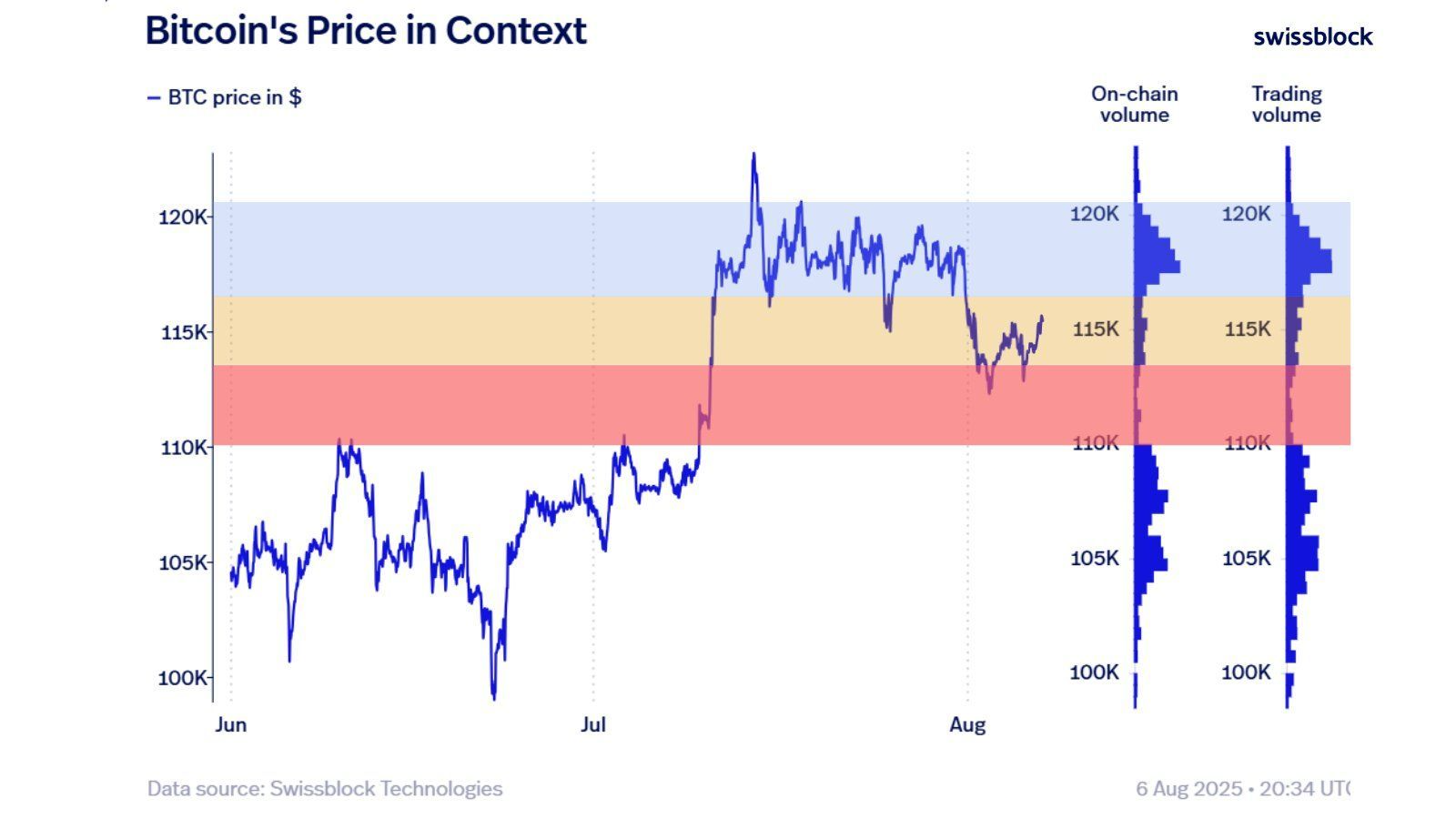


Carmelita
2025-08-07 14:10
🎯 Le marché du Bitcoin est en mode "stand-by" — pas de cassure haussière, pas d’effondrement non pl
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Protect Your Crypto Assets from Scams
Cryptocurrency investments have surged in popularity, but with this growth comes an increased risk of scams and security breaches. Whether you're a seasoned trader or just starting out, understanding how to safeguard your digital assets is essential. This guide covers the most effective strategies to protect your crypto holdings from common threats like phishing, fraud, and hacking.
Understanding Common Cryptocurrency Scams
Crypto scams come in various forms, often targeting individuals who are less familiar with digital security practices. Phishing remains one of the most prevalent tactics—fraudulent emails or messages impersonate legitimate exchanges or service providers to steal private keys or login credentials. Ponzi schemes promise high returns but collapse once new investors stop joining. Fake exchanges lure users into depositing funds that are never recovered, while social engineering attacks manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information.
Recent incidents highlight these risks: for example, a widespread toll road scam via text messages has been circulating across the U.S., emphasizing how scammers exploit public trust and fear. Additionally, ransomware attacks on organizations like PowerSchool demonstrate ongoing extortion threats that can impact both institutions and individual users.
Use Secure Wallets for Storing Crypto Assets
A critical step in safeguarding your cryptocurrencies is choosing secure wallets designed specifically for crypto storage. Hardware wallets such as Ledger Nano S/X and Trezor offer cold storage solutions—meaning they are offline and immune to online hacking attempts—which significantly reduces vulnerability compared to hot wallets connected directly to the internet.
Multi-signature wallets add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple approvals before any transaction can be executed. This setup prevents unauthorized transfers even if one device or key is compromised. Always opt for reputable wallet providers with strong security track records rather than unverified options promising quick gains.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding two-factor authentication (2FA) on all accounts related to cryptocurrency activities dramatically enhances account security. 2FA requires a second verification step—such as a code sent via SMS or generated through an authenticator app like Google Authenticator—to access your exchange accounts or wallets.
This measure ensures that even if someone obtains your password through phishing or data breaches, they cannot access your assets without the second factor—a crucial safeguard given recent data breaches at platforms like Coinbase exposed user information but did not necessarily compromise assets directly when 2FA was enabled.
Be Vigilant Against Phishing Attempts
Phishing remains one of the leading causes of asset theft in crypto markets today. Always verify URLs before entering login details; scammers often create fake websites resembling legitimate exchanges such as Binance or Coinbase to trick users into revealing private keys or passwords.
Avoid clicking links from unsolicited emails or messages claiming urgent issues with your account unless you confirm their authenticity through official channels. Remember: reputable services will never ask you for sensitive information via email nor request private keys under any circumstances.
Keep Software Up-to-Date
Cybercriminals frequently exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software systems—be it operating systems, browsers, or wallet applications—to gain unauthorized access to devices containing crypto assets. Regularly updating all software ensures you benefit from patches fixing known security flaws.
Set automatic updates where possible and avoid downloading files from untrusted sources. Using up-to-date antivirus programs adds another layer of defense against malware designed explicitly for stealing cryptocurrencies stored on infected devices.
Monitor Accounts Regularly
Active monitoring helps detect suspicious activity early before significant damage occurs. Many exchanges provide alert features—for example, notifications about large transactions—that enable prompt responses if something unusual happens within your account history.
Periodically review transaction histories across all platforms linked with your holdings; unfamiliar transfers should trigger immediate investigation and potential reporting to authorities if necessary.
Educate Yourself About Security Best Practices
Staying informed about emerging scams and evolving cybersecurity techniques empowers you against potential threats effectively reducing vulnerability exposure over time.Follow trusted industry sources such as official exchange blogs, cybersecurity news outlets specializing in blockchain technology updates—and participate in community forums where experienced traders share insights.Understanding concepts like seed phrases recovery methods further enhances resilience against hardware failures while maintaining control over private keys securely stored offline.
Choose Reputable Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Not all trading platforms are created equal; some may lack robust security measures making them attractive targets for hackers.Prioritize well-established exchanges known for strong regulatory compliance standards—including multi-layered security protocols—and transparent operational histories.Avoid new entrants without verifiable credentials who might be more susceptible targets due to weaker defenses.
Diversify Your Investments
Spreading investments across multiple cryptocurrencies reduces overall risk exposure associated with individual token volatility—or targeted scams aimed at specific coins.Implementing diversification strategies also minimizes potential losses should one asset become compromised due to unforeseen vulnerabilities.
Use Advanced Security Tools
Beyond basic protections like 2FA and secure wallets — consider deploying additional tools:
- Anti-virus software capable of detecting malware targeting cryptocurrency files
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) ensuring encrypted online activity
- Hardware-based biometric authentication methods where available
These measures collectively strengthen defenses against cyberattacks aiming at stealing digital assets
Report Suspicious Activity Promptly
If you encounter suspicious emails, links claiming false promotions, unexpected transfer requests—or notice irregularities within accounts—report immediately:
- Contact customer support through verified channels
- Notify relevant authorities such as local cybercrime unitsSharing experiences within trusted communities helps others recognize similar threats early
Staying Ahead: The Future of Crypto Asset Security
Recent developments indicate increasing sophistication among scammers alongside advancements in protective technologies:
- Enhanced AI-driven fraud detection models by companies like Stripe now identify hundreds more subtle transaction signals—raising detection rates significantly
- Major players including Google are expanding their online scam protection features beyond tech support fraud toward broader threat categories
Simultaneously evolving regulations aim at creating safer environments but require active participation from users committed to best practices
By adopting comprehensive safety measures—from using secure hardware wallets and enabling two-factor authentication—to staying informed about latest scams—you can significantly reduce risks associated with cryptocurrency investments.
Remember: Protecting digital assets isn’t a one-time effort but an ongoing process requiring vigilance amid constantly changing threat landscapes.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 06:04
What are the most effective ways to protect my crypto assets from scams?
How to Protect Your Crypto Assets from Scams
Cryptocurrency investments have surged in popularity, but with this growth comes an increased risk of scams and security breaches. Whether you're a seasoned trader or just starting out, understanding how to safeguard your digital assets is essential. This guide covers the most effective strategies to protect your crypto holdings from common threats like phishing, fraud, and hacking.
Understanding Common Cryptocurrency Scams
Crypto scams come in various forms, often targeting individuals who are less familiar with digital security practices. Phishing remains one of the most prevalent tactics—fraudulent emails or messages impersonate legitimate exchanges or service providers to steal private keys or login credentials. Ponzi schemes promise high returns but collapse once new investors stop joining. Fake exchanges lure users into depositing funds that are never recovered, while social engineering attacks manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information.
Recent incidents highlight these risks: for example, a widespread toll road scam via text messages has been circulating across the U.S., emphasizing how scammers exploit public trust and fear. Additionally, ransomware attacks on organizations like PowerSchool demonstrate ongoing extortion threats that can impact both institutions and individual users.
Use Secure Wallets for Storing Crypto Assets
A critical step in safeguarding your cryptocurrencies is choosing secure wallets designed specifically for crypto storage. Hardware wallets such as Ledger Nano S/X and Trezor offer cold storage solutions—meaning they are offline and immune to online hacking attempts—which significantly reduces vulnerability compared to hot wallets connected directly to the internet.
Multi-signature wallets add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple approvals before any transaction can be executed. This setup prevents unauthorized transfers even if one device or key is compromised. Always opt for reputable wallet providers with strong security track records rather than unverified options promising quick gains.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding two-factor authentication (2FA) on all accounts related to cryptocurrency activities dramatically enhances account security. 2FA requires a second verification step—such as a code sent via SMS or generated through an authenticator app like Google Authenticator—to access your exchange accounts or wallets.
This measure ensures that even if someone obtains your password through phishing or data breaches, they cannot access your assets without the second factor—a crucial safeguard given recent data breaches at platforms like Coinbase exposed user information but did not necessarily compromise assets directly when 2FA was enabled.
Be Vigilant Against Phishing Attempts
Phishing remains one of the leading causes of asset theft in crypto markets today. Always verify URLs before entering login details; scammers often create fake websites resembling legitimate exchanges such as Binance or Coinbase to trick users into revealing private keys or passwords.
Avoid clicking links from unsolicited emails or messages claiming urgent issues with your account unless you confirm their authenticity through official channels. Remember: reputable services will never ask you for sensitive information via email nor request private keys under any circumstances.
Keep Software Up-to-Date
Cybercriminals frequently exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software systems—be it operating systems, browsers, or wallet applications—to gain unauthorized access to devices containing crypto assets. Regularly updating all software ensures you benefit from patches fixing known security flaws.
Set automatic updates where possible and avoid downloading files from untrusted sources. Using up-to-date antivirus programs adds another layer of defense against malware designed explicitly for stealing cryptocurrencies stored on infected devices.
Monitor Accounts Regularly
Active monitoring helps detect suspicious activity early before significant damage occurs. Many exchanges provide alert features—for example, notifications about large transactions—that enable prompt responses if something unusual happens within your account history.
Periodically review transaction histories across all platforms linked with your holdings; unfamiliar transfers should trigger immediate investigation and potential reporting to authorities if necessary.
Educate Yourself About Security Best Practices
Staying informed about emerging scams and evolving cybersecurity techniques empowers you against potential threats effectively reducing vulnerability exposure over time.Follow trusted industry sources such as official exchange blogs, cybersecurity news outlets specializing in blockchain technology updates—and participate in community forums where experienced traders share insights.Understanding concepts like seed phrases recovery methods further enhances resilience against hardware failures while maintaining control over private keys securely stored offline.
Choose Reputable Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Not all trading platforms are created equal; some may lack robust security measures making them attractive targets for hackers.Prioritize well-established exchanges known for strong regulatory compliance standards—including multi-layered security protocols—and transparent operational histories.Avoid new entrants without verifiable credentials who might be more susceptible targets due to weaker defenses.
Diversify Your Investments
Spreading investments across multiple cryptocurrencies reduces overall risk exposure associated with individual token volatility—or targeted scams aimed at specific coins.Implementing diversification strategies also minimizes potential losses should one asset become compromised due to unforeseen vulnerabilities.
Use Advanced Security Tools
Beyond basic protections like 2FA and secure wallets — consider deploying additional tools:
- Anti-virus software capable of detecting malware targeting cryptocurrency files
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) ensuring encrypted online activity
- Hardware-based biometric authentication methods where available
These measures collectively strengthen defenses against cyberattacks aiming at stealing digital assets
Report Suspicious Activity Promptly
If you encounter suspicious emails, links claiming false promotions, unexpected transfer requests—or notice irregularities within accounts—report immediately:
- Contact customer support through verified channels
- Notify relevant authorities such as local cybercrime unitsSharing experiences within trusted communities helps others recognize similar threats early
Staying Ahead: The Future of Crypto Asset Security
Recent developments indicate increasing sophistication among scammers alongside advancements in protective technologies:
- Enhanced AI-driven fraud detection models by companies like Stripe now identify hundreds more subtle transaction signals—raising detection rates significantly
- Major players including Google are expanding their online scam protection features beyond tech support fraud toward broader threat categories
Simultaneously evolving regulations aim at creating safer environments but require active participation from users committed to best practices
By adopting comprehensive safety measures—from using secure hardware wallets and enabling two-factor authentication—to staying informed about latest scams—you can significantly reduce risks associated with cryptocurrency investments.
Remember: Protecting digital assets isn’t a one-time effort but an ongoing process requiring vigilance amid constantly changing threat landscapes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding Builder-Extractor-Sequencer (BES) Architectures
Builder-Extractor-Sequencer (BES) architectures are a modern approach to managing complex data processing tasks, especially within blockchain and cryptocurrency systems. As digital assets and decentralized applications grow in scale and complexity, traditional data handling methods often struggle to keep up. BES architectures offer a scalable, efficient solution by breaking down the data processing workflow into three specialized components: the builder, extractor, and sequencer.
This architecture is gaining recognition for its ability to handle high transaction volumes while maintaining data integrity and order—crucial factors in blockchain technology. By understanding each component's role and how they work together, developers can design systems that are both robust and adaptable to future technological advancements.
What Are the Core Components of BES Architecture?
A BES system is built around three core modules that perform distinct functions:
1. Builder
The builder acts as the initial point of contact for incoming data from various sources such as user transactions, sensors, or external APIs. Its primary responsibility is collecting this raw information efficiently while ensuring completeness. The builder aggregates data streams into manageable batches or blocks suitable for further processing.
In blockchain contexts, the builder might gather transaction details from multiple users or nodes before passing them along for validation or inclusion in a block. Its effectiveness directly impacts overall system throughput because it determines how quickly new data enters the pipeline.
2. Extractor
Once the builder has collected raw data, it moves on to extraction—the process handled by the extractor component. This module processes incoming datasets by filtering relevant information, transforming formats if necessary (e.g., converting JSON to binary), and performing preliminary validations.
For example, in smart contract execution environments, extractors might parse transaction inputs to identify specific parameters needed for contract activation or verify signatures before passing validated info downstream. The extractor ensures that only pertinent and correctly formatted data proceeds further—reducing errors downstream.
3. Sequencer
The final piece of a BES architecture is responsible for organizing processed information into an ordered sequence suitable for application use—this is where the sequencer comes into play. It arranges extracted data based on timestamps or logical dependencies so that subsequent operations like consensus algorithms or ledger updates occur accurately.
In blockchain networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum, sequencing ensures transactions are added sequentially according to their timestamp or block height—a critical factor in maintaining trustless consensus mechanisms.
Practical Applications of BES Architectures
BES architectures find their most natural fit within systems requiring high throughput combined with strict ordering guarantees:
Blockchain Transaction Management: They streamline transaction collection from multiple sources (builder), validate content (extractor), then order transactions chronologically before adding them onto blocks via miners/validators.
Data Analytics Platforms: Large-scale analytics tools utilize BES structures to ingest vast datasets rapidly; extract meaningful features; then organize insights logically—enabling real-time trend detection.
Smart Contract Execution: In decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms where numerous conditions must be met simultaneously before executing contracts — such as collateral checks — BES helps manage input flow efficiently while preserving correct execution order.
By modularizing these steps into dedicated components with clear responsibilities—and optimizing each independently—systems can achieve higher scalability without sacrificing security or accuracy.
Recent Innovations Enhancing BES Systems
Recent developments have focused on improving scalability through integration with emerging technologies:
Blockchain Scalability Solutions
As demand surges driven by DeFi applications and NFTs (non-fungible tokens), traditional blockchains face congestion issues. Adapting BES architectures allows these networks to process more transactions concurrently by optimizing each component’s performance—for example:
- Parallelizing building processes
- Using advanced filtering techniques during extraction
- Implementing sophisticated sequencing algorithms based on timestamps
These improvements help maintain low latency even during peak usage periods.
Cloud Computing Integration
Cloud services enable dynamic resource allocation which complements BE S workflows well:
- Builders can scale up during traffic spikes
- Extractors benefit from distributed computing power
- Sequencers leverage cloud-based databases for rapid organization
This flexibility enhances reliability across diverse operational environments—from private enterprise chains to public networks.
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Enhancements
AI/ML models now assist each phase:
- Builders* predict incoming load patterns,
- Extractors* automatically identify relevant features,
- Sequencers* optimize ordering based on predictive analytics.
Such integrations lead not only toward increased efficiency but also improved adaptability amid evolving workloads—a key advantage given rapid technological changes in blockchain landscapes.
Challenges Facing BE S Architectures: Security & Privacy Concerns
Despite their advantages, implementing BE S architectures involves navigating several challenges:
Security Risks: Since builders aggregate sensitive transactional information from multiple sources—including potentially untrusted ones—they become attractive targets for malicious actors aiming at injecting false data or disrupting workflows through denial-of-service attacks.
Data Privacy Issues: Handling large volumes of user-specific information raises privacy concerns; without proper encryption protocols and access controls—as mandated under regulations like GDPR—the risk of exposing personal details increases significantly.
Technical Complexity: Integrating AI/ML modules adds layers of complexity requiring specialized expertise; maintaining system stability becomes more difficult when components depend heavily on accurate predictions rather than deterministic rules.
Best Practices For Deploying Effective BE S Systems
To maximize benefits while mitigating risks associated with BE S designs consider these best practices:
Prioritize Security Measures
- Use cryptographic techniques such as digital signatures
- Implement multi-layered authentication protocols
- Regularly audit codebases
Ensure Data Privacy
- Encrypt sensitive datasets at rest/in transit
- Apply privacy-preserving computation methods where possible
Design Modular & Scalable Components
- Use microservices architecture principles
- Leverage cloud infrastructure capabilities
Integrate AI Responsibly
- Validate ML models thoroughly before deployment
- Monitor model performance continuously
How Builder-Extractor-Sequencer Fits Into Broader Data Processing Ecosystems
Understanding how B E S fits within larger infrastructures reveals its strategic importance:
While traditional ETL pipelines focus mainly on batch processing static datasets over extended periods—which may introduce latency—in contrast BES systems excel at real-time streaming scenarios where immediate insights matter. Their modular nature allows seamless integration with other distributed ledger technologies (DLT) frameworks like Hyperledger Fabric or Corda alongside conventional big-data tools such as Apache Kafka & Spark ecosystems—all contributing toward comprehensive enterprise-grade solutions capable of handling today's demanding workloads effectively.
By dissecting each element’s role—from collection through transformation up until ordered delivery—developers gain clarity about designing resilient blockchain solutions capable of scaling securely amidst increasing demands worldwide.
Keywords: Blockchain architecture | Data processing | Cryptocurrency systems | Smart contracts | Scalability solutions | Distributed ledger technology


Lo
2025-05-14 13:42
What are builder-extractor-sequencer (BES) architectures?
Understanding Builder-Extractor-Sequencer (BES) Architectures
Builder-Extractor-Sequencer (BES) architectures are a modern approach to managing complex data processing tasks, especially within blockchain and cryptocurrency systems. As digital assets and decentralized applications grow in scale and complexity, traditional data handling methods often struggle to keep up. BES architectures offer a scalable, efficient solution by breaking down the data processing workflow into three specialized components: the builder, extractor, and sequencer.
This architecture is gaining recognition for its ability to handle high transaction volumes while maintaining data integrity and order—crucial factors in blockchain technology. By understanding each component's role and how they work together, developers can design systems that are both robust and adaptable to future technological advancements.
What Are the Core Components of BES Architecture?
A BES system is built around three core modules that perform distinct functions:
1. Builder
The builder acts as the initial point of contact for incoming data from various sources such as user transactions, sensors, or external APIs. Its primary responsibility is collecting this raw information efficiently while ensuring completeness. The builder aggregates data streams into manageable batches or blocks suitable for further processing.
In blockchain contexts, the builder might gather transaction details from multiple users or nodes before passing them along for validation or inclusion in a block. Its effectiveness directly impacts overall system throughput because it determines how quickly new data enters the pipeline.
2. Extractor
Once the builder has collected raw data, it moves on to extraction—the process handled by the extractor component. This module processes incoming datasets by filtering relevant information, transforming formats if necessary (e.g., converting JSON to binary), and performing preliminary validations.
For example, in smart contract execution environments, extractors might parse transaction inputs to identify specific parameters needed for contract activation or verify signatures before passing validated info downstream. The extractor ensures that only pertinent and correctly formatted data proceeds further—reducing errors downstream.
3. Sequencer
The final piece of a BES architecture is responsible for organizing processed information into an ordered sequence suitable for application use—this is where the sequencer comes into play. It arranges extracted data based on timestamps or logical dependencies so that subsequent operations like consensus algorithms or ledger updates occur accurately.
In blockchain networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum, sequencing ensures transactions are added sequentially according to their timestamp or block height—a critical factor in maintaining trustless consensus mechanisms.
Practical Applications of BES Architectures
BES architectures find their most natural fit within systems requiring high throughput combined with strict ordering guarantees:
Blockchain Transaction Management: They streamline transaction collection from multiple sources (builder), validate content (extractor), then order transactions chronologically before adding them onto blocks via miners/validators.
Data Analytics Platforms: Large-scale analytics tools utilize BES structures to ingest vast datasets rapidly; extract meaningful features; then organize insights logically—enabling real-time trend detection.
Smart Contract Execution: In decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms where numerous conditions must be met simultaneously before executing contracts — such as collateral checks — BES helps manage input flow efficiently while preserving correct execution order.
By modularizing these steps into dedicated components with clear responsibilities—and optimizing each independently—systems can achieve higher scalability without sacrificing security or accuracy.
Recent Innovations Enhancing BES Systems
Recent developments have focused on improving scalability through integration with emerging technologies:
Blockchain Scalability Solutions
As demand surges driven by DeFi applications and NFTs (non-fungible tokens), traditional blockchains face congestion issues. Adapting BES architectures allows these networks to process more transactions concurrently by optimizing each component’s performance—for example:
- Parallelizing building processes
- Using advanced filtering techniques during extraction
- Implementing sophisticated sequencing algorithms based on timestamps
These improvements help maintain low latency even during peak usage periods.
Cloud Computing Integration
Cloud services enable dynamic resource allocation which complements BE S workflows well:
- Builders can scale up during traffic spikes
- Extractors benefit from distributed computing power
- Sequencers leverage cloud-based databases for rapid organization
This flexibility enhances reliability across diverse operational environments—from private enterprise chains to public networks.
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Enhancements
AI/ML models now assist each phase:
- Builders* predict incoming load patterns,
- Extractors* automatically identify relevant features,
- Sequencers* optimize ordering based on predictive analytics.
Such integrations lead not only toward increased efficiency but also improved adaptability amid evolving workloads—a key advantage given rapid technological changes in blockchain landscapes.
Challenges Facing BE S Architectures: Security & Privacy Concerns
Despite their advantages, implementing BE S architectures involves navigating several challenges:
Security Risks: Since builders aggregate sensitive transactional information from multiple sources—including potentially untrusted ones—they become attractive targets for malicious actors aiming at injecting false data or disrupting workflows through denial-of-service attacks.
Data Privacy Issues: Handling large volumes of user-specific information raises privacy concerns; without proper encryption protocols and access controls—as mandated under regulations like GDPR—the risk of exposing personal details increases significantly.
Technical Complexity: Integrating AI/ML modules adds layers of complexity requiring specialized expertise; maintaining system stability becomes more difficult when components depend heavily on accurate predictions rather than deterministic rules.
Best Practices For Deploying Effective BE S Systems
To maximize benefits while mitigating risks associated with BE S designs consider these best practices:
Prioritize Security Measures
- Use cryptographic techniques such as digital signatures
- Implement multi-layered authentication protocols
- Regularly audit codebases
Ensure Data Privacy
- Encrypt sensitive datasets at rest/in transit
- Apply privacy-preserving computation methods where possible
Design Modular & Scalable Components
- Use microservices architecture principles
- Leverage cloud infrastructure capabilities
Integrate AI Responsibly
- Validate ML models thoroughly before deployment
- Monitor model performance continuously
How Builder-Extractor-Sequencer Fits Into Broader Data Processing Ecosystems
Understanding how B E S fits within larger infrastructures reveals its strategic importance:
While traditional ETL pipelines focus mainly on batch processing static datasets over extended periods—which may introduce latency—in contrast BES systems excel at real-time streaming scenarios where immediate insights matter. Their modular nature allows seamless integration with other distributed ledger technologies (DLT) frameworks like Hyperledger Fabric or Corda alongside conventional big-data tools such as Apache Kafka & Spark ecosystems—all contributing toward comprehensive enterprise-grade solutions capable of handling today's demanding workloads effectively.
By dissecting each element’s role—from collection through transformation up until ordered delivery—developers gain clarity about designing resilient blockchain solutions capable of scaling securely amidst increasing demands worldwide.
Keywords: Blockchain architecture | Data processing | Cryptocurrency systems | Smart contracts | Scalability solutions | Distributed ledger technology
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Software Features That Support Common-Size Financial Analysis?
Common-size analysis is a fundamental technique in financial analysis that allows investors, analysts, and corporate managers to compare companies or track performance over time by standardizing financial statements. As the demand for accurate and efficient analysis grows, software tools have evolved to incorporate features that streamline this process. These features not only improve accuracy but also enhance visualization and interpretability of complex data.
Financial statement analysis tools embedded within various software platforms typically include templates specifically designed for common-size statements. These templates automate the calculation of percentages—such as expressing each line item on an income statement as a percentage of total revenue or each balance sheet item as a percentage of total assets—saving users considerable time and reducing manual errors. Automated calculations ensure consistency across analyses, which is crucial when comparing multiple companies or historical periods.
Data visualization capabilities are another critical feature in modern financial software supporting common-size analysis. Visual representations like bar charts, pie charts, and trend lines help users quickly grasp key insights from their data. For example, visualizing expense categories as proportions of total revenue can reveal cost structure trends over time or highlight areas where efficiency improvements could be made.
Access to comprehensive historical data is vital for meaningful common-size comparisons across different periods or industry benchmarks. Many advanced platforms provide extensive archives of past financial reports, enabling users to perform longitudinal studies that identify patterns or shifts in company performance over years. This historical perspective adds depth to the analysis by contextualizing current figures within broader trends.
In addition to core functionalities, some tools integrate access to earnings reports and stock split histories directly within their interface. Understanding how stock splits impact share prices or how earnings fluctuate after specific events helps refine the interpretation of common-size results by accounting for structural changes in capital structure.
Furthermore, integration with market data feeds and analyst ratings enhances the analytical context around a company's financials. Market sentiment indicators can influence how one interprets ratios derived from common-size statements—providing a more holistic view that combines quantitative metrics with qualitative insights from industry experts.
Recent Innovations Enhancing Common-Size Analysis Software
The landscape of software supporting common-size analysis has seen significant advancements recently — particularly in areas related to data visualization and automation through artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Enhanced visualization techniques now allow analysts not only to generate static charts but also interactive dashboards where they can drill down into specific segments or compare multiple datasets side-by-side effortlessly.
These innovations make it easier for users at all levels—from seasoned professionals to individual investors—to interpret complex datasets without requiring deep technical expertise. For instance, dynamic heat maps highlighting anomalies across different periods enable quick identification of outliers needing further investigation.
Accessibility has also improved dramatically due to widespread availability of cloud-based solutions offering real-time updates on market conditions alongside financial data repositories accessible via subscription models or open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). This democratization means small businesses and individual investors now have powerful tools previously limited mainly to large corporations with dedicated finance teams.
The integration of AI/ML algorithms marks one of the most transformative recent developments in this field. These intelligent systems can automatically detect patterns such as declining margins or rising debt ratios across multiple years without manual intervention — providing early warning signals that might otherwise go unnoticed until too late. They also assist in scenario modeling by simulating potential outcomes based on varying assumptions about future revenues or costs derived from historical trends observed through common-size frameworks.
Regulatory changes are influencing how these analytical tools evolve too; new standards around transparency and disclosure require firms’ reporting practices—and consequently their analytical methods—to adapt accordingly. Software developers are continuously updating their platforms so they remain compliant while offering enhanced functionalities aligned with evolving standards like IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) or GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles).
Risks Linked With Heavy Dependence on Common-Size Analysis Tools
While these technological advancements significantly improve efficiency and insight generation, relying heavily on automated software features carries certain risks worth considering carefully:
Overreliance on Quantitative Data: Focusing predominantly on numerical outputs may lead analysts away from qualitative factors such as management quality, competitive positioning, regulatory environment impacts—all essential elements influencing overall company health.
Misinterpretation Risks: Without proper understanding about what certain ratios mean within specific contexts—for example, high operating expenses relative to revenue—it’s easy for users unfamiliar with nuanced interpretations to draw incorrect conclusions.
Technological Vulnerabilities: The increasing use of AI/ML introduces concerns related not just purely technical issues like algorithm bias but also cybersecurity threats targeting sensitive financial information stored within cloud-based systems.
To mitigate these risks effectively:
- Users should combine automated insights with expert judgment.
- Training programs should emphasize understanding underlying assumptions behind calculations.
- Regular audits must verify algorithms’ accuracy against known benchmarks.
By maintaining awareness around these potential pitfalls while leveraging advanced features responsibly—and always supplementing quantitative findings with qualitative assessments—users can maximize benefits while minimizing adverse outcomes associated with heavy reliance solely on technology-driven analyses.
How Software Enhances Accuracy And Efficiency In Common-Size Analysis
Modern software solutions significantly reduce manual effort involved in preparing standardized financial statements through automation features such as batch processing capabilities which handle large datasets efficiently — especially useful when analyzing multiple entities simultaneously during peer comparisons.[1]
Moreover:
- Automated percentage calculations eliminate human error inherent in manual computations,
- Real-time updates ensure analyses reflect current market conditions,
- Interactive dashboards facilitate quick scenario testing,
- Export options support seamless sharing among stakeholders,
This combination accelerates decision-making processes while improving overall reliability—a critical advantage given today’s fast-paced business environment.[2]
Additionally, many platforms incorporate user-friendly interfaces designed specifically for non-expert users who need straightforward yet powerful tools without extensive training requirements.[1] Such accessibility broadens participation beyond specialized finance teams into departments like marketing or operations seeking strategic insights based on robust quantitative foundations provided by common-size frameworks.
Final Thoughts: The Future Of Common-Size Financial Software Tools
As technology continues advancing rapidly—with AI becoming more sophisticated—the future landscape promises even more intuitive interfaces capable not only of automating routine tasks but also providing predictive analytics rooted deeply in machine learning models.[1]
Expect increased integration between external market intelligence sources—including news feeds—and internal company data streams; this will enable real-time contextualized analyses tailored precisely toward strategic decision-making needs.[2]
Furthermore:
- Enhanced customization options will allow tailored reporting aligned closely with organizational goals,
- Greater emphasis will be placed on ensuring compliance amid evolving regulatory environments,
- Continued focus will be placed upon safeguarding sensitive information against cyber threats,
Ultimately these developments aim at empowering analysts at all levels—from junior staff members conducting initial reviews up through senior executives making high-stakes decisions—with smarter tools capable both quantitatively precise assessments supported by rich visualizations combined seamlessly into actionable insights.[1][2]
By embracing these innovations responsibly—balancing technological power with sound judgment—the effectiveness and reliability of common-size analysis will continue strengthening its role as an indispensable component within comprehensive financial evaluation strategies.
References
[1] Financial Analysis Tools & Techniques – Modern Approaches
[2] Advances In Data Visualization & AI Integration In Finance


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 13:15
What software features facilitate common-size analysis?
What Are Software Features That Support Common-Size Financial Analysis?
Common-size analysis is a fundamental technique in financial analysis that allows investors, analysts, and corporate managers to compare companies or track performance over time by standardizing financial statements. As the demand for accurate and efficient analysis grows, software tools have evolved to incorporate features that streamline this process. These features not only improve accuracy but also enhance visualization and interpretability of complex data.
Financial statement analysis tools embedded within various software platforms typically include templates specifically designed for common-size statements. These templates automate the calculation of percentages—such as expressing each line item on an income statement as a percentage of total revenue or each balance sheet item as a percentage of total assets—saving users considerable time and reducing manual errors. Automated calculations ensure consistency across analyses, which is crucial when comparing multiple companies or historical periods.
Data visualization capabilities are another critical feature in modern financial software supporting common-size analysis. Visual representations like bar charts, pie charts, and trend lines help users quickly grasp key insights from their data. For example, visualizing expense categories as proportions of total revenue can reveal cost structure trends over time or highlight areas where efficiency improvements could be made.
Access to comprehensive historical data is vital for meaningful common-size comparisons across different periods or industry benchmarks. Many advanced platforms provide extensive archives of past financial reports, enabling users to perform longitudinal studies that identify patterns or shifts in company performance over years. This historical perspective adds depth to the analysis by contextualizing current figures within broader trends.
In addition to core functionalities, some tools integrate access to earnings reports and stock split histories directly within their interface. Understanding how stock splits impact share prices or how earnings fluctuate after specific events helps refine the interpretation of common-size results by accounting for structural changes in capital structure.
Furthermore, integration with market data feeds and analyst ratings enhances the analytical context around a company's financials. Market sentiment indicators can influence how one interprets ratios derived from common-size statements—providing a more holistic view that combines quantitative metrics with qualitative insights from industry experts.
Recent Innovations Enhancing Common-Size Analysis Software
The landscape of software supporting common-size analysis has seen significant advancements recently — particularly in areas related to data visualization and automation through artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Enhanced visualization techniques now allow analysts not only to generate static charts but also interactive dashboards where they can drill down into specific segments or compare multiple datasets side-by-side effortlessly.
These innovations make it easier for users at all levels—from seasoned professionals to individual investors—to interpret complex datasets without requiring deep technical expertise. For instance, dynamic heat maps highlighting anomalies across different periods enable quick identification of outliers needing further investigation.
Accessibility has also improved dramatically due to widespread availability of cloud-based solutions offering real-time updates on market conditions alongside financial data repositories accessible via subscription models or open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). This democratization means small businesses and individual investors now have powerful tools previously limited mainly to large corporations with dedicated finance teams.
The integration of AI/ML algorithms marks one of the most transformative recent developments in this field. These intelligent systems can automatically detect patterns such as declining margins or rising debt ratios across multiple years without manual intervention — providing early warning signals that might otherwise go unnoticed until too late. They also assist in scenario modeling by simulating potential outcomes based on varying assumptions about future revenues or costs derived from historical trends observed through common-size frameworks.
Regulatory changes are influencing how these analytical tools evolve too; new standards around transparency and disclosure require firms’ reporting practices—and consequently their analytical methods—to adapt accordingly. Software developers are continuously updating their platforms so they remain compliant while offering enhanced functionalities aligned with evolving standards like IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) or GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles).
Risks Linked With Heavy Dependence on Common-Size Analysis Tools
While these technological advancements significantly improve efficiency and insight generation, relying heavily on automated software features carries certain risks worth considering carefully:
Overreliance on Quantitative Data: Focusing predominantly on numerical outputs may lead analysts away from qualitative factors such as management quality, competitive positioning, regulatory environment impacts—all essential elements influencing overall company health.
Misinterpretation Risks: Without proper understanding about what certain ratios mean within specific contexts—for example, high operating expenses relative to revenue—it’s easy for users unfamiliar with nuanced interpretations to draw incorrect conclusions.
Technological Vulnerabilities: The increasing use of AI/ML introduces concerns related not just purely technical issues like algorithm bias but also cybersecurity threats targeting sensitive financial information stored within cloud-based systems.
To mitigate these risks effectively:
- Users should combine automated insights with expert judgment.
- Training programs should emphasize understanding underlying assumptions behind calculations.
- Regular audits must verify algorithms’ accuracy against known benchmarks.
By maintaining awareness around these potential pitfalls while leveraging advanced features responsibly—and always supplementing quantitative findings with qualitative assessments—users can maximize benefits while minimizing adverse outcomes associated with heavy reliance solely on technology-driven analyses.
How Software Enhances Accuracy And Efficiency In Common-Size Analysis
Modern software solutions significantly reduce manual effort involved in preparing standardized financial statements through automation features such as batch processing capabilities which handle large datasets efficiently — especially useful when analyzing multiple entities simultaneously during peer comparisons.[1]
Moreover:
- Automated percentage calculations eliminate human error inherent in manual computations,
- Real-time updates ensure analyses reflect current market conditions,
- Interactive dashboards facilitate quick scenario testing,
- Export options support seamless sharing among stakeholders,
This combination accelerates decision-making processes while improving overall reliability—a critical advantage given today’s fast-paced business environment.[2]
Additionally, many platforms incorporate user-friendly interfaces designed specifically for non-expert users who need straightforward yet powerful tools without extensive training requirements.[1] Such accessibility broadens participation beyond specialized finance teams into departments like marketing or operations seeking strategic insights based on robust quantitative foundations provided by common-size frameworks.
Final Thoughts: The Future Of Common-Size Financial Software Tools
As technology continues advancing rapidly—with AI becoming more sophisticated—the future landscape promises even more intuitive interfaces capable not only of automating routine tasks but also providing predictive analytics rooted deeply in machine learning models.[1]
Expect increased integration between external market intelligence sources—including news feeds—and internal company data streams; this will enable real-time contextualized analyses tailored precisely toward strategic decision-making needs.[2]
Furthermore:
- Enhanced customization options will allow tailored reporting aligned closely with organizational goals,
- Greater emphasis will be placed on ensuring compliance amid evolving regulatory environments,
- Continued focus will be placed upon safeguarding sensitive information against cyber threats,
Ultimately these developments aim at empowering analysts at all levels—from junior staff members conducting initial reviews up through senior executives making high-stakes decisions—with smarter tools capable both quantitatively precise assessments supported by rich visualizations combined seamlessly into actionable insights.[1][2]
By embracing these innovations responsibly—balancing technological power with sound judgment—the effectiveness and reliability of common-size analysis will continue strengthening its role as an indispensable component within comprehensive financial evaluation strategies.
References
[1] Financial Analysis Tools & Techniques – Modern Approaches
[2] Advances In Data Visualization & AI Integration In Finance
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The Travel Rule and Cryptocurrency Transfers: A Complete Guide
Understanding the Travel Rule in Financial Transactions
The Travel Rule, also known as Customer Due Diligence (CDD), is a key regulation designed to combat money laundering and illicit financial activities. Originally introduced by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) in 2012, it mandates that financial institutions share specific information about both parties involved in cross-border transactions. This information typically includes names, addresses, account numbers, and other identifying details. The goal is to create transparency around international transfers of funds so authorities can track suspicious activity more effectively.
In traditional banking systems, this rule has been well-established for decades. Banks are required to verify customer identities before processing transactions and share relevant data with each other when transferring funds across borders. This process helps prevent illegal activities such as terrorism financing or tax evasion by ensuring that all parties involved are properly identified.
Applying the Travel Rule to Cryptocurrency Transfers
With the rise of digital assets like cryptocurrencies, regulators faced new challenges in applying existing anti-money laundering (AML) standards. In 2019, FATF issued specific guidance on how the Travel Rule should be implemented within virtual asset markets—covering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
This guidance emphasizes that Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs)—which include cryptocurrency exchanges and wallet providers—must adhere to similar standards as traditional financial institutions regarding customer due diligence and information sharing. Essentially, VASPs are expected to verify user identities before facilitating transactions involving digital assets.
Key aspects of this application include:
- Customer Due Diligence: VASPs need to conduct identity verification for their users—collecting documents such as passports or driver’s licenses—to confirm who they are.
- Information Sharing: When a user sends cryptocurrency from one VASP to another across borders, both entities must exchange relevant transaction data about originators and beneficiaries.
- Technical Standards: To facilitate seamless compliance, FATF recommends developing standardized technical solutions—like APIs—that enable secure data exchange between different VASPs.
Challenges arise because blockchain technology inherently offers pseudonymity rather than full anonymity; users can transact without revealing personal details unless they voluntarily provide them during onboarding processes at exchanges or wallets.
Recent Developments in Enforcement & Industry Response
Since FATF’s guidance was issued, several notable developments have shaped how the industry approaches compliance with the Travel Rule:
Regulatory Clarifications: In 2020, FinCEN—the U.S.’s primary AML regulator—clarified that cryptocurrency exchanges operating within its jurisdiction must follow existing AML laws similar to banks’ requirements under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA). This included implementing procedures for collecting customer info during cross-border transfers[1].
Industry Adoption: Many crypto platforms have begun integrating compliance measures such as mandatory identity verification before enabling international transfers[2]. These steps aim not only at legal adherence but also at building trust among users concerned about privacy risks associated with data sharing.
Development of Technical Solutions: Several organizations are working on creating standardized APIs and protocols designed specifically for compliant crypto transactions[3]. These innovations seek to streamline information exchange while maintaining security standards necessary for privacy protection.
Global Coordination Efforts: Countries like Japan and South Korea have issued their own guidelines aligning with FATF recommendations; this underscores an increasing push toward harmonized international enforcement efforts[5].
Despite these positive steps forward, implementing the Travel Rule remains complex due primarily to technological limitations—and concerns over user privacy—which continue fueling debates within regulatory circles.
Potential Impacts on Cryptocurrency Ecosystem
Enforcing strict adherence to the Travel Rule could lead to significant changes within crypto markets:
- Increased operational costs may burden smaller exchanges unable yet fully equipped with compliant infrastructure.
- Privacy concerns might deter some users from engaging fully with digital assets if they fear personal data could be exposed or misused.
- Overly stringent regulations risk stifling innovation by discouraging startups from entering space or developing new blockchain-based solutions.
However—and importantly—it could also bolster security by making it harder for illicit actors like money launderers or terrorist financiers operating anonymously online[4].
Why Stakeholders Need To Stay Informed
For investors, developers, regulators—and anyone involved in cryptocurrency—the evolving landscape surrounding AML regulations is critical knowledge area. Staying updated ensures compliance while avoiding potential penalties or reputational damage resulting from non-adherence.
Moreover understanding how technical solutions evolve can help industry players implement effective measures without compromising user experience unnecessarily—a balance essential for sustainable growth amid tightening global standards.
How Compliance Shapes Future Crypto Regulations
As countries continue refining their policies around virtual assets’ AML obligations—including enforcing measures akin to those mandated by FATF—the entire ecosystem faces increased scrutiny but also opportunities for legitimacy enhancement through transparent practices.
The ongoing development of interoperable technical frameworks promises smoother cross-border operations while safeguarding user privacy where possible—a challenge requiring collaboration among regulators worldwide alongside technological innovation.
Summary of Key Points About How The Travel Rule Applies To Crypto Transfers
- The original purpose of the rule is transparency in cross-border payments
- Regulators now extend these principles into virtual asset markets
- VASPs must verify identities before processing certain transactions
- Information sharing between platforms is crucial
- Implementation faces hurdles related mainly to technology & privacy concerns
By understanding these elements thoroughly—from regulatory background through recent industry responses—you gain insight into how global efforts aim at making cryptocurrency transfers safer yet compliant with established anti-money laundering standards.
References:
- FinCEN Ruling (2020): https://www.fincen.gov/news/news-releases/fincen-issues-final-rule-regarding-implementation-travel-rule-virtual-assets
- Industry Implementation: https://www.coindesk.com/2020/06/01/cryptocurrency-exchanges-start-implementing-travel-rule/
- Technical Solutions Development: https://www.ccn.com/developers-create-api-standardize-travel-rule-cryptocurrency-transactions/
- Regulatory Challenges & Privacy Concerns: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-07-14/cryptocurrency-regulations-could-hurt-industry-growth
- International Coordination Efforts: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-crypto-regulation-japan-idUSKBN23I2ZT


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-11 12:32
How does the Travel Rule apply to cryptocurrency transfers?
The Travel Rule and Cryptocurrency Transfers: A Complete Guide
Understanding the Travel Rule in Financial Transactions
The Travel Rule, also known as Customer Due Diligence (CDD), is a key regulation designed to combat money laundering and illicit financial activities. Originally introduced by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) in 2012, it mandates that financial institutions share specific information about both parties involved in cross-border transactions. This information typically includes names, addresses, account numbers, and other identifying details. The goal is to create transparency around international transfers of funds so authorities can track suspicious activity more effectively.
In traditional banking systems, this rule has been well-established for decades. Banks are required to verify customer identities before processing transactions and share relevant data with each other when transferring funds across borders. This process helps prevent illegal activities such as terrorism financing or tax evasion by ensuring that all parties involved are properly identified.
Applying the Travel Rule to Cryptocurrency Transfers
With the rise of digital assets like cryptocurrencies, regulators faced new challenges in applying existing anti-money laundering (AML) standards. In 2019, FATF issued specific guidance on how the Travel Rule should be implemented within virtual asset markets—covering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
This guidance emphasizes that Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs)—which include cryptocurrency exchanges and wallet providers—must adhere to similar standards as traditional financial institutions regarding customer due diligence and information sharing. Essentially, VASPs are expected to verify user identities before facilitating transactions involving digital assets.
Key aspects of this application include:
- Customer Due Diligence: VASPs need to conduct identity verification for their users—collecting documents such as passports or driver’s licenses—to confirm who they are.
- Information Sharing: When a user sends cryptocurrency from one VASP to another across borders, both entities must exchange relevant transaction data about originators and beneficiaries.
- Technical Standards: To facilitate seamless compliance, FATF recommends developing standardized technical solutions—like APIs—that enable secure data exchange between different VASPs.
Challenges arise because blockchain technology inherently offers pseudonymity rather than full anonymity; users can transact without revealing personal details unless they voluntarily provide them during onboarding processes at exchanges or wallets.
Recent Developments in Enforcement & Industry Response
Since FATF’s guidance was issued, several notable developments have shaped how the industry approaches compliance with the Travel Rule:
Regulatory Clarifications: In 2020, FinCEN—the U.S.’s primary AML regulator—clarified that cryptocurrency exchanges operating within its jurisdiction must follow existing AML laws similar to banks’ requirements under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA). This included implementing procedures for collecting customer info during cross-border transfers[1].
Industry Adoption: Many crypto platforms have begun integrating compliance measures such as mandatory identity verification before enabling international transfers[2]. These steps aim not only at legal adherence but also at building trust among users concerned about privacy risks associated with data sharing.
Development of Technical Solutions: Several organizations are working on creating standardized APIs and protocols designed specifically for compliant crypto transactions[3]. These innovations seek to streamline information exchange while maintaining security standards necessary for privacy protection.
Global Coordination Efforts: Countries like Japan and South Korea have issued their own guidelines aligning with FATF recommendations; this underscores an increasing push toward harmonized international enforcement efforts[5].
Despite these positive steps forward, implementing the Travel Rule remains complex due primarily to technological limitations—and concerns over user privacy—which continue fueling debates within regulatory circles.
Potential Impacts on Cryptocurrency Ecosystem
Enforcing strict adherence to the Travel Rule could lead to significant changes within crypto markets:
- Increased operational costs may burden smaller exchanges unable yet fully equipped with compliant infrastructure.
- Privacy concerns might deter some users from engaging fully with digital assets if they fear personal data could be exposed or misused.
- Overly stringent regulations risk stifling innovation by discouraging startups from entering space or developing new blockchain-based solutions.
However—and importantly—it could also bolster security by making it harder for illicit actors like money launderers or terrorist financiers operating anonymously online[4].
Why Stakeholders Need To Stay Informed
For investors, developers, regulators—and anyone involved in cryptocurrency—the evolving landscape surrounding AML regulations is critical knowledge area. Staying updated ensures compliance while avoiding potential penalties or reputational damage resulting from non-adherence.
Moreover understanding how technical solutions evolve can help industry players implement effective measures without compromising user experience unnecessarily—a balance essential for sustainable growth amid tightening global standards.
How Compliance Shapes Future Crypto Regulations
As countries continue refining their policies around virtual assets’ AML obligations—including enforcing measures akin to those mandated by FATF—the entire ecosystem faces increased scrutiny but also opportunities for legitimacy enhancement through transparent practices.
The ongoing development of interoperable technical frameworks promises smoother cross-border operations while safeguarding user privacy where possible—a challenge requiring collaboration among regulators worldwide alongside technological innovation.
Summary of Key Points About How The Travel Rule Applies To Crypto Transfers
- The original purpose of the rule is transparency in cross-border payments
- Regulators now extend these principles into virtual asset markets
- VASPs must verify identities before processing certain transactions
- Information sharing between platforms is crucial
- Implementation faces hurdles related mainly to technology & privacy concerns
By understanding these elements thoroughly—from regulatory background through recent industry responses—you gain insight into how global efforts aim at making cryptocurrency transfers safer yet compliant with established anti-money laundering standards.
References:
- FinCEN Ruling (2020): https://www.fincen.gov/news/news-releases/fincen-issues-final-rule-regarding-implementation-travel-rule-virtual-assets
- Industry Implementation: https://www.coindesk.com/2020/06/01/cryptocurrency-exchanges-start-implementing-travel-rule/
- Technical Solutions Development: https://www.ccn.com/developers-create-api-standardize-travel-rule-cryptocurrency-transactions/
- Regulatory Challenges & Privacy Concerns: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-07-14/cryptocurrency-regulations-could-hurt-industry-growth
- International Coordination Efforts: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-crypto-regulation-japan-idUSKBN23I2ZT
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Partnerships with Content Platforms Are Driving TRON (TRX) Ecosystem Growth
The TRON blockchain platform has gained significant attention in the digital content and cryptocurrency space, largely due to its strategic partnerships with various content platforms. These collaborations are key drivers of ecosystem expansion, user engagement, and technological adoption. Understanding how these partnerships influence TRON’s growth provides valuable insights into the evolving landscape of blockchain-based content sharing.
The Role of Strategic Partnerships in Blockchain Ecosystems
Partnerships are fundamental for blockchain projects aiming to scale their reach and functionality. For TRON, collaborating with content platforms allows it to tap into existing user bases while offering innovative solutions like decentralized content sharing, NFTs, and DeFi applications. These alliances help build a more robust ecosystem where users benefit from transparency, security, and ownership rights that blockchain technology offers.
By integrating with popular platforms such as BitTorrent or NFT marketplaces like Rarible and OpenSea, TRON enhances its visibility within both the crypto community and mainstream digital entertainment markets. Such collaborations also serve as validation points for investors looking for sustainable growth pathways rooted in real-world utility.
Key Content Platform Partnerships Fueling Growth
One of the most notable milestones for TRON was its acquisition of BitTorrent in 2019. As one of the largest peer-to-peer file-sharing services globally—with millions of active users—BitTorrent provided an immediate boost to TRON’s network activity. This move allowed TRON to leverage BitTorrent's infrastructure while integrating blockchain features such as token rewards for file sharing.
In addition to BitTorrent, TRON has partnered with several decentralized content sharing platforms like DLive and Rize. These platforms utilize blockchain technology to ensure transparent monetization models where creators retain control over their work without relying on centralized authorities or intermediaries.
Furthermore, the rise of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has prompted partnerships between TRON and leading NFT marketplaces such as Rarible and OpenSea. These collaborations facilitate seamless creation, trading, and ownership verification of unique digital assets on the Tron network—expanding opportunities for artists, collectors, and developers alike.
Challenges Facing Content Platform Collaborations
While these partnerships have propelled growth within the ecosystem—boosting transaction volumes & token demand—they also introduce certain risks that need careful management:
Regulatory Scrutiny: As more content is shared via blockchain-based systems globally—especially involving NFTs—the regulatory environment becomes increasingly complex. Governments are scrutinizing issues related to copyright infringement or money laundering concerns associated with digital assets.
Security Concerns: Integrating large-scale user bases from popular platforms increases vulnerabilities related to hacking attempts or smart contract exploits. Maintaining high-security standards is crucial for safeguarding user data & assets.
Market Volatility: The value proposition tied directly to these partnerships can be affected by broader market trends or negative news cycles impacting cryptocurrencies generally—including regulatory crackdowns or technological setbacks.
Despite these challenges—and when managed properly—such collaborations continue fueling demand for TRX tokens by increasing platform utility & attracting new users interested in decentralized entertainment options.
Impact on Tron's Token Value
Partnership-driven growth often correlates positively with token performance; increased activity on partnered platforms leads directly to higher demand for native tokens like TRX used within those ecosystems—for transactions or governance purposes. Since 2019’s acquisition of BitTorrent alone contributed significantly toward boosting transaction volume—and consequently token value—the trend persists today across newer integrations involving NFTs & dApps.
However—as seen throughout crypto markets—price fluctuations remain common due to external factors including regulatory developments or macroeconomic shifts affecting investor sentiment overall.
Future Outlook: Opportunities & Risks
Looking ahead at how partnerships might evolve reveals both promising opportunities—and potential pitfalls—for Tron’s ecosystem expansion:
Opportunities:
- Continued integration into mainstream media through strategic alliances
- Expansion into emerging sectors like metaverse applications
- Increased adoption driven by innovative use cases around NFTs & DeFi
Risks:
- Regulatory clampdowns could restrict certain activities
- Security breaches could undermine trust
- Market volatility may impact investor confidence
To sustain long-term growth amid these dynamics requires balancing innovation with prudent risk management strategies—a challenge that experienced teams within Tron seem prepared to meet given their track record so far.
By forging meaningful relationships across diverse segments—from peer-to-peer file sharing via BitTorrent—to cutting-edge NFT marketplaces—TRON demonstrates a clear commitment toward building a comprehensive decentralized entertainment ecosystem rooted in real-world utility rather than speculation alone. This approach not only enhances its competitive edge but also aligns well with global trends favoring decentralization — making it a noteworthy player shaping future digital economies.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-14 22:50
What partnerships with content platforms drive TRON (TRX) ecosystem growth?
How Partnerships with Content Platforms Are Driving TRON (TRX) Ecosystem Growth
The TRON blockchain platform has gained significant attention in the digital content and cryptocurrency space, largely due to its strategic partnerships with various content platforms. These collaborations are key drivers of ecosystem expansion, user engagement, and technological adoption. Understanding how these partnerships influence TRON’s growth provides valuable insights into the evolving landscape of blockchain-based content sharing.
The Role of Strategic Partnerships in Blockchain Ecosystems
Partnerships are fundamental for blockchain projects aiming to scale their reach and functionality. For TRON, collaborating with content platforms allows it to tap into existing user bases while offering innovative solutions like decentralized content sharing, NFTs, and DeFi applications. These alliances help build a more robust ecosystem where users benefit from transparency, security, and ownership rights that blockchain technology offers.
By integrating with popular platforms such as BitTorrent or NFT marketplaces like Rarible and OpenSea, TRON enhances its visibility within both the crypto community and mainstream digital entertainment markets. Such collaborations also serve as validation points for investors looking for sustainable growth pathways rooted in real-world utility.
Key Content Platform Partnerships Fueling Growth
One of the most notable milestones for TRON was its acquisition of BitTorrent in 2019. As one of the largest peer-to-peer file-sharing services globally—with millions of active users—BitTorrent provided an immediate boost to TRON’s network activity. This move allowed TRON to leverage BitTorrent's infrastructure while integrating blockchain features such as token rewards for file sharing.
In addition to BitTorrent, TRON has partnered with several decentralized content sharing platforms like DLive and Rize. These platforms utilize blockchain technology to ensure transparent monetization models where creators retain control over their work without relying on centralized authorities or intermediaries.
Furthermore, the rise of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has prompted partnerships between TRON and leading NFT marketplaces such as Rarible and OpenSea. These collaborations facilitate seamless creation, trading, and ownership verification of unique digital assets on the Tron network—expanding opportunities for artists, collectors, and developers alike.
Challenges Facing Content Platform Collaborations
While these partnerships have propelled growth within the ecosystem—boosting transaction volumes & token demand—they also introduce certain risks that need careful management:
Regulatory Scrutiny: As more content is shared via blockchain-based systems globally—especially involving NFTs—the regulatory environment becomes increasingly complex. Governments are scrutinizing issues related to copyright infringement or money laundering concerns associated with digital assets.
Security Concerns: Integrating large-scale user bases from popular platforms increases vulnerabilities related to hacking attempts or smart contract exploits. Maintaining high-security standards is crucial for safeguarding user data & assets.
Market Volatility: The value proposition tied directly to these partnerships can be affected by broader market trends or negative news cycles impacting cryptocurrencies generally—including regulatory crackdowns or technological setbacks.
Despite these challenges—and when managed properly—such collaborations continue fueling demand for TRX tokens by increasing platform utility & attracting new users interested in decentralized entertainment options.
Impact on Tron's Token Value
Partnership-driven growth often correlates positively with token performance; increased activity on partnered platforms leads directly to higher demand for native tokens like TRX used within those ecosystems—for transactions or governance purposes. Since 2019’s acquisition of BitTorrent alone contributed significantly toward boosting transaction volume—and consequently token value—the trend persists today across newer integrations involving NFTs & dApps.
However—as seen throughout crypto markets—price fluctuations remain common due to external factors including regulatory developments or macroeconomic shifts affecting investor sentiment overall.
Future Outlook: Opportunities & Risks
Looking ahead at how partnerships might evolve reveals both promising opportunities—and potential pitfalls—for Tron’s ecosystem expansion:
Opportunities:
- Continued integration into mainstream media through strategic alliances
- Expansion into emerging sectors like metaverse applications
- Increased adoption driven by innovative use cases around NFTs & DeFi
Risks:
- Regulatory clampdowns could restrict certain activities
- Security breaches could undermine trust
- Market volatility may impact investor confidence
To sustain long-term growth amid these dynamics requires balancing innovation with prudent risk management strategies—a challenge that experienced teams within Tron seem prepared to meet given their track record so far.
By forging meaningful relationships across diverse segments—from peer-to-peer file sharing via BitTorrent—to cutting-edge NFT marketplaces—TRON demonstrates a clear commitment toward building a comprehensive decentralized entertainment ecosystem rooted in real-world utility rather than speculation alone. This approach not only enhances its competitive edge but also aligns well with global trends favoring decentralization — making it a noteworthy player shaping future digital economies.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
In order to ensure the fairness and sustainability of the trading environment on the platform, and to prevent potential impact of abnormal trading behavior on market order, the platform has recently monitored some accounts that frequently engage in ultra-short-term trading (such as holding positions for significantly less than normal trading hours) and use this to obtain rebates. In order to maintain the effectiveness and long-term stability of the rebate mechanism, the platform has made the following supplementary adjustments to the rebate rules for futures trading.
📌 Starting from the effective date, orders with a Futures trading position time of less than 3 minutes (180 seconds) will no longer be counted as valid trading volume, and will not enjoy any form of commission, commission deduction, and activity rewards .
👉 Details: https://bit.ly/4oG6uUr
#Jucoin #JucoinVietnam #Futures #JucoinTrading


Lee Jucoin
2025-08-14 03:25
🚨 Announcement on Adjusting the Futures Trading Commission Rebate Rules
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Managing Flaky Networks in Mobile Apps: Strategies and Technologies
Understanding Flaky Networks in Mobile Applications
In today’s digital landscape, mobile apps are integral to daily life, from social media and banking to healthcare and e-commerce. These applications depend heavily on stable network connectivity to deliver seamless user experiences. However, network instability—commonly known as flaky networks—poses significant challenges for developers and users alike. Flaky networks refer to intermittent or unreliable internet connections that can cause apps to malfunction, crash, or behave unpredictably.
Such network issues often stem from various factors including congestion during peak usage times, infrastructure problems like server outages or poor ISP quality, and device limitations such as hardware constraints or software bugs. For users, this translates into frustrating experiences marked by slow load times, failed transactions, or app crashes. For businesses relying on mobile platforms for revenue generation and customer engagement, flaky networks can lead to lost sales, negative reviews, and diminished trust.
Recent technological advancements are shaping how developers address these challenges. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into network management systems to predict potential disruptions before they impact the user experience. Edge computing is another promising development that processes data closer to the user’s device—reducing latency and improving real-time communication even when connectivity is unstable.
Key Techniques for Managing Unreliable Network Conditions
To mitigate the effects of flaky networks on mobile applications effectively, developers employ several core strategies:
Retry Mechanisms: Implementing automatic retries allows an app to attempt reconnecting after a failed request due to poor connectivity. This approach helps ensure data synchronization without requiring user intervention.
Data Caching: Storing critical information locally enables apps to function smoothly even when offline temporarily. Cached data ensures continuity of essential features like viewing previously loaded content or composing messages that sync once the connection stabilizes.
Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous tracking of network parameters such as packet loss rates and latency provides insights into current conditions. Developers can use this data for dynamic adjustments—for example adjusting image quality based on bandwidth availability—to optimize performance under varying circumstances.
These techniques collectively enhance resilience against unpredictable network environments while maintaining a positive user experience.
Impact of Flaky Networks on Users and Businesses
Persistent connectivity issues not only frustrate users but also have tangible business consequences. When an app frequently encounters flaky connections leading to crashes or slow responses—users may lose confidence in its reliability—and switch over competitors offering more consistent service levels.
Furthermore, certain industries like finance or healthcare have strict regulatory requirements regarding data security and system uptime; failure here could result in legal penalties alongside reputational damage. Ensuring reliable connectivity becomes not just a matter of convenience but also compliance with industry standards designed around robust system performance.
Emerging Trends Improving Network Reliability
The evolution toward 5G technology promises faster speeds with lower latency—a game-changer for mobile app stability amid fluctuating conditions—but it also introduces new hurdles such as ensuring compatibility across diverse devices while upgrading infrastructure[2].
Simultaneously, AI-driven solutions are becoming more sophisticated at predicting network failures by analyzing patterns in real-time data streams[4]. These predictive models enable proactive adjustments within apps—for instance switching between different servers dynamically—to prevent disruptions before they occur.
Security remains a critical concern as well; with increased reliance on edge computing devices connected via IoT ecosystems[3], safeguarding these systems against malicious attacks is paramount for maintaining trustworthiness in managing flaky networks effectively.
Best Practices for Developers Handling Flaky Networks
Developers aiming at resilient mobile applications should adopt comprehensive strategies:
- Incorporate intelligent retry logic with exponential backoff algorithms.
- Use local caching judiciously for critical functionalities.
- Monitor key performance indicators continuously using analytics tools.
- Design adaptive UI/UX elements that inform users about ongoing reconnection attempts without causing frustration.
- Stay updated with emerging technologies like AI-powered predictive analytics and edge computing solutions which offer proactive management capabilities.6.. Prioritize security measures especially when integrating new technologies prone to vulnerabilities if improperly managed[3].
By combining these practices with ongoing industry insights—such as upcoming 5G deployments—they can significantly improve their application's robustness against unreliable networks while enhancing overall user satisfaction.
The Future of Managing Network Instability in Mobile Apps
As technology advances rapidly—with innovations like 5G rollout accelerating—the landscape of mobile networking will continue evolving[2]. While faster speeds promise better stability overall; new challenges related to backward compatibility—and ensuring security across complex distributed systems—will require continuous adaptation from developers.
AI's role will likely expand further into predictive maintenance models capable of preemptively addressing potential disruptions based on historical patterns[4]. Edge computing will become more prevalent by processing sensitive data locally near the device rather than relying solely on distant servers—a move that reduces latency dramatically but demands rigorous security protocols[1][3].
Ultimately, building resilient mobile applications capable of handling flaky networks involves embracing emerging tech trends while adhering strictly to best practices rooted in cybersecurity principlesand proven engineering methods — ensuring both reliabilityand trustworthinessfor end-users worldwide


Lo
2025-05-26 17:36
How do mobile apps manage flaky networks?
Managing Flaky Networks in Mobile Apps: Strategies and Technologies
Understanding Flaky Networks in Mobile Applications
In today’s digital landscape, mobile apps are integral to daily life, from social media and banking to healthcare and e-commerce. These applications depend heavily on stable network connectivity to deliver seamless user experiences. However, network instability—commonly known as flaky networks—poses significant challenges for developers and users alike. Flaky networks refer to intermittent or unreliable internet connections that can cause apps to malfunction, crash, or behave unpredictably.
Such network issues often stem from various factors including congestion during peak usage times, infrastructure problems like server outages or poor ISP quality, and device limitations such as hardware constraints or software bugs. For users, this translates into frustrating experiences marked by slow load times, failed transactions, or app crashes. For businesses relying on mobile platforms for revenue generation and customer engagement, flaky networks can lead to lost sales, negative reviews, and diminished trust.
Recent technological advancements are shaping how developers address these challenges. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into network management systems to predict potential disruptions before they impact the user experience. Edge computing is another promising development that processes data closer to the user’s device—reducing latency and improving real-time communication even when connectivity is unstable.
Key Techniques for Managing Unreliable Network Conditions
To mitigate the effects of flaky networks on mobile applications effectively, developers employ several core strategies:
Retry Mechanisms: Implementing automatic retries allows an app to attempt reconnecting after a failed request due to poor connectivity. This approach helps ensure data synchronization without requiring user intervention.
Data Caching: Storing critical information locally enables apps to function smoothly even when offline temporarily. Cached data ensures continuity of essential features like viewing previously loaded content or composing messages that sync once the connection stabilizes.
Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous tracking of network parameters such as packet loss rates and latency provides insights into current conditions. Developers can use this data for dynamic adjustments—for example adjusting image quality based on bandwidth availability—to optimize performance under varying circumstances.
These techniques collectively enhance resilience against unpredictable network environments while maintaining a positive user experience.
Impact of Flaky Networks on Users and Businesses
Persistent connectivity issues not only frustrate users but also have tangible business consequences. When an app frequently encounters flaky connections leading to crashes or slow responses—users may lose confidence in its reliability—and switch over competitors offering more consistent service levels.
Furthermore, certain industries like finance or healthcare have strict regulatory requirements regarding data security and system uptime; failure here could result in legal penalties alongside reputational damage. Ensuring reliable connectivity becomes not just a matter of convenience but also compliance with industry standards designed around robust system performance.
Emerging Trends Improving Network Reliability
The evolution toward 5G technology promises faster speeds with lower latency—a game-changer for mobile app stability amid fluctuating conditions—but it also introduces new hurdles such as ensuring compatibility across diverse devices while upgrading infrastructure[2].
Simultaneously, AI-driven solutions are becoming more sophisticated at predicting network failures by analyzing patterns in real-time data streams[4]. These predictive models enable proactive adjustments within apps—for instance switching between different servers dynamically—to prevent disruptions before they occur.
Security remains a critical concern as well; with increased reliance on edge computing devices connected via IoT ecosystems[3], safeguarding these systems against malicious attacks is paramount for maintaining trustworthiness in managing flaky networks effectively.
Best Practices for Developers Handling Flaky Networks
Developers aiming at resilient mobile applications should adopt comprehensive strategies:
- Incorporate intelligent retry logic with exponential backoff algorithms.
- Use local caching judiciously for critical functionalities.
- Monitor key performance indicators continuously using analytics tools.
- Design adaptive UI/UX elements that inform users about ongoing reconnection attempts without causing frustration.
- Stay updated with emerging technologies like AI-powered predictive analytics and edge computing solutions which offer proactive management capabilities.6.. Prioritize security measures especially when integrating new technologies prone to vulnerabilities if improperly managed[3].
By combining these practices with ongoing industry insights—such as upcoming 5G deployments—they can significantly improve their application's robustness against unreliable networks while enhancing overall user satisfaction.
The Future of Managing Network Instability in Mobile Apps
As technology advances rapidly—with innovations like 5G rollout accelerating—the landscape of mobile networking will continue evolving[2]. While faster speeds promise better stability overall; new challenges related to backward compatibility—and ensuring security across complex distributed systems—will require continuous adaptation from developers.
AI's role will likely expand further into predictive maintenance models capable of preemptively addressing potential disruptions based on historical patterns[4]. Edge computing will become more prevalent by processing sensitive data locally near the device rather than relying solely on distant servers—a move that reduces latency dramatically but demands rigorous security protocols[1][3].
Ultimately, building resilient mobile applications capable of handling flaky networks involves embracing emerging tech trends while adhering strictly to best practices rooted in cybersecurity principlesand proven engineering methods — ensuring both reliabilityand trustworthinessfor end-users worldwide
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Notifications Do TradingView’s Mobile Apps Support?
TradingView has established itself as a leading platform for traders and investors seeking real-time market insights, advanced charting tools, and comprehensive analysis features. A key component of its mobile app experience is the notification system, which helps users stay informed about critical market movements and updates without constantly monitoring the app. Understanding what types of notifications are supported—and how they have evolved—can significantly enhance your trading strategy and user experience.
Types of Notifications Available on TradingView Mobile Apps
TradingView’s mobile applications support a diverse range of notifications tailored to meet different user needs. These alerts serve to keep traders updated on price movements, news events, system statuses, and more. The main categories include:
Price Alerts: Users can set specific price points for stocks, cryptocurrencies, forex pairs, or other financial instruments. When the asset reaches or crosses these thresholds, an alert is triggered—either via push notification or email—enabling timely decision-making.
News Updates: Market-moving news can significantly influence trading decisions. TradingView provides notifications about breaking news or significant events that could impact particular assets or sectors.
System Notifications: These alerts inform users about app updates, scheduled maintenance windows, connectivity issues, or other technical matters affecting service availability.
Market Data Updates: Real-time data such as price changes, volume shifts in specific assets or indices are communicated through instant notifications to help traders react swiftly.
These notification types collectively ensure that users remain well-informed about their investments while reducing the need for manual checks.
Customization Options for User Preferences
One of TradingView’s strengths lies in its flexible customization capabilities regarding notifications. Users can tailor their alert settings based on individual trading strategies and preferences. For example:
- Setting multiple price alerts with different thresholds
- Choosing preferred notification channels (push notifications vs email)
- Adjusting alert frequency to avoid excessive interruptions
- Filtering news updates by asset class or relevance
This level of personalization ensures that each trader receives only pertinent information aligned with their investment goals while minimizing unnecessary distractions.
Integration with External Services and Platforms
TradingView's mobile apps seamlessly integrate with various third-party services like brokerage accounts and financial news platforms. This integration allows users to receive consolidated notifications from multiple sources within a single interface—a feature particularly valuable for active traders managing diverse portfolios.
For instance:
- Alerts from connected brokerage accounts can trigger in-app notifications
- News feeds from external providers may be pushed directly into the app
Such integrations streamline information flow but also raise considerations around data privacy and security—topics worth exploring further.
Recent Developments Enhancing Notification Features
Over recent years, TradingView has made notable improvements aimed at refining its notification system:
Enhanced Customization (2023)
In 2023, TradingView introduced more granular control over alert parameters. Users gained options such as setting conditional alerts based on multiple criteria (e.g., price crossing above a moving average combined with volume spikes). This enhancement allows traders to create highly targeted signals aligned precisely with their strategies.
AI-Powered Price Alerts (2024)
The most recent innovation involves integrating artificial intelligence into the alert generation process. AI-driven algorithms analyze historical data patterns alongside current market conditions to generate more accurate and timely price alerts—reducing false positives common in traditional systems. This advancement aims to improve overall user trust in automated signals while supporting better decision-making during volatile periods.
Potential Challenges: Information Overload & Privacy Concerns
While these advancements offer significant benefits—they also introduce potential drawbacks that users should be aware of:
Information Overload
As notification options expand—and especially when combined with AI-generated alerts—the risk of overwhelming users increases. Excessive alerts may lead to "alert fatigue," where important signals get lost amidst less relevant ones; this diminishes overall effectiveness and could cause missed opportunities if not managed carefully through customization settings.
Privacy Implications
Personalized notifications often rely on collecting user data such as browsing habits or trading behavior patterns. Although intended to improve relevance—and indeed beneficial—the collection raises privacy concerns regarding how this data is stored/shared? Are third-party services involved? Ensuring transparency around data handling practices remains essential for maintaining trust among users who value confidentiality.
How To Optimize Your Notification Experience on TradingView Mobile Apps
To maximize benefits while minimizing downsides:
- Regularly review your alert settings; disable unnecessary ones.
- Use filtering options effectively—for example: only receive critical market updates during certain hours.
- Be cautious when enabling AI-driven alerts; customize sensitivity levels if possible.
- Stay informed about privacy policies related to data collection practices within the platform.5.. Consider consolidating multiple sources into fewer notification channels where feasible—to reduce clutter without missing vital information.
By actively managing your preferences thoughtfully—as part of an overall strategic approach—you can leverage TradingView’s powerful notification system effectively without becoming overwhelmed by constant pings.
In summary, TradingView’s mobile apps support a broad spectrum of notifications designed specifically for active traders seeking real-time insights—from customizable price alarms to timely news updates enhanced by artificial intelligence innovations—all aimed at improving decision-making efficiency while balancing potential challenges like information overload and privacy concerns.Understanding these features enables you not only to stay ahead in dynamic markets but also ensures you use them responsibly within your broader investment framework.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-26 22:09
What notifications do TradingView’s mobile apps support?
What Notifications Do TradingView’s Mobile Apps Support?
TradingView has established itself as a leading platform for traders and investors seeking real-time market insights, advanced charting tools, and comprehensive analysis features. A key component of its mobile app experience is the notification system, which helps users stay informed about critical market movements and updates without constantly monitoring the app. Understanding what types of notifications are supported—and how they have evolved—can significantly enhance your trading strategy and user experience.
Types of Notifications Available on TradingView Mobile Apps
TradingView’s mobile applications support a diverse range of notifications tailored to meet different user needs. These alerts serve to keep traders updated on price movements, news events, system statuses, and more. The main categories include:
Price Alerts: Users can set specific price points for stocks, cryptocurrencies, forex pairs, or other financial instruments. When the asset reaches or crosses these thresholds, an alert is triggered—either via push notification or email—enabling timely decision-making.
News Updates: Market-moving news can significantly influence trading decisions. TradingView provides notifications about breaking news or significant events that could impact particular assets or sectors.
System Notifications: These alerts inform users about app updates, scheduled maintenance windows, connectivity issues, or other technical matters affecting service availability.
Market Data Updates: Real-time data such as price changes, volume shifts in specific assets or indices are communicated through instant notifications to help traders react swiftly.
These notification types collectively ensure that users remain well-informed about their investments while reducing the need for manual checks.
Customization Options for User Preferences
One of TradingView’s strengths lies in its flexible customization capabilities regarding notifications. Users can tailor their alert settings based on individual trading strategies and preferences. For example:
- Setting multiple price alerts with different thresholds
- Choosing preferred notification channels (push notifications vs email)
- Adjusting alert frequency to avoid excessive interruptions
- Filtering news updates by asset class or relevance
This level of personalization ensures that each trader receives only pertinent information aligned with their investment goals while minimizing unnecessary distractions.
Integration with External Services and Platforms
TradingView's mobile apps seamlessly integrate with various third-party services like brokerage accounts and financial news platforms. This integration allows users to receive consolidated notifications from multiple sources within a single interface—a feature particularly valuable for active traders managing diverse portfolios.
For instance:
- Alerts from connected brokerage accounts can trigger in-app notifications
- News feeds from external providers may be pushed directly into the app
Such integrations streamline information flow but also raise considerations around data privacy and security—topics worth exploring further.
Recent Developments Enhancing Notification Features
Over recent years, TradingView has made notable improvements aimed at refining its notification system:
Enhanced Customization (2023)
In 2023, TradingView introduced more granular control over alert parameters. Users gained options such as setting conditional alerts based on multiple criteria (e.g., price crossing above a moving average combined with volume spikes). This enhancement allows traders to create highly targeted signals aligned precisely with their strategies.
AI-Powered Price Alerts (2024)
The most recent innovation involves integrating artificial intelligence into the alert generation process. AI-driven algorithms analyze historical data patterns alongside current market conditions to generate more accurate and timely price alerts—reducing false positives common in traditional systems. This advancement aims to improve overall user trust in automated signals while supporting better decision-making during volatile periods.
Potential Challenges: Information Overload & Privacy Concerns
While these advancements offer significant benefits—they also introduce potential drawbacks that users should be aware of:
Information Overload
As notification options expand—and especially when combined with AI-generated alerts—the risk of overwhelming users increases. Excessive alerts may lead to "alert fatigue," where important signals get lost amidst less relevant ones; this diminishes overall effectiveness and could cause missed opportunities if not managed carefully through customization settings.
Privacy Implications
Personalized notifications often rely on collecting user data such as browsing habits or trading behavior patterns. Although intended to improve relevance—and indeed beneficial—the collection raises privacy concerns regarding how this data is stored/shared? Are third-party services involved? Ensuring transparency around data handling practices remains essential for maintaining trust among users who value confidentiality.
How To Optimize Your Notification Experience on TradingView Mobile Apps
To maximize benefits while minimizing downsides:
- Regularly review your alert settings; disable unnecessary ones.
- Use filtering options effectively—for example: only receive critical market updates during certain hours.
- Be cautious when enabling AI-driven alerts; customize sensitivity levels if possible.
- Stay informed about privacy policies related to data collection practices within the platform.5.. Consider consolidating multiple sources into fewer notification channels where feasible—to reduce clutter without missing vital information.
By actively managing your preferences thoughtfully—as part of an overall strategic approach—you can leverage TradingView’s powerful notification system effectively without becoming overwhelmed by constant pings.
In summary, TradingView’s mobile apps support a broad spectrum of notifications designed specifically for active traders seeking real-time insights—from customizable price alarms to timely news updates enhanced by artificial intelligence innovations—all aimed at improving decision-making efficiency while balancing potential challenges like information overload and privacy concerns.Understanding these features enables you not only to stay ahead in dynamic markets but also ensures you use them responsibly within your broader investment framework.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Stay Informed About Emerging Threats and Scams
In today’s digital environment, cyber threats and scams are evolving at an unprecedented pace. From zero-day exploits to sophisticated phishing schemes, staying informed is essential for individuals and organizations alike. Being proactive in understanding the latest risks can significantly reduce your vulnerability and help you respond effectively when threats arise. This guide provides practical insights into how you can stay ahead of emerging cybersecurity threats and scams.
Understanding the Current Cyber Threat Landscape
The cybersecurity landscape is increasingly complex, with threat actors ranging from lone hackers to nation-states. These actors employ advanced techniques such as zero-day exploits—vulnerabilities unknown to vendors until exploited—to breach systems undetected. Recent developments highlight that government-backed hackers are responsible for a significant portion of these exploits, making it crucial for organizations to adopt robust security measures.
Sophisticated attacks now target not only large corporations but also small businesses and individual users. High-profile incidents like cyberattacks on major retailers or breaches involving communication apps demonstrate that no one is immune. Staying informed about these trends helps you recognize potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Key Sources for Cybersecurity Updates
To keep up with emerging threats, rely on reputable sources that provide timely and accurate information:
- Cybersecurity agencies: Organizations like the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) regularly publish alerts about new vulnerabilities.
- Threat intelligence reports: Companies such as Google’s Threat Intelligence Group release detailed analyses of recent attack vectors.
- Security vendors: Leading cybersecurity firms like Check Point Software offer updates on threat prevention technologies and emerging risks.
- Industry news outlets: Tech-focused news platforms often cover significant cyber incidents promptly.
Subscribing to newsletters or RSS feeds from these sources ensures a steady flow of relevant updates directly in your inbox or feed reader.
Recognizing Recent Developments in Cybersecurity
Staying current involves understanding recent key events that signal evolving threats:
- Zero-click device takeovers—Vulnerabilities like those found in AirPlay devices allow attackers to seize control without user interaction; patching such flaws underscores the importance of software updates.
- State-sponsored hacking activities—Reports indicate increased use of zero-day exploits by nation-states targeting critical infrastructure or sensitive data.
- High-profile cyberattacks—Incidents involving major retailers or government agencies serve as reminders that even well-defended organizations remain targets.
- Communication app breaches—Compromised messaging platforms used by officials highlight risks associated with cloned or maliciously altered apps.
Monitoring these developments helps anticipate future attack patterns and reinforces the need for proactive defenses.
Practical Steps to Stay Informed
Being aware isn’t enough—you must actively seek out knowledge through consistent practices:
- Regularly update all software, operating systems, browsers, and applications — patches fix known vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Follow trusted cybersecurity blogs, official advisories, and industry reports for real-time alerts on new threats.
- Subscribe to alerts from security providers who specialize in threat detection technology leveraging AI-driven solutions.
- Participate in webinars or training sessions offered by cybersecurity experts; continuous education enhances your ability to identify scams early.
Additionally, engaging with online communities focused on cybersecurity can provide peer insights into emerging scams specific to certain sectors or regions.
Protecting Yourself Against Crypto & Investment Scams
Crypto investments have surged in popularity but come with heightened scam risks due to promises of quick profits without proper due diligence. To safeguard your finances:
- Verify the legitimacy of investment platforms through regulatory bodies’ registries
- Be skeptical of offers promising guaranteed high returns
- Use secure wallets rather than sharing private keys
Remaining cautious reduces exposure not only financially but also emotionally when dealing with unfamiliar entities promising extraordinary gains.
The Role of Advanced Technologies in Threat Prevention
Modern threat prevention tools incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) which enhances detection capabilities beyond traditional signature-based methods. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data continuously looking for anomalies indicative of malicious activity — enabling faster response times against zero-day attacks or sophisticated malware campaigns.
Organizations investing in AI-powered security solutions tend toward better resilience against rapidly evolving threats because they adapt dynamically rather than relying solely on static rulesets.
Final Tips: Building a Resilient Security Posture
To effectively stay informed about emerging threats:
- Maintain regular software updates across all devices
- Verify authenticity before installing apps or clicking links
- Invest in advanced threat prevention tools suited for your needs
- Keep abreast through reputable sources dedicated to cybersecurity news5.. Exercise caution especially around crypto investments; conduct thorough research
By integrating these practices into daily routines—and fostering a culture attentive toward digital safety—you significantly enhance your defenses against ever-changing cyber dangers.
Staying informed about emerging threats requires ongoing effort but pays dividends by reducing risk exposure over time. Combining vigilance with technological safeguards creates a resilient approach capable of navigating today’s complex digital world safely—and confidently.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 03:21
How can you stay informed about emerging threats and scams?
How to Stay Informed About Emerging Threats and Scams
In today’s digital environment, cyber threats and scams are evolving at an unprecedented pace. From zero-day exploits to sophisticated phishing schemes, staying informed is essential for individuals and organizations alike. Being proactive in understanding the latest risks can significantly reduce your vulnerability and help you respond effectively when threats arise. This guide provides practical insights into how you can stay ahead of emerging cybersecurity threats and scams.
Understanding the Current Cyber Threat Landscape
The cybersecurity landscape is increasingly complex, with threat actors ranging from lone hackers to nation-states. These actors employ advanced techniques such as zero-day exploits—vulnerabilities unknown to vendors until exploited—to breach systems undetected. Recent developments highlight that government-backed hackers are responsible for a significant portion of these exploits, making it crucial for organizations to adopt robust security measures.
Sophisticated attacks now target not only large corporations but also small businesses and individual users. High-profile incidents like cyberattacks on major retailers or breaches involving communication apps demonstrate that no one is immune. Staying informed about these trends helps you recognize potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Key Sources for Cybersecurity Updates
To keep up with emerging threats, rely on reputable sources that provide timely and accurate information:
- Cybersecurity agencies: Organizations like the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) regularly publish alerts about new vulnerabilities.
- Threat intelligence reports: Companies such as Google’s Threat Intelligence Group release detailed analyses of recent attack vectors.
- Security vendors: Leading cybersecurity firms like Check Point Software offer updates on threat prevention technologies and emerging risks.
- Industry news outlets: Tech-focused news platforms often cover significant cyber incidents promptly.
Subscribing to newsletters or RSS feeds from these sources ensures a steady flow of relevant updates directly in your inbox or feed reader.
Recognizing Recent Developments in Cybersecurity
Staying current involves understanding recent key events that signal evolving threats:
- Zero-click device takeovers—Vulnerabilities like those found in AirPlay devices allow attackers to seize control without user interaction; patching such flaws underscores the importance of software updates.
- State-sponsored hacking activities—Reports indicate increased use of zero-day exploits by nation-states targeting critical infrastructure or sensitive data.
- High-profile cyberattacks—Incidents involving major retailers or government agencies serve as reminders that even well-defended organizations remain targets.
- Communication app breaches—Compromised messaging platforms used by officials highlight risks associated with cloned or maliciously altered apps.
Monitoring these developments helps anticipate future attack patterns and reinforces the need for proactive defenses.
Practical Steps to Stay Informed
Being aware isn’t enough—you must actively seek out knowledge through consistent practices:
- Regularly update all software, operating systems, browsers, and applications — patches fix known vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Follow trusted cybersecurity blogs, official advisories, and industry reports for real-time alerts on new threats.
- Subscribe to alerts from security providers who specialize in threat detection technology leveraging AI-driven solutions.
- Participate in webinars or training sessions offered by cybersecurity experts; continuous education enhances your ability to identify scams early.
Additionally, engaging with online communities focused on cybersecurity can provide peer insights into emerging scams specific to certain sectors or regions.
Protecting Yourself Against Crypto & Investment Scams
Crypto investments have surged in popularity but come with heightened scam risks due to promises of quick profits without proper due diligence. To safeguard your finances:
- Verify the legitimacy of investment platforms through regulatory bodies’ registries
- Be skeptical of offers promising guaranteed high returns
- Use secure wallets rather than sharing private keys
Remaining cautious reduces exposure not only financially but also emotionally when dealing with unfamiliar entities promising extraordinary gains.
The Role of Advanced Technologies in Threat Prevention
Modern threat prevention tools incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) which enhances detection capabilities beyond traditional signature-based methods. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data continuously looking for anomalies indicative of malicious activity — enabling faster response times against zero-day attacks or sophisticated malware campaigns.
Organizations investing in AI-powered security solutions tend toward better resilience against rapidly evolving threats because they adapt dynamically rather than relying solely on static rulesets.
Final Tips: Building a Resilient Security Posture
To effectively stay informed about emerging threats:
- Maintain regular software updates across all devices
- Verify authenticity before installing apps or clicking links
- Invest in advanced threat prevention tools suited for your needs
- Keep abreast through reputable sources dedicated to cybersecurity news5.. Exercise caution especially around crypto investments; conduct thorough research
By integrating these practices into daily routines—and fostering a culture attentive toward digital safety—you significantly enhance your defenses against ever-changing cyber dangers.
Staying informed about emerging threats requires ongoing effort but pays dividends by reducing risk exposure over time. Combining vigilance with technological safeguards creates a resilient approach capable of navigating today’s complex digital world safely—and confidently.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Intraday Charts?
Intraday charts are essential tools used by traders and technical analysts to monitor the price movements of financial instruments within a single trading day. Unlike daily or weekly charts that aggregate data over longer periods, intraday charts focus on short-term fluctuations, providing real-time insights into market behavior. This makes them particularly valuable for day traders who aim to capitalize on quick price changes and need immediate data to inform their trading decisions.
These charts typically display data at intervals ranging from one minute to several hours, allowing traders to observe detailed patterns and trends as they unfold throughout the trading session. By visualizing these rapid movements, intraday charts help identify entry and exit points with greater precision, ultimately supporting more effective risk management strategies.
How Do Intraday Charts Work?
Intraday charts operate by plotting price data collected during a single trading session in real time. They can be configured with various timeframes—such as 1-minute, 5-minute, 15-minute, or hourly intervals—depending on the trader’s strategy and preference. The chart updates continuously during market hours, reflecting every tick or trade executed in the market.
Most intraday charts incorporate technical indicators like moving averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, and volume overlays. These tools help traders interpret short-term momentum and volatility while identifying potential support or resistance levels. For example:
- Moving Averages smooth out price fluctuations to reveal underlying trends.
- RSI measures overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands indicate volatility levels based on standard deviations from a moving average.
By combining these indicators with raw price data displayed visually through candlestick or bar formats, traders gain a comprehensive view of current market dynamics.
Why Are Intraday Charts Important for Day Trading?
Day traders rely heavily on intraday charts because they provide immediate feedback about ongoing market conditions. Since their goal is to profit from short-term price swings within a single session—often holding positions for minutes or hours—they need access to real-time information that longer-term charts cannot offer.
Using intraday analysis allows traders to:
- Spot emerging trends early
- Recognize reversal signals
- Set precise stop-loss orders
- Take profits at optimal moments
This granular level of detail enhances decision-making speed and accuracy in fast-moving markets such as stocks, cryptocurrencies, commodities, and forex pairs.
Furthermore, intraday chart analysis supports disciplined trading by enabling systematic entry/exit strategies based on technical signals rather than emotions alone. It also helps manage risk effectively through timely adjustments aligned with current market momentum.
The Role of Technical Analysis Using Intraday Charts
Technical analysis is fundamental when working with intraday charts because it involves studying historical prices and patterns to forecast future movements. Traders analyze support/resistance levels—price points where an asset tends to reverse direction—and identify chart formations like flags or pennants that suggest continuation patterns.
Popular technical indicators applied on intraday timeframes include:
- Moving averages (e.g., EMA 20)
- RSI for momentum assessment
- Bollinger Bands for volatility detection
- Volume profiles indicating buying/selling pressure
Combining these tools enables traders not only to confirm trend directions but also anticipate potential reversals before they occur—a critical advantage in high-frequency environments where timing is everything.
Recent Advances Enhancing Intraday Chart Usage
The landscape of intraday charting has evolved significantly due to technological advancements:
Improved Trading Platforms
Modern platforms now offer customizable dashboards featuring multiple chart types simultaneously—candlestick patterns alongside volume heatmaps—and integrate real-time news feeds alongside live data streams. Automated alerts notify users when specific technical criteria are met without constant monitoring manually.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI-driven algorithms analyze vast datasets rapidly beyond human capacity; they detect complex pattern formations often missed by manual analysis. Machine learning models predict probable short-term moves based on historical behavior combined with current sentiment indicators—a game-changer for sophisticated day-traders seeking an edge in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies.
Regulatory Environment Changes
Regulatory bodies worldwide have increased oversight over high-frequency trading practices due partly to concerns about manipulation risks associated with rapid trades enabled by advanced charting tools. These regulations aim at ensuring fairer markets but also influence how some platforms operate regarding transparency standards around algorithmic strategies used alongside intra-day analysis techniques.
Risks Associated With Heavy Reliance On Intraday Data
While intraday charts provide invaluable insights into short-term movements — especially when combined with robust analytical methods — there are notable risks involved:
Overdependence On Technology
Heavy reliance on AI-powered systems might lead some traders neglect fundamental factors influencing asset prices such as earnings reports or macroeconomic news events which can override technical signals quickly during volatile sessions.
Market Manipulation Concerns
High-frequency trades facilitated through sophisticated algorithms may contribute toward manipulative practices like spoofing (placing fake orders) designed solely for misleading other participants about true supply/demand dynamics.
Trader Burnout & Educational Gaps
The intense pace required when constantly analyzing minute-by-minute changes can cause fatigue leading eventually toward poor decision-making under stress; additionally many new entrants lack sufficient training in interpreting complex indicator combinations accurately.
How To Use Intraday Charts Effectively
To maximize benefits while minimizing pitfalls:
- Combine multiple indicators judiciously rather than relying solely on one signal
- Maintain discipline by setting predefined stop-losses/take-profit levels
- Stay updated with relevant news impacting your traded assets
- Practice continuous learning about evolving techniques & platform features
5.. Avoid emotional reactions; stick strictly within your strategic plan
By following these principles grounded in sound risk management practices backed up by thorough understanding of intra-day dynamics you’ll improve your chances of successful trades.
Understanding what intradayercharts are—and how best they can be utilized—is crucial whether you're an experienced trader seeking sharper insights or just starting out exploring active markets like stocks or cryptocurrencies . As technology continues advancing rapidly coupled with regulatory shifts aimed at safeguarding investors’ interests , staying informed will remain key component towards mastering this powerful analytical tool effectively .


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-19 18:47
What are intraday charts?
What Are Intraday Charts?
Intraday charts are essential tools used by traders and technical analysts to monitor the price movements of financial instruments within a single trading day. Unlike daily or weekly charts that aggregate data over longer periods, intraday charts focus on short-term fluctuations, providing real-time insights into market behavior. This makes them particularly valuable for day traders who aim to capitalize on quick price changes and need immediate data to inform their trading decisions.
These charts typically display data at intervals ranging from one minute to several hours, allowing traders to observe detailed patterns and trends as they unfold throughout the trading session. By visualizing these rapid movements, intraday charts help identify entry and exit points with greater precision, ultimately supporting more effective risk management strategies.
How Do Intraday Charts Work?
Intraday charts operate by plotting price data collected during a single trading session in real time. They can be configured with various timeframes—such as 1-minute, 5-minute, 15-minute, or hourly intervals—depending on the trader’s strategy and preference. The chart updates continuously during market hours, reflecting every tick or trade executed in the market.
Most intraday charts incorporate technical indicators like moving averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, and volume overlays. These tools help traders interpret short-term momentum and volatility while identifying potential support or resistance levels. For example:
- Moving Averages smooth out price fluctuations to reveal underlying trends.
- RSI measures overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands indicate volatility levels based on standard deviations from a moving average.
By combining these indicators with raw price data displayed visually through candlestick or bar formats, traders gain a comprehensive view of current market dynamics.
Why Are Intraday Charts Important for Day Trading?
Day traders rely heavily on intraday charts because they provide immediate feedback about ongoing market conditions. Since their goal is to profit from short-term price swings within a single session—often holding positions for minutes or hours—they need access to real-time information that longer-term charts cannot offer.
Using intraday analysis allows traders to:
- Spot emerging trends early
- Recognize reversal signals
- Set precise stop-loss orders
- Take profits at optimal moments
This granular level of detail enhances decision-making speed and accuracy in fast-moving markets such as stocks, cryptocurrencies, commodities, and forex pairs.
Furthermore, intraday chart analysis supports disciplined trading by enabling systematic entry/exit strategies based on technical signals rather than emotions alone. It also helps manage risk effectively through timely adjustments aligned with current market momentum.
The Role of Technical Analysis Using Intraday Charts
Technical analysis is fundamental when working with intraday charts because it involves studying historical prices and patterns to forecast future movements. Traders analyze support/resistance levels—price points where an asset tends to reverse direction—and identify chart formations like flags or pennants that suggest continuation patterns.
Popular technical indicators applied on intraday timeframes include:
- Moving averages (e.g., EMA 20)
- RSI for momentum assessment
- Bollinger Bands for volatility detection
- Volume profiles indicating buying/selling pressure
Combining these tools enables traders not only to confirm trend directions but also anticipate potential reversals before they occur—a critical advantage in high-frequency environments where timing is everything.
Recent Advances Enhancing Intraday Chart Usage
The landscape of intraday charting has evolved significantly due to technological advancements:
Improved Trading Platforms
Modern platforms now offer customizable dashboards featuring multiple chart types simultaneously—candlestick patterns alongside volume heatmaps—and integrate real-time news feeds alongside live data streams. Automated alerts notify users when specific technical criteria are met without constant monitoring manually.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI-driven algorithms analyze vast datasets rapidly beyond human capacity; they detect complex pattern formations often missed by manual analysis. Machine learning models predict probable short-term moves based on historical behavior combined with current sentiment indicators—a game-changer for sophisticated day-traders seeking an edge in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies.
Regulatory Environment Changes
Regulatory bodies worldwide have increased oversight over high-frequency trading practices due partly to concerns about manipulation risks associated with rapid trades enabled by advanced charting tools. These regulations aim at ensuring fairer markets but also influence how some platforms operate regarding transparency standards around algorithmic strategies used alongside intra-day analysis techniques.
Risks Associated With Heavy Reliance On Intraday Data
While intraday charts provide invaluable insights into short-term movements — especially when combined with robust analytical methods — there are notable risks involved:
Overdependence On Technology
Heavy reliance on AI-powered systems might lead some traders neglect fundamental factors influencing asset prices such as earnings reports or macroeconomic news events which can override technical signals quickly during volatile sessions.
Market Manipulation Concerns
High-frequency trades facilitated through sophisticated algorithms may contribute toward manipulative practices like spoofing (placing fake orders) designed solely for misleading other participants about true supply/demand dynamics.
Trader Burnout & Educational Gaps
The intense pace required when constantly analyzing minute-by-minute changes can cause fatigue leading eventually toward poor decision-making under stress; additionally many new entrants lack sufficient training in interpreting complex indicator combinations accurately.
How To Use Intraday Charts Effectively
To maximize benefits while minimizing pitfalls:
- Combine multiple indicators judiciously rather than relying solely on one signal
- Maintain discipline by setting predefined stop-losses/take-profit levels
- Stay updated with relevant news impacting your traded assets
- Practice continuous learning about evolving techniques & platform features
5.. Avoid emotional reactions; stick strictly within your strategic plan
By following these principles grounded in sound risk management practices backed up by thorough understanding of intra-day dynamics you’ll improve your chances of successful trades.
Understanding what intradayercharts are—and how best they can be utilized—is crucial whether you're an experienced trader seeking sharper insights or just starting out exploring active markets like stocks or cryptocurrencies . As technology continues advancing rapidly coupled with regulatory shifts aimed at safeguarding investors’ interests , staying informed will remain key component towards mastering this powerful analytical tool effectively .
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Perpetual Swaps?
Perpetual swaps, also known as perpetual futures or inverse futures, have become a cornerstone of modern cryptocurrency trading. Unlike traditional futures contracts that have fixed expiration dates, perpetual swaps allow traders to maintain open positions indefinitely. This flexibility has made them highly attractive in the fast-paced and volatile world of digital assets.
Understanding Perpetual Swaps
At their core, perpetual swaps are financial derivatives designed to mimic the price movements of underlying cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH). They enable traders to speculate on whether prices will rise or fall without owning the actual asset. The defining feature that sets them apart from standard futures is their lack of an expiration date—traders can hold these contracts for as long as they wish.
One key mechanism that helps keep perpetual swap prices aligned with the underlying asset is the "funding rate." This rate is a periodic fee exchanged between long and short position holders based on market conditions. If the contract’s price exceeds the spot price of the asset, longs pay shorts; if it’s below, shorts pay longs. This system encourages market equilibrium and prevents significant divergence between contract prices and real-world prices.
Another important aspect is leverage trading. Perpetual swaps often allow high leverage—sometimes up to 100x—meaning traders can control large positions with relatively small capital outlays. While this amplifies potential gains, it equally increases risk exposure, making risk management strategies essential for participants.
Why Are Perpetual Swaps Popular in Cryptocurrency Markets?
The surge in popularity of perpetual swaps stems from several factors unique to cryptocurrency markets:
- High Liquidity: Major exchanges like Binance, FTX, and Bybit offer deep liquidity pools for perpetual swap trading across various cryptocurrencies.
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their rapid price swings; perpetual swaps provide an efficient way for traders to capitalize on short-term movements.
- Regulatory Environment: Compared to traditional derivatives markets—which often face stringent regulations—the crypto space offers more flexible options for derivative trading due to lighter regulatory oversight in many jurisdictions.
These features make perpetual swaps particularly appealing not only for institutional investors but also retail traders seeking quick profits through technical analysis or momentum trading strategies.
Key Features That Define Perpetual Swaps
Understanding some fundamental characteristics helps clarify how these instruments function:
- No Fixed Expiration Date: Traders can hold positions indefinitely unless they choose to close them or face liquidation.
- Mark Price & Funding Rate: The mark price acts as a reference point used by exchanges to calculate funding payments periodically.
- Leverage Trading Capabilities: High leverage options increase both profit potential and risk exposure.
These features collectively contribute toward creating a dynamic yet complex trading environment where continuous monitoring is necessary.
Recent Trends & Developments
Over recent years, several notable trends have shaped how perpetual swaps are traded:
- Growing Market Adoption: As more traders recognize their utility in speculative strategies, volume metrics continue rising globally across multiple platforms.
- Enhanced Trading Tools: Advanced features like stop-loss orders and automated margin calls help manage risks associated with high leverage trades.
- Regulatory Attention: Authorities worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing these instruments due to concerns over market manipulation and investor protection—prompting discussions about possible regulation frameworks tailored specifically for crypto derivatives.
Additionally, technological advancements such as improved matching engines and real-time data analytics have enhanced user experience while reducing systemic risks associated with rapid liquidations during volatile periods.
Risks Associated With Perpetual Swaps
Despite their advantages, perpetually traded derivatives carry significant risks:
Market Instability: High leverage can lead to cascading liquidations if sudden adverse moves occur—a phenomenon sometimes called “liquidation cascades”—which may destabilize entire markets temporarily.
Regulatory Challenges: As regulators begin imposing restrictions or licensing requirements on derivative products within crypto markets—including mandatory disclosures—they could limit access or increase compliance costs significantly.
Technological Vulnerabilities: Dependence on sophisticated technology infrastructure exposes users—and platforms—to cyber threats like hacking attempts or system failures that could disrupt trades unexpectedly.
It’s crucial that traders understand these risks thoroughly before engaging heavily in leveraged derivative activities involving perpetual swaps.
How Traders Can Manage Risks Effectively
To navigate this complex landscape safely:
- Use appropriate stop-loss orders
- Limit leverage levels according to personal risk appetite
- Stay informed about regulatory developments affecting derivatives
- Regularly monitor market conditions using advanced analytical tools
By adopting disciplined risk management practices alongside continuous education about evolving market dynamics—and understanding how funding rates influence position costs—traders can better protect themselves against unforeseen losses.
The Future Outlook For Perpetual Swaps
As cryptocurrency adoption accelerates globally—with increasing institutional interest—the role of perpetual swaps is likely set to expand further. Innovations such as decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols are exploring ways to offer similar instruments without centralized intermediaries which might democratize access even more while introducing new layers of complexity regarding security standards.
However, ongoing regulatory scrutiny remains a critical factor influencing future development paths; stricter rules could either curb excessive speculation or foster safer environments conducive for sustainable growth within crypto derivatives markets.
Final Thoughts
Perpetual swaps represent a powerful tool within modern crypto trading ecosystems—they combine flexibility with high liquidity but demand careful attention due diligence given inherent volatility and leverage-related risks. For both individual investors seeking quick gains and institutions aiming at hedging strategies—or diversifying portfolios—they offer opportunities worth understanding deeply through ongoing education coupled with prudent risk management practices.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 16:04
What are perpetual swaps?
What Are Perpetual Swaps?
Perpetual swaps, also known as perpetual futures or inverse futures, have become a cornerstone of modern cryptocurrency trading. Unlike traditional futures contracts that have fixed expiration dates, perpetual swaps allow traders to maintain open positions indefinitely. This flexibility has made them highly attractive in the fast-paced and volatile world of digital assets.
Understanding Perpetual Swaps
At their core, perpetual swaps are financial derivatives designed to mimic the price movements of underlying cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH). They enable traders to speculate on whether prices will rise or fall without owning the actual asset. The defining feature that sets them apart from standard futures is their lack of an expiration date—traders can hold these contracts for as long as they wish.
One key mechanism that helps keep perpetual swap prices aligned with the underlying asset is the "funding rate." This rate is a periodic fee exchanged between long and short position holders based on market conditions. If the contract’s price exceeds the spot price of the asset, longs pay shorts; if it’s below, shorts pay longs. This system encourages market equilibrium and prevents significant divergence between contract prices and real-world prices.
Another important aspect is leverage trading. Perpetual swaps often allow high leverage—sometimes up to 100x—meaning traders can control large positions with relatively small capital outlays. While this amplifies potential gains, it equally increases risk exposure, making risk management strategies essential for participants.
Why Are Perpetual Swaps Popular in Cryptocurrency Markets?
The surge in popularity of perpetual swaps stems from several factors unique to cryptocurrency markets:
- High Liquidity: Major exchanges like Binance, FTX, and Bybit offer deep liquidity pools for perpetual swap trading across various cryptocurrencies.
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their rapid price swings; perpetual swaps provide an efficient way for traders to capitalize on short-term movements.
- Regulatory Environment: Compared to traditional derivatives markets—which often face stringent regulations—the crypto space offers more flexible options for derivative trading due to lighter regulatory oversight in many jurisdictions.
These features make perpetual swaps particularly appealing not only for institutional investors but also retail traders seeking quick profits through technical analysis or momentum trading strategies.
Key Features That Define Perpetual Swaps
Understanding some fundamental characteristics helps clarify how these instruments function:
- No Fixed Expiration Date: Traders can hold positions indefinitely unless they choose to close them or face liquidation.
- Mark Price & Funding Rate: The mark price acts as a reference point used by exchanges to calculate funding payments periodically.
- Leverage Trading Capabilities: High leverage options increase both profit potential and risk exposure.
These features collectively contribute toward creating a dynamic yet complex trading environment where continuous monitoring is necessary.
Recent Trends & Developments
Over recent years, several notable trends have shaped how perpetual swaps are traded:
- Growing Market Adoption: As more traders recognize their utility in speculative strategies, volume metrics continue rising globally across multiple platforms.
- Enhanced Trading Tools: Advanced features like stop-loss orders and automated margin calls help manage risks associated with high leverage trades.
- Regulatory Attention: Authorities worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing these instruments due to concerns over market manipulation and investor protection—prompting discussions about possible regulation frameworks tailored specifically for crypto derivatives.
Additionally, technological advancements such as improved matching engines and real-time data analytics have enhanced user experience while reducing systemic risks associated with rapid liquidations during volatile periods.
Risks Associated With Perpetual Swaps
Despite their advantages, perpetually traded derivatives carry significant risks:
Market Instability: High leverage can lead to cascading liquidations if sudden adverse moves occur—a phenomenon sometimes called “liquidation cascades”—which may destabilize entire markets temporarily.
Regulatory Challenges: As regulators begin imposing restrictions or licensing requirements on derivative products within crypto markets—including mandatory disclosures—they could limit access or increase compliance costs significantly.
Technological Vulnerabilities: Dependence on sophisticated technology infrastructure exposes users—and platforms—to cyber threats like hacking attempts or system failures that could disrupt trades unexpectedly.
It’s crucial that traders understand these risks thoroughly before engaging heavily in leveraged derivative activities involving perpetual swaps.
How Traders Can Manage Risks Effectively
To navigate this complex landscape safely:
- Use appropriate stop-loss orders
- Limit leverage levels according to personal risk appetite
- Stay informed about regulatory developments affecting derivatives
- Regularly monitor market conditions using advanced analytical tools
By adopting disciplined risk management practices alongside continuous education about evolving market dynamics—and understanding how funding rates influence position costs—traders can better protect themselves against unforeseen losses.
The Future Outlook For Perpetual Swaps
As cryptocurrency adoption accelerates globally—with increasing institutional interest—the role of perpetual swaps is likely set to expand further. Innovations such as decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols are exploring ways to offer similar instruments without centralized intermediaries which might democratize access even more while introducing new layers of complexity regarding security standards.
However, ongoing regulatory scrutiny remains a critical factor influencing future development paths; stricter rules could either curb excessive speculation or foster safer environments conducive for sustainable growth within crypto derivatives markets.
Final Thoughts
Perpetual swaps represent a powerful tool within modern crypto trading ecosystems—they combine flexibility with high liquidity but demand careful attention due diligence given inherent volatility and leverage-related risks. For both individual investors seeking quick gains and institutions aiming at hedging strategies—or diversifying portfolios—they offer opportunities worth understanding deeply through ongoing education coupled with prudent risk management practices.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen Interact as Trading Signals?
Understanding how Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen work together is essential for traders who utilize the Ichimoku Cloud system. These two indicators serve as foundational tools in technical analysis, helping traders identify potential trend reversals, confirm market momentum, and make informed trading decisions. Their interaction provides clear signals that can be interpreted across various markets such as forex, cryptocurrencies, and stocks.
What Are Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen?
Tenkan-sen (Conversion Line) and Kijun-sen (Base Line) are moving averages calculated over different periods to capture short-term and medium-term price trends. The Tenkan-sen is derived from the highest high and lowest low over the past 9 periods, making it a responsive indicator for recent price movements. Conversely, the Kijun-sen uses a longer window of 26 periods to smooth out fluctuations, providing insight into broader market trends.
These lines are integral components of the Ichimoku Cloud system but can also be used independently or in conjunction with other technical tools. Their primary purpose is to gauge trend direction—whether bullish or bearish—and signal potential entry or exit points based on their interactions.
How Do Crossovers Signal Market Trends?
One of the most straightforward ways to interpret Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen interactions is through crossovers:
Bullish Crossover (Buy Signal): When the Tenkan-sen crosses above the Kijun-sen, it indicates that short-term momentum has shifted upward relative to longer-term trends. This crossover suggests increasing buying pressure and potential for an upward price move.
Bearish Crossover (Sell Signal): Conversely, when the Tenkan-sen crosses below the Kijun-sen, it signals weakening short-term momentum compared to longer-term trends. This event often precedes downward price movements or confirms existing bearish sentiment.
These crossovers are particularly valuable because they provide early indications of trend changes before they become evident in price action alone.
The Significance of Relative Positioning
Beyond crossovers, where these lines sit relative to each other—and relative to key support/resistance levels—adds depth to their signals:
- When both lines are above a significant support level like the Ichimoku Cloud or recent highs/lows, it reinforces bullish sentiment.
- If both lines are below critical resistance zones or within a declining cloud formation, bearish conditions are likely prevailing.
The distance between Tenkan-sen and Kijun-san also matters; wider gaps often indicate stronger momentum behind a trend change. Rapid crossings with large gaps suggest increased market volatility but may also signal more reliable shifts if confirmed by other indicators.
Interaction with Price Action
The relationship between these two lines isn't just about their crossing points; it's also about how they interact with current prices:
- Price Above Both Lines: Indicates strong bullishness; buy signals gain confirmation when crossovers occur above key support levels.
- Price Below Both Lines: Suggests bearish conditions; sell signals become more credible when crossovers happen below resistance zones.
Traders often look for confluence—where crossover signals align with price breaking through support/resistance—to increase confidence in their trades.
Incorporating Other Technical Indicators
While tenkansens provide valuable insights on their own, combining them with additional tools enhances decision-making accuracy:
- Moving Averages: Confirm overall trend direction.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Detects overbought/oversold conditions that might influence signal reliability.
- Volume Analysis: Validates whether breakouts or crossovers have sufficient market participation.
This multi-layered approach reduces false positives common in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies or during economic news releases in forex trading.
Recent Trends: Automated Trading & Sentiment Analysis
Advancements in technology have led many traders toward algorithmic strategies that incorporate these indicators automatically. Algorithms analyze real-time data streams—spotting crossover events instantly—and execute trades based on predefined criteria. This automation minimizes emotional bias while capitalizing on rapid market movements typical of forex pairs or crypto assets.
Additionally, integrating sentiment analysis from news feeds or social media platforms helps contextualize technical signals within broader market narratives—a practice increasingly adopted by professional traders seeking comprehensive insights before acting on indicator-based cues.
Risks Associated With Overreliance
Despite their usefulness, relying solely on Tenkan-kisen interactions without considering broader factors can lead traders astray:
- False Signals During Volatility: Rapid swings may produce misleading crossovers not supported by fundamental developments.
- Lagging Nature: As moving averages derived from past prices—they inherently lag behind current market conditions—meaning some delays exist before confirming actual trend shifts.
- Market Noise: In choppy markets without clear directional movement—as seen during economic uncertainty—the effectiveness of these indicators diminishes significantly.
To mitigate these risks: combine them with fundamental analysis where appropriate; set proper stop-loss orders; monitor multiple timeframes for confirmation; avoid overtrading based solely on single indicator events.
Using Tendencies Effectively: Best Practices for Traders
To maximize benefits from analyzing how Tenkan-San and Kijun-San interact as trading signals:
- Look for confluence — ensure crossover events align with other technical cues like volume spikes or breakout confirmations.
- Use multiple timeframes — shorter charts reveal immediate entries while longer ones confirm overarching trends.
- Manage risk diligently — always employ stop-loss orders especially around volatile crossover points prone to false alarms.
Final Thoughts: Combining Technical Insights With Market Context
While understanding how tenkansen interacts provides valuable clues about potential future moves—including early signs of reversals—it’s crucial not to treat them as standalone solutions but rather part of an integrated trading strategy rooted in comprehensive analysis practices.
By combining these insights with fundamental data releases—or macroeconomic factors influencing currency pairs—they become even more powerful tools capable of guiding well-informed decisions across diverse financial markets such as forex exchanges—or emerging crypto assets—with greater confidence.
Note: Always remember that no single indicator guarantees success; continuous learning combined with disciplined risk management remains key for sustainable trading performance involving tools like Tenkan-San and Kijun-San interactions


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 07:05
How do Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen interact as signals?
How Do Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen Interact as Trading Signals?
Understanding how Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen work together is essential for traders who utilize the Ichimoku Cloud system. These two indicators serve as foundational tools in technical analysis, helping traders identify potential trend reversals, confirm market momentum, and make informed trading decisions. Their interaction provides clear signals that can be interpreted across various markets such as forex, cryptocurrencies, and stocks.
What Are Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen?
Tenkan-sen (Conversion Line) and Kijun-sen (Base Line) are moving averages calculated over different periods to capture short-term and medium-term price trends. The Tenkan-sen is derived from the highest high and lowest low over the past 9 periods, making it a responsive indicator for recent price movements. Conversely, the Kijun-sen uses a longer window of 26 periods to smooth out fluctuations, providing insight into broader market trends.
These lines are integral components of the Ichimoku Cloud system but can also be used independently or in conjunction with other technical tools. Their primary purpose is to gauge trend direction—whether bullish or bearish—and signal potential entry or exit points based on their interactions.
How Do Crossovers Signal Market Trends?
One of the most straightforward ways to interpret Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen interactions is through crossovers:
Bullish Crossover (Buy Signal): When the Tenkan-sen crosses above the Kijun-sen, it indicates that short-term momentum has shifted upward relative to longer-term trends. This crossover suggests increasing buying pressure and potential for an upward price move.
Bearish Crossover (Sell Signal): Conversely, when the Tenkan-sen crosses below the Kijun-sen, it signals weakening short-term momentum compared to longer-term trends. This event often precedes downward price movements or confirms existing bearish sentiment.
These crossovers are particularly valuable because they provide early indications of trend changes before they become evident in price action alone.
The Significance of Relative Positioning
Beyond crossovers, where these lines sit relative to each other—and relative to key support/resistance levels—adds depth to their signals:
- When both lines are above a significant support level like the Ichimoku Cloud or recent highs/lows, it reinforces bullish sentiment.
- If both lines are below critical resistance zones or within a declining cloud formation, bearish conditions are likely prevailing.
The distance between Tenkan-sen and Kijun-san also matters; wider gaps often indicate stronger momentum behind a trend change. Rapid crossings with large gaps suggest increased market volatility but may also signal more reliable shifts if confirmed by other indicators.
Interaction with Price Action
The relationship between these two lines isn't just about their crossing points; it's also about how they interact with current prices:
- Price Above Both Lines: Indicates strong bullishness; buy signals gain confirmation when crossovers occur above key support levels.
- Price Below Both Lines: Suggests bearish conditions; sell signals become more credible when crossovers happen below resistance zones.
Traders often look for confluence—where crossover signals align with price breaking through support/resistance—to increase confidence in their trades.
Incorporating Other Technical Indicators
While tenkansens provide valuable insights on their own, combining them with additional tools enhances decision-making accuracy:
- Moving Averages: Confirm overall trend direction.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Detects overbought/oversold conditions that might influence signal reliability.
- Volume Analysis: Validates whether breakouts or crossovers have sufficient market participation.
This multi-layered approach reduces false positives common in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies or during economic news releases in forex trading.
Recent Trends: Automated Trading & Sentiment Analysis
Advancements in technology have led many traders toward algorithmic strategies that incorporate these indicators automatically. Algorithms analyze real-time data streams—spotting crossover events instantly—and execute trades based on predefined criteria. This automation minimizes emotional bias while capitalizing on rapid market movements typical of forex pairs or crypto assets.
Additionally, integrating sentiment analysis from news feeds or social media platforms helps contextualize technical signals within broader market narratives—a practice increasingly adopted by professional traders seeking comprehensive insights before acting on indicator-based cues.
Risks Associated With Overreliance
Despite their usefulness, relying solely on Tenkan-kisen interactions without considering broader factors can lead traders astray:
- False Signals During Volatility: Rapid swings may produce misleading crossovers not supported by fundamental developments.
- Lagging Nature: As moving averages derived from past prices—they inherently lag behind current market conditions—meaning some delays exist before confirming actual trend shifts.
- Market Noise: In choppy markets without clear directional movement—as seen during economic uncertainty—the effectiveness of these indicators diminishes significantly.
To mitigate these risks: combine them with fundamental analysis where appropriate; set proper stop-loss orders; monitor multiple timeframes for confirmation; avoid overtrading based solely on single indicator events.
Using Tendencies Effectively: Best Practices for Traders
To maximize benefits from analyzing how Tenkan-San and Kijun-San interact as trading signals:
- Look for confluence — ensure crossover events align with other technical cues like volume spikes or breakout confirmations.
- Use multiple timeframes — shorter charts reveal immediate entries while longer ones confirm overarching trends.
- Manage risk diligently — always employ stop-loss orders especially around volatile crossover points prone to false alarms.
Final Thoughts: Combining Technical Insights With Market Context
While understanding how tenkansen interacts provides valuable clues about potential future moves—including early signs of reversals—it’s crucial not to treat them as standalone solutions but rather part of an integrated trading strategy rooted in comprehensive analysis practices.
By combining these insights with fundamental data releases—or macroeconomic factors influencing currency pairs—they become even more powerful tools capable of guiding well-informed decisions across diverse financial markets such as forex exchanges—or emerging crypto assets—with greater confidence.
Note: Always remember that no single indicator guarantees success; continuous learning combined with disciplined risk management remains key for sustainable trading performance involving tools like Tenkan-San and Kijun-San interactions
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Harold just wanted to hit a $100K money goal trading crypto this year… Now he’s deep in the red — and questioning all his life decisions 😂 If you’ve ever set big money goals and ended up further behind… you’re not alone. Watch this short, laugh (or cry), and remember: risk management is everything.
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉 Not financial advice. Always DYOR. #moneygoals #cryptomeme


JuCoin Media
2025-08-07 14:38
When Your Money Goal Is $100K and You’re -$52K In 🤡
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Consensus Mechanism in Blockchain?
A consensus mechanism is the backbone of blockchain technology, ensuring that all participants in a decentralized network agree on the validity of transactions and the state of the ledger. Without it, maintaining trust and security across distributed nodes would be nearly impossible. This process enables blockchain networks to operate without a central authority, making them resilient, transparent, and tamper-proof.
Why Are Consensus Mechanisms Essential for Blockchain Networks?
In traditional centralized systems, a single authority verifies transactions and maintains records. However, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer basis where multiple nodes (computers) validate data independently. To prevent issues like double-spending or fraudulent entries, these nodes need an effective way to reach agreement — this is where consensus mechanisms come into play.
By establishing rules for validation and agreement, consensus mechanisms uphold data integrity while allowing for decentralization. They also help defend against malicious attacks by making it computationally or economically unfeasible to manipulate the system.
Common Types of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
There are several types of consensus algorithms used across different blockchain platforms. Each has its strengths and trade-offs concerning security, scalability, energy consumption, and decentralization.
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work is perhaps the most well-known consensus method—used by Bitcoin since its inception. In PoW systems, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles using significant computational power. The first miner who solves the puzzle earns the right to add a new block to the chain and receives cryptocurrency as reward.
Advantages:
- High security due to energy-intensive puzzle-solving
- Well-tested with proven resilience against attacks
Disadvantages:
- Very high energy consumption leading to environmental concerns
- Slower transaction processing times compared to newer methods
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake shifts away from computational puzzles toward economic incentives. Nodes (validators) are chosen based on how much cryptocurrency they "stake" or lock up as collateral. The higher their stake relative to others', the more likely they are selected for validation duties.
Advantages:
- Significantly reduces energy use compared to PoW
- Enhances scalability with faster transaction confirmation
Disadvantages:
- Potential vulnerability called "nothing-at-stake," where validators might act dishonestly without penalty if not properly designed
Ethereum’s transition from PoW towards PoS exemplifies this shift aiming at sustainability and efficiency.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Delegated Proof of Stake introduces an element of voting within community members who elect trusted validators—often called delegates—to confirm transactions on their behalf. This model aims at improving speed while maintaining democratic participation.
Advantages:
- Faster transaction speeds suitable for large-scale applications
- Greater community involvement through voting mechanisms
Disadvantages:
- Risked centralization if few delegates dominate decision-making processes
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)
BFT algorithms are designed specifically for environments where some nodes may act maliciously or fail unexpectedly—a common scenario in private blockchains or permissioned networks. These algorithms enable honest nodes to reach agreement even when some participants behave unpredictably or maliciously.
Advantages:
- Extremely secure under fault conditions
- Suitable for enterprise-level applications requiring high trust levels
Limitations:
- Less scalable than other methods due to communication overheads involved in reaching consensus
Leased Proof-of-Stake (LPoS)
Leased Proof-of-Stake combines elements from both PoS and DPoS models by allowing stakeholders ("lessees") to lease their stakes temporarily via smart contracts rather than permanently locking funds themselves—this creates more flexibility in validator selection processes.
Examples & Benefits:
- Used by projects like Tezos
- Balances efficiency with community participation
However, managing leasing agreements can introduce complexity that affects network performance if not handled carefully.
Recent Innovations in Consensus Algorithms
Blockchain developers continue innovating beyond traditional models:
- Ethereum 2.0 Transition
Ethereum’s move from proof-of-work toward proof-of-stake aims at reducing environmental impact while increasing throughput capacity—a critical step given Ethereum's widespread adoption as a platform for decentralized applications (dApps).
- Cardano’s Ouroboros
Launched in 2017 but continuously refined since then, Ouroboros offers an energy-efficient yet secure proof-of-stake protocol tailored specifically for academic rigor and formal verification methods—enhancing trustworthiness especially important within financial services sectors.
- Polkadot’s Nominated Proof-of-Stake
Polkadot employs NPoS which allows token holders not only stakers but also nominators who select trustworthy validators through staking nominations—improving decentralization alongside security features necessary for multi-chain interoperability projects like Polkadot ecosystem hubs.
- Solana’s Proof of History
Unique among many protocols today; Solana integrates “Proof of History,” which timestamps events cryptographically before validating blocks—enabling extremely high throughput rates suitable even during peak usage periods.
Challenges Facing Consensus Mechanisms Today
While innovative solutions have advanced blockchain technology significantly over recent years; several challenges remain:
Environmental Impact
Energy-intensive protocols such as PoW have faced criticism due mainly because mining consumes vast amounts of electricity comparable with small countries’ total usage levels—which raises sustainability concerns amid global climate change efforts.
Centralization Risks
Certain models like DPoS can lead toward centralization if power concentrates among few validators or delegates controlling most validation rights—a concern that undermines one core tenet: decentralization itself.
Scalability Limitations
Some algorithms struggle under heavy load; BFT-based systems often face difficulties scaling efficiently beyond small networks without sacrificing speed or security.
Regulatory Environment
As governments scrutinize cryptocurrency activities more closely—including mining operations—the future regulatory landscape could impose restrictions affecting how these mechanisms operate globally.
How Choosing The Right Consensus Method Matters
Selecting an appropriate consensus mechanism depends heavily on specific project goals:
- For maximum security — especially critical financial applications — proof-of-work remains popular despite its drawbacks.
- For eco-conscious projects seeking scalability — proof-of-stake variants offer promising alternatives.
- For enterprise solutions requiring fault tolerance — BFT-based protocols provide robust options.
- For fast-paced decentralized apps needing quick confirmation times — delegated models like DPoS excel when managed properly.
Understanding these differences helps developers build sustainable platforms aligned with user needs while adhering best practices around transparency & governance standards rooted in industry research.
Final Thoughts: Evolving Landscape With Long-Term Implications
Consensus mechanisms form the foundation upon which modern blockchain ecosystems operate securely without centralized oversight—they ensure data integrity through diverse approaches balancing decentralization with performance needs worldwide innovation continues apace here—from Ethereum's transition towards greener protocols through emerging hybrid models combining multiple techniques such as Solana's unique approach leveraging historical cryptographic proofs—all aimed at creating scalable yet environmentally responsible distributed ledgers capable enough today but adaptable enough tomorrow amidst evolving regulatory landscapes—and growing societal expectations around sustainability & fairness within digital economies.
This ongoing evolution underscores why understanding different types—and their respective advantages—is vital whether you're developing new blockchain solutions or evaluating existing ones' suitability based on your organizational priorities regarding security standards versus ecological impact versus operational efficiency.
This comprehensive overview provides clarity about what constitutes a consensus mechanism within blockchain technology—their importance—and how ongoing innovations shape future possibilities while addressing current challenges facing this critical component behind decentralized digital assets worldwide


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-15 00:00
What is a consensus mechanism?
What Is a Consensus Mechanism in Blockchain?
A consensus mechanism is the backbone of blockchain technology, ensuring that all participants in a decentralized network agree on the validity of transactions and the state of the ledger. Without it, maintaining trust and security across distributed nodes would be nearly impossible. This process enables blockchain networks to operate without a central authority, making them resilient, transparent, and tamper-proof.
Why Are Consensus Mechanisms Essential for Blockchain Networks?
In traditional centralized systems, a single authority verifies transactions and maintains records. However, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer basis where multiple nodes (computers) validate data independently. To prevent issues like double-spending or fraudulent entries, these nodes need an effective way to reach agreement — this is where consensus mechanisms come into play.
By establishing rules for validation and agreement, consensus mechanisms uphold data integrity while allowing for decentralization. They also help defend against malicious attacks by making it computationally or economically unfeasible to manipulate the system.
Common Types of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
There are several types of consensus algorithms used across different blockchain platforms. Each has its strengths and trade-offs concerning security, scalability, energy consumption, and decentralization.
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work is perhaps the most well-known consensus method—used by Bitcoin since its inception. In PoW systems, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles using significant computational power. The first miner who solves the puzzle earns the right to add a new block to the chain and receives cryptocurrency as reward.
Advantages:
- High security due to energy-intensive puzzle-solving
- Well-tested with proven resilience against attacks
Disadvantages:
- Very high energy consumption leading to environmental concerns
- Slower transaction processing times compared to newer methods
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake shifts away from computational puzzles toward economic incentives. Nodes (validators) are chosen based on how much cryptocurrency they "stake" or lock up as collateral. The higher their stake relative to others', the more likely they are selected for validation duties.
Advantages:
- Significantly reduces energy use compared to PoW
- Enhances scalability with faster transaction confirmation
Disadvantages:
- Potential vulnerability called "nothing-at-stake," where validators might act dishonestly without penalty if not properly designed
Ethereum’s transition from PoW towards PoS exemplifies this shift aiming at sustainability and efficiency.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Delegated Proof of Stake introduces an element of voting within community members who elect trusted validators—often called delegates—to confirm transactions on their behalf. This model aims at improving speed while maintaining democratic participation.
Advantages:
- Faster transaction speeds suitable for large-scale applications
- Greater community involvement through voting mechanisms
Disadvantages:
- Risked centralization if few delegates dominate decision-making processes
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)
BFT algorithms are designed specifically for environments where some nodes may act maliciously or fail unexpectedly—a common scenario in private blockchains or permissioned networks. These algorithms enable honest nodes to reach agreement even when some participants behave unpredictably or maliciously.
Advantages:
- Extremely secure under fault conditions
- Suitable for enterprise-level applications requiring high trust levels
Limitations:
- Less scalable than other methods due to communication overheads involved in reaching consensus
Leased Proof-of-Stake (LPoS)
Leased Proof-of-Stake combines elements from both PoS and DPoS models by allowing stakeholders ("lessees") to lease their stakes temporarily via smart contracts rather than permanently locking funds themselves—this creates more flexibility in validator selection processes.
Examples & Benefits:
- Used by projects like Tezos
- Balances efficiency with community participation
However, managing leasing agreements can introduce complexity that affects network performance if not handled carefully.
Recent Innovations in Consensus Algorithms
Blockchain developers continue innovating beyond traditional models:
- Ethereum 2.0 Transition
Ethereum’s move from proof-of-work toward proof-of-stake aims at reducing environmental impact while increasing throughput capacity—a critical step given Ethereum's widespread adoption as a platform for decentralized applications (dApps).
- Cardano’s Ouroboros
Launched in 2017 but continuously refined since then, Ouroboros offers an energy-efficient yet secure proof-of-stake protocol tailored specifically for academic rigor and formal verification methods—enhancing trustworthiness especially important within financial services sectors.
- Polkadot’s Nominated Proof-of-Stake
Polkadot employs NPoS which allows token holders not only stakers but also nominators who select trustworthy validators through staking nominations—improving decentralization alongside security features necessary for multi-chain interoperability projects like Polkadot ecosystem hubs.
- Solana’s Proof of History
Unique among many protocols today; Solana integrates “Proof of History,” which timestamps events cryptographically before validating blocks—enabling extremely high throughput rates suitable even during peak usage periods.
Challenges Facing Consensus Mechanisms Today
While innovative solutions have advanced blockchain technology significantly over recent years; several challenges remain:
Environmental Impact
Energy-intensive protocols such as PoW have faced criticism due mainly because mining consumes vast amounts of electricity comparable with small countries’ total usage levels—which raises sustainability concerns amid global climate change efforts.
Centralization Risks
Certain models like DPoS can lead toward centralization if power concentrates among few validators or delegates controlling most validation rights—a concern that undermines one core tenet: decentralization itself.
Scalability Limitations
Some algorithms struggle under heavy load; BFT-based systems often face difficulties scaling efficiently beyond small networks without sacrificing speed or security.
Regulatory Environment
As governments scrutinize cryptocurrency activities more closely—including mining operations—the future regulatory landscape could impose restrictions affecting how these mechanisms operate globally.
How Choosing The Right Consensus Method Matters
Selecting an appropriate consensus mechanism depends heavily on specific project goals:
- For maximum security — especially critical financial applications — proof-of-work remains popular despite its drawbacks.
- For eco-conscious projects seeking scalability — proof-of-stake variants offer promising alternatives.
- For enterprise solutions requiring fault tolerance — BFT-based protocols provide robust options.
- For fast-paced decentralized apps needing quick confirmation times — delegated models like DPoS excel when managed properly.
Understanding these differences helps developers build sustainable platforms aligned with user needs while adhering best practices around transparency & governance standards rooted in industry research.
Final Thoughts: Evolving Landscape With Long-Term Implications
Consensus mechanisms form the foundation upon which modern blockchain ecosystems operate securely without centralized oversight—they ensure data integrity through diverse approaches balancing decentralization with performance needs worldwide innovation continues apace here—from Ethereum's transition towards greener protocols through emerging hybrid models combining multiple techniques such as Solana's unique approach leveraging historical cryptographic proofs—all aimed at creating scalable yet environmentally responsible distributed ledgers capable enough today but adaptable enough tomorrow amidst evolving regulatory landscapes—and growing societal expectations around sustainability & fairness within digital economies.
This ongoing evolution underscores why understanding different types—and their respective advantages—is vital whether you're developing new blockchain solutions or evaluating existing ones' suitability based on your organizational priorities regarding security standards versus ecological impact versus operational efficiency.
This comprehensive overview provides clarity about what constitutes a consensus mechanism within blockchain technology—their importance—and how ongoing innovations shape future possibilities while addressing current challenges facing this critical component behind decentralized digital assets worldwide
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
