What Are Fibonacci Extensions in Technical Analysis?
Fibonacci extensions are a popular tool used by traders and investors to forecast potential future price levels of financial assets, including cryptocurrencies, stocks, and commodities. Rooted in the mathematical principles of the Fibonacci sequence, these extensions help identify areas where an asset’s price might encounter support or resistance after a significant move. Unlike Fibonacci retracements that measure potential pullbacks within a trend, extensions project where prices could go beyond previous highs or lows.
The core idea behind Fibonacci extensions is that markets often react at specific levels derived from the ratios of Fibonacci numbers. These levels serve as psychological markers for traders—areas where buying or selling pressure may intensify—making them valuable for planning entries, exits, and stop-loss placements.
How Do Fibonacci Extensions Work?
Using Fibonacci extensions involves several steps that combine technical analysis with pattern recognition:
Identify Key Price Points: Traders start by pinpointing significant high and low points on a chart — typically swing highs and swing lows that define the current trend.
Draw Retracement Levels: Once key points are identified, traders apply Fibonacci retracement tools to measure how much of a prior move has been retraced during corrections or consolidations.
Calculate Extension Levels: After establishing retracement levels within a trend, traders project extension levels by adding certain ratios (such as 161.8%, 261.8%) to the initial move's length beyond the original high or low point.
Analyze Market Context: These projected levels act as potential zones where price might reverse again or accelerate further based on market momentum and sentiment.
By combining these steps with other technical indicators like moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index), traders can develop more robust trading strategies centered around these projection points.
Commonly Used Fibonacci Extension Ratios
Fibonacci extension levels are derived from key ratios associated with the sequence:
- 161.8%: Known as "the golden ratio," this level is one of the most widely watched in trading circles.
- 261.8%: Indicates an even stronger extension beyond previous highs/lows.
- 423.6%: Less common but still relevant for very strong trends.
These percentages are calculated based on differences between key swings in price action and are used to anticipate how far an asset might extend after breaking through resistance or support zones.
In addition to these extension ratios, some traders also consider intermediate levels such as 200%, 300%, etc., depending on their strategy and market conditions.
When Are Fibonacci Extensions Used?
Fibonacci extensions are primarily employed during trending markets when prices exhibit clear directional movement—either upward (bullish) or downward (bearish). They serve multiple purposes:
Forecasting Future Resistance/Support: Traders use extension levels to predict where an ongoing trend might pause before continuing its trajectory.
Setting Profit Targets: Many investors set take-profit orders at key extension zones because historical data suggests increased likelihoods of reversals or consolidations there.
Confirming Breakouts: When prices break through established resistance/support lines near extension zones with high volume, it can signal strong continuation signals aligned with those projections.
It’s important to note that while they work well in trending environments, using them during sideways markets may lead to false signals due to lack of directional momentum.
The Rise of Fib Extensions in Cryptocurrency Trading
Since their introduction into technical analysis decades ago—and especially following cryptocurrency’s explosive growth post-2017—Fibonacci extensions have gained popularity among crypto traders worldwide. The volatile nature of digital assets makes traditional technical tools less predictable; however, fib-based projections help navigate rapid swings by providing structured reference points amid chaos.
Modern trading platforms now incorporate advanced charting software featuring automated fib tools that allow quick calculation without manual plotting—a boon for fast-paced crypto markets requiring real-time decision-making.
Furthermore, many crypto analysts combine fib extensions with other indicators like Bollinger Bands and RSI for more comprehensive insights into potential reversal zones amidst extreme volatility typical in digital currencies like Bitcoin and altcoins.
Limitations & Risks Associated With Using Fib Extensions
While powerful when applied correctly, relying solely on Fibonacci extensions carries risks:
Overdependence can lead to overtrading; not every projected level will hold due to unpredictable market factors.
Crypto markets’ inherent volatility means prices often overshoot predicted targets before reversing unexpectedly—a phenomenon known as “whipsaw.”
Psychological biases such as confirmation bias may cause traders only see signals aligning with their expectations rather than objective data interpretation.
To mitigate these issues:
- Combine fib analysis with fundamental research about underlying assets
- Use proper risk management strategies including stop-loss orders
- Confirm signals across multiple indicators
This balanced approach enhances decision-making accuracy while reducing exposure risks inherent in speculative trading environments like cryptocurrencies.
Practical Tips for Using Fibonacci Extensions Effectively
For both novice and experienced traders looking to incorporate fib extensions into their toolkit:
- Always identify clear swing highs/lows before applying any projection tool; ambiguous points reduce reliability.
- Use multiple timeframes—for example daily charts combined with shorter-term intraday charts—to validate signals across different perspectives.
- Integrate other technical indicators such as moving averages (to confirm trend direction) or volume spikes (to validate breakout strength).
- Remember that no indicator guarantees success; treat fibonacci projections as part of a broader strategic framework rather than standalone solutions.
By understanding what Fibonacci extensions are—and knowing how they fit into broader technical analysis—you can better anticipate possible future movements within volatile markets like cryptocurrencies while managing your risk effectively.
Keywords:
Fibonacciextensions | TechnicalAnalysis | CryptoTradingTools | SupportAndResistance | PriceProjection | TrendFollowingStrategies


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 06:50
What are Fibonacci extensions and when are they used?
What Are Fibonacci Extensions in Technical Analysis?
Fibonacci extensions are a popular tool used by traders and investors to forecast potential future price levels of financial assets, including cryptocurrencies, stocks, and commodities. Rooted in the mathematical principles of the Fibonacci sequence, these extensions help identify areas where an asset’s price might encounter support or resistance after a significant move. Unlike Fibonacci retracements that measure potential pullbacks within a trend, extensions project where prices could go beyond previous highs or lows.
The core idea behind Fibonacci extensions is that markets often react at specific levels derived from the ratios of Fibonacci numbers. These levels serve as psychological markers for traders—areas where buying or selling pressure may intensify—making them valuable for planning entries, exits, and stop-loss placements.
How Do Fibonacci Extensions Work?
Using Fibonacci extensions involves several steps that combine technical analysis with pattern recognition:
Identify Key Price Points: Traders start by pinpointing significant high and low points on a chart — typically swing highs and swing lows that define the current trend.
Draw Retracement Levels: Once key points are identified, traders apply Fibonacci retracement tools to measure how much of a prior move has been retraced during corrections or consolidations.
Calculate Extension Levels: After establishing retracement levels within a trend, traders project extension levels by adding certain ratios (such as 161.8%, 261.8%) to the initial move's length beyond the original high or low point.
Analyze Market Context: These projected levels act as potential zones where price might reverse again or accelerate further based on market momentum and sentiment.
By combining these steps with other technical indicators like moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index), traders can develop more robust trading strategies centered around these projection points.
Commonly Used Fibonacci Extension Ratios
Fibonacci extension levels are derived from key ratios associated with the sequence:
- 161.8%: Known as "the golden ratio," this level is one of the most widely watched in trading circles.
- 261.8%: Indicates an even stronger extension beyond previous highs/lows.
- 423.6%: Less common but still relevant for very strong trends.
These percentages are calculated based on differences between key swings in price action and are used to anticipate how far an asset might extend after breaking through resistance or support zones.
In addition to these extension ratios, some traders also consider intermediate levels such as 200%, 300%, etc., depending on their strategy and market conditions.
When Are Fibonacci Extensions Used?
Fibonacci extensions are primarily employed during trending markets when prices exhibit clear directional movement—either upward (bullish) or downward (bearish). They serve multiple purposes:
Forecasting Future Resistance/Support: Traders use extension levels to predict where an ongoing trend might pause before continuing its trajectory.
Setting Profit Targets: Many investors set take-profit orders at key extension zones because historical data suggests increased likelihoods of reversals or consolidations there.
Confirming Breakouts: When prices break through established resistance/support lines near extension zones with high volume, it can signal strong continuation signals aligned with those projections.
It’s important to note that while they work well in trending environments, using them during sideways markets may lead to false signals due to lack of directional momentum.
The Rise of Fib Extensions in Cryptocurrency Trading
Since their introduction into technical analysis decades ago—and especially following cryptocurrency’s explosive growth post-2017—Fibonacci extensions have gained popularity among crypto traders worldwide. The volatile nature of digital assets makes traditional technical tools less predictable; however, fib-based projections help navigate rapid swings by providing structured reference points amid chaos.
Modern trading platforms now incorporate advanced charting software featuring automated fib tools that allow quick calculation without manual plotting—a boon for fast-paced crypto markets requiring real-time decision-making.
Furthermore, many crypto analysts combine fib extensions with other indicators like Bollinger Bands and RSI for more comprehensive insights into potential reversal zones amidst extreme volatility typical in digital currencies like Bitcoin and altcoins.
Limitations & Risks Associated With Using Fib Extensions
While powerful when applied correctly, relying solely on Fibonacci extensions carries risks:
Overdependence can lead to overtrading; not every projected level will hold due to unpredictable market factors.
Crypto markets’ inherent volatility means prices often overshoot predicted targets before reversing unexpectedly—a phenomenon known as “whipsaw.”
Psychological biases such as confirmation bias may cause traders only see signals aligning with their expectations rather than objective data interpretation.
To mitigate these issues:
- Combine fib analysis with fundamental research about underlying assets
- Use proper risk management strategies including stop-loss orders
- Confirm signals across multiple indicators
This balanced approach enhances decision-making accuracy while reducing exposure risks inherent in speculative trading environments like cryptocurrencies.
Practical Tips for Using Fibonacci Extensions Effectively
For both novice and experienced traders looking to incorporate fib extensions into their toolkit:
- Always identify clear swing highs/lows before applying any projection tool; ambiguous points reduce reliability.
- Use multiple timeframes—for example daily charts combined with shorter-term intraday charts—to validate signals across different perspectives.
- Integrate other technical indicators such as moving averages (to confirm trend direction) or volume spikes (to validate breakout strength).
- Remember that no indicator guarantees success; treat fibonacci projections as part of a broader strategic framework rather than standalone solutions.
By understanding what Fibonacci extensions are—and knowing how they fit into broader technical analysis—you can better anticipate possible future movements within volatile markets like cryptocurrencies while managing your risk effectively.
Keywords:
Fibonacciextensions | TechnicalAnalysis | CryptoTradingTools | SupportAndResistance | PriceProjection | TrendFollowingStrategies
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Keltner Channels Differ from Bollinger Bands?
When it comes to technical analysis in trading—whether in traditional markets or cryptocurrencies—volatility indicators are essential tools. Among the most popular are Keltner Channels and Bollinger Bands. While both serve similar purposes, they differ significantly in their calculation methods, sensitivity, and practical application. Understanding these differences can help traders select the right indicator for their strategy and improve decision-making.
What Are Keltner Channels?
Keltner Channels are a volatility-based indicator developed by Chester Keltner that helps traders identify potential trend reversals or breakouts. The core idea is to combine a moving average with bands that expand or contract based on market volatility, measured by the Average True Range (ATR).
The middle line of a Keltner Channel is typically an exponential moving average (EMA) or simple moving average (SMA). The upper and lower bands are set at a multiple of ATR above and below this central line. For example, if the ATR multiplier is 2, then the upper band equals the EMA plus twice the ATR; similarly, the lower band equals the EMA minus twice the ATR.
This setup makes Keltner Channels particularly responsive to recent price movements because ATR adjusts quickly during volatile periods. Traders often interpret touches or breaches of these bands as signals of strong momentum—either indicating potential trend continuation when prices break above or below them—or signaling reversals when prices revert toward the centerline.
What Are Bollinger Bands?
Bollinger Bands were created by John Bollinger and have become one of the most widely used volatility indicators across various markets—including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Like Keltner Channels, they consist of three lines: a central moving average (usually SMA), an upper band above it, and a lower band below it.
What sets Bollinger Bands apart is how their outer bands are calculated: they use standard deviation—a statistical measure that captures how much prices deviate from their mean—to determine bandwidths around this central line. Typically set at two standard deviations from an SMA (often 20 periods), these bands expand during high volatility periods and contract during calmer market phases.
Because standard deviation smooths out short-term fluctuations more than ATR does—and responds differently depending on recent price behavior—Bollinger Bands tend to provide clearer visual cues about overbought or oversold conditions when prices touch or cross these boundaries.
Key Differences Between Keltner Channels and Bollinger Bands
While both indicators aim to measure market volatility through dynamic bands around price action, several fundamental differences influence how traders interpret them:
Volatility Measurement
- Keltner Channels: Use Average True Range (ATR) as their basis for calculating band distance from the moving average.
- Bollinger Bands: Use standard deviation derived from historical price data for setting bandwidths.
Band Calculation Method
- Keltner Channels: Set at a multiple of ATR; generally more reactive due to ATR's sensitivity.
- Bollinger Bands: Set at multiples of standard deviation; tend to be smoother because standard deviation incorporates broader statistical properties over time.
Sensitivity to Price Movements
- Keltner Channels: Usually more sensitive due to reliance on ATR; quick reactions make them suitable for short-term trading like day trading.
- Bollinger Bars: Less sensitive but better suited for identifying longer-term trends because they filter out some noise through smoothing effects inherent in standard deviation calculations.
Practical Trading Applications
| Aspect | Keltner Channels | Bollinger Bands |
|---|---|---|
| Best suited for | Short-term strategies such as scalping & day trading | Longer-term strategies & swing trading |
| Signal interpretation | Breakouts beyond channels suggest strong momentum | Touching/ crossing outer bands indicates overbought/oversold conditions |
| Response speed | Faster response due to ATR's responsiveness | Slower but smoother signals |
Understanding these distinctions allows traders not only to choose between them based on preferred timeframes but also potentially combine both tools within comprehensive strategies for confirmation signals.
Recent Trends in Usage Across Markets
In recent years—and especially within cryptocurrency markets—the adoption of both Keltner Channels and Bollinger Bands has surged owing to increased market volatility characteristic of digital assets like Bitcoin and altcoins. Traders leverage these indicators alongside other tools such as RSI or MACD for enhanced accuracy in predicting moves amid rapid swings.
Algorithmic trading systems increasingly incorporate these indicators into automated decision-making processes since real-time data processing enables swift responses aligned with volatile crypto environments. Moreover, community discussions on platforms like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency highlight ongoing experimentation with combining multiple volatility measures—including blending features from both indicators—to refine entry/exit points further.
Educational content focusing on practical applications has also expanded dramatically—from webinars explaining parameter adjustments tailored specifically for crypto assets—to tutorials illustrating how adjusting period lengths impacts signal reliability under different market conditions.
Potential Risks When Relying Solely on These Indicators
Despite their usefulness, overdependence solely upon either indicator can lead traders into pitfalls:
False Signals During High Volatility: Both tools may generate misleading signals if used without considering broader context—for instance,
- A breach outside typical ranges might be just noise rather than genuine trend shifts.
Market Conditions Impact: In highly volatile environments like crypto markets,
- Standard settings might produce too many false positives unless parameters are fine-tuned.
Ignoring Fundamental Factors: Technical signals should complement fundamental analysis rather than replace it entirely—especially important given regulatory changes affecting certain asset classes which can cause abrupt shifts not captured by technical metrics alone.
How To Choose Between Them?
Selecting between Keltner Channels versus Bollinger Bands depends largely on your specific trading style:
If you prefer rapid reactions suitable for intraday trades where quick entries/exits matter most:
- Consider using KeltnerChannels due to its higher sensitivity driven by ATR responsiveness.
For longer-term perspectives emphasizing broader trends:
- BollINGER BANDS may offer clearer insights into overall market sentiment without excessive false alarms caused by short-lived fluctuations.
Combining Both:
- Some experienced traders overlay both indicators—for example,
- Using bollINGER BANDS’ overbought/oversold cues alongside kELTNER CHANNELS’ breakout signals—to confirm trade entries.
- Some experienced traders overlay both indicators—for example,
Staying informed about updates related specifically to cryptocurrency markets—as well as understanding each indicator’s strengths—is crucial in adapting your approach amid evolving financial landscapes.
Final Thoughts
Both Keltner Lines and BollINGER BANDS remain vital components within any trader’s toolkit—they provide valuable insights into market volatility patterns that underpin effective risk management strategies across diverse asset classes including cryptocurrencies today’s fast-paced environment demands nuanced understanding—and knowing when each tool excels enhances your ability not only to spot opportunities but also avoid common pitfalls associated with false signals.
By mastering their differences—from calculation methods through practical applications—you position yourself better equipped with robust analytical skills necessary in today’s competitive financial arena.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 05:35
How do Keltner Channels differ from Bollinger Bands?
How Do Keltner Channels Differ from Bollinger Bands?
When it comes to technical analysis in trading—whether in traditional markets or cryptocurrencies—volatility indicators are essential tools. Among the most popular are Keltner Channels and Bollinger Bands. While both serve similar purposes, they differ significantly in their calculation methods, sensitivity, and practical application. Understanding these differences can help traders select the right indicator for their strategy and improve decision-making.
What Are Keltner Channels?
Keltner Channels are a volatility-based indicator developed by Chester Keltner that helps traders identify potential trend reversals or breakouts. The core idea is to combine a moving average with bands that expand or contract based on market volatility, measured by the Average True Range (ATR).
The middle line of a Keltner Channel is typically an exponential moving average (EMA) or simple moving average (SMA). The upper and lower bands are set at a multiple of ATR above and below this central line. For example, if the ATR multiplier is 2, then the upper band equals the EMA plus twice the ATR; similarly, the lower band equals the EMA minus twice the ATR.
This setup makes Keltner Channels particularly responsive to recent price movements because ATR adjusts quickly during volatile periods. Traders often interpret touches or breaches of these bands as signals of strong momentum—either indicating potential trend continuation when prices break above or below them—or signaling reversals when prices revert toward the centerline.
What Are Bollinger Bands?
Bollinger Bands were created by John Bollinger and have become one of the most widely used volatility indicators across various markets—including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Like Keltner Channels, they consist of three lines: a central moving average (usually SMA), an upper band above it, and a lower band below it.
What sets Bollinger Bands apart is how their outer bands are calculated: they use standard deviation—a statistical measure that captures how much prices deviate from their mean—to determine bandwidths around this central line. Typically set at two standard deviations from an SMA (often 20 periods), these bands expand during high volatility periods and contract during calmer market phases.
Because standard deviation smooths out short-term fluctuations more than ATR does—and responds differently depending on recent price behavior—Bollinger Bands tend to provide clearer visual cues about overbought or oversold conditions when prices touch or cross these boundaries.
Key Differences Between Keltner Channels and Bollinger Bands
While both indicators aim to measure market volatility through dynamic bands around price action, several fundamental differences influence how traders interpret them:
Volatility Measurement
- Keltner Channels: Use Average True Range (ATR) as their basis for calculating band distance from the moving average.
- Bollinger Bands: Use standard deviation derived from historical price data for setting bandwidths.
Band Calculation Method
- Keltner Channels: Set at a multiple of ATR; generally more reactive due to ATR's sensitivity.
- Bollinger Bands: Set at multiples of standard deviation; tend to be smoother because standard deviation incorporates broader statistical properties over time.
Sensitivity to Price Movements
- Keltner Channels: Usually more sensitive due to reliance on ATR; quick reactions make them suitable for short-term trading like day trading.
- Bollinger Bars: Less sensitive but better suited for identifying longer-term trends because they filter out some noise through smoothing effects inherent in standard deviation calculations.
Practical Trading Applications
| Aspect | Keltner Channels | Bollinger Bands |
|---|---|---|
| Best suited for | Short-term strategies such as scalping & day trading | Longer-term strategies & swing trading |
| Signal interpretation | Breakouts beyond channels suggest strong momentum | Touching/ crossing outer bands indicates overbought/oversold conditions |
| Response speed | Faster response due to ATR's responsiveness | Slower but smoother signals |
Understanding these distinctions allows traders not only to choose between them based on preferred timeframes but also potentially combine both tools within comprehensive strategies for confirmation signals.
Recent Trends in Usage Across Markets
In recent years—and especially within cryptocurrency markets—the adoption of both Keltner Channels and Bollinger Bands has surged owing to increased market volatility characteristic of digital assets like Bitcoin and altcoins. Traders leverage these indicators alongside other tools such as RSI or MACD for enhanced accuracy in predicting moves amid rapid swings.
Algorithmic trading systems increasingly incorporate these indicators into automated decision-making processes since real-time data processing enables swift responses aligned with volatile crypto environments. Moreover, community discussions on platforms like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency highlight ongoing experimentation with combining multiple volatility measures—including blending features from both indicators—to refine entry/exit points further.
Educational content focusing on practical applications has also expanded dramatically—from webinars explaining parameter adjustments tailored specifically for crypto assets—to tutorials illustrating how adjusting period lengths impacts signal reliability under different market conditions.
Potential Risks When Relying Solely on These Indicators
Despite their usefulness, overdependence solely upon either indicator can lead traders into pitfalls:
False Signals During High Volatility: Both tools may generate misleading signals if used without considering broader context—for instance,
- A breach outside typical ranges might be just noise rather than genuine trend shifts.
Market Conditions Impact: In highly volatile environments like crypto markets,
- Standard settings might produce too many false positives unless parameters are fine-tuned.
Ignoring Fundamental Factors: Technical signals should complement fundamental analysis rather than replace it entirely—especially important given regulatory changes affecting certain asset classes which can cause abrupt shifts not captured by technical metrics alone.
How To Choose Between Them?
Selecting between Keltner Channels versus Bollinger Bands depends largely on your specific trading style:
If you prefer rapid reactions suitable for intraday trades where quick entries/exits matter most:
- Consider using KeltnerChannels due to its higher sensitivity driven by ATR responsiveness.
For longer-term perspectives emphasizing broader trends:
- BollINGER BANDS may offer clearer insights into overall market sentiment without excessive false alarms caused by short-lived fluctuations.
Combining Both:
- Some experienced traders overlay both indicators—for example,
- Using bollINGER BANDS’ overbought/oversold cues alongside kELTNER CHANNELS’ breakout signals—to confirm trade entries.
- Some experienced traders overlay both indicators—for example,
Staying informed about updates related specifically to cryptocurrency markets—as well as understanding each indicator’s strengths—is crucial in adapting your approach amid evolving financial landscapes.
Final Thoughts
Both Keltner Lines and BollINGER BANDS remain vital components within any trader’s toolkit—they provide valuable insights into market volatility patterns that underpin effective risk management strategies across diverse asset classes including cryptocurrencies today’s fast-paced environment demands nuanced understanding—and knowing when each tool excels enhances your ability not only to spot opportunities but also avoid common pitfalls associated with false signals.
By mastering their differences—from calculation methods through practical applications—you position yourself better equipped with robust analytical skills necessary in today’s competitive financial arena.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Therapist wants a crypto bag too 🧠👜 He spent the rent on Elon Musk Coin 🚀, she doubts the diamond hands 💎✋— but the real alpha lives with whoever gets the contract address first 🧾🔥.


JuCoin Media
2025-08-04 09:26
Therapist Becomes an Exit Liquidity Provider 🛋️📉
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do I Report Suspicious Activity on Investing.com?
When using online financial platforms like Investing.com, maintaining security and integrity is essential for all users. Reporting suspicious activity plays a vital role in safeguarding your investments and ensuring the platform remains trustworthy. This guide provides a clear overview of how to report suspicious activities on Investing.com, what to look out for, and why timely reporting matters.
Understanding Why Reporting Suspicious Activity Is Important
Investing.com serves millions of users worldwide by providing real-time financial news, data analysis, and trading tools. However, as with any online platform handling sensitive financial information, it can be targeted by malicious actors engaging in market manipulation, fake accounts, insider trading schemes, or fraudulent activities. These threats not only jeopardize individual investors but also threaten the platform’s reputation and regulatory compliance.
Timely reporting helps prevent potential losses from scams or manipulative practices. It also assists the platform’s security teams in identifying vulnerabilities early on. For users committed to responsible investing and maintaining a secure environment for all participants, understanding how to report suspicious activity is an essential part of their digital safety toolkit.
How Does Investing.com Handle Reports of Suspicious Activities?
Investing.com typically offers dedicated channels or features designed specifically for reporting concerns about suspicious behavior. These mechanisms are often accessible directly through user account settings or via prominent "Report" buttons integrated into various sections of the website.
Once a user identifies unusual activity—such as abnormal trading patterns, fake profiles impersonating legitimate accounts, or signs of potential fraud—they can submit detailed reports through these channels. The process usually involves filling out an online form that captures critical information like:
- The nature of the suspicious activity
- Details about involved accounts
- Relevant evidence (screenshots or transaction records)
- Any additional comments that may assist investigators
This structured approach ensures that reports contain sufficient context for security teams to evaluate threats effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide: Reporting Suspicious Activity on Investing.com
To ensure your report is comprehensive and actionable:
- Log into Your Account: Access your Investing.com account securely.
- Locate the Reporting Feature: Look for options such as "Report Issue," "Security Concern," or similar links within account settings or footer menus.
- Fill Out the Report Form: Provide detailed descriptions including:
- Specific behaviors observed (e.g., unusual trades)
- Account details involved
- Evidence supporting your claim (attachments if possible)
- Submit Your Report: Confirm all information is accurate before submitting.
- Follow Up if Necessary: Some platforms may offer confirmation emails; keep track of any case numbers provided.
By following this process carefully—ensuring clarity and detail—you help facilitate swift action from security teams who investigate reported issues promptly.
Security Measures Supporting Fraud Prevention
Investing.com's commitment to cybersecurity includes deploying advanced monitoring systems capable of detecting anomalies in real time—such as irregular trading volumes or login attempts from suspicious IP addresses—which could indicate malicious intent.
Furthermore, they implement strict verification procedures during account creation and ongoing user authentication processes to prevent fake profiles from proliferating on their platform. These measures work together with user-reported concerns to create a layered defense system against fraudsters.
Recent Developments & Ongoing Improvements
While there have been no major recent announcements specifically related to changes in investing.com's reporting mechanisms as of October 2023, continuous updates are common across reputable platforms aiming at enhancing security protocols further.
The company's ongoing efforts include integrating AI-driven threat detection tools and refining their incident response strategies based on emerging cyber threats within global financial markets—a reflection of their commitment toward regulatory compliance under authorities like FINRA and SEC standards.
Risks Associated With Not Reporting Suspicious Activities
Failing to report suspected misconduct can have serious consequences:
- Users might suffer significant financial losses due to unaddressed scams
- Malicious actors could manipulate markets undetected
- The overall trustworthiness of the platform diminishes
- Regulatory bodies may impose penalties if platforms are found negligent regarding fraud prevention measures
Conversely, active participation by informed users greatly enhances collective security—helping maintain fair trading environments where everyone’s investments are protected under law enforcement oversight when necessary.
Key Takeaways:
Always stay vigilant when noticing unusual behavior such as unexpected trades or profile impersonations.
Use official channels provided by Investing.com—like dedicated forms—to report suspicions accurately.
Include detailed evidence whenever possible; this accelerates investigations.
Remember that timely reporting supports both personal safety and broader market integrity.
By understanding these steps thoroughly—and remaining proactive—you contribute significantly toward creating safer online investment spaces while protecting your assets effectively.
Keywords: reporting suspicious activity investing.com | how to report scam | online fraud prevention | secure investing practices | investment platform safety


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-26 23:42
How do I report suspicious activity on Investing.com?
How Do I Report Suspicious Activity on Investing.com?
When using online financial platforms like Investing.com, maintaining security and integrity is essential for all users. Reporting suspicious activity plays a vital role in safeguarding your investments and ensuring the platform remains trustworthy. This guide provides a clear overview of how to report suspicious activities on Investing.com, what to look out for, and why timely reporting matters.
Understanding Why Reporting Suspicious Activity Is Important
Investing.com serves millions of users worldwide by providing real-time financial news, data analysis, and trading tools. However, as with any online platform handling sensitive financial information, it can be targeted by malicious actors engaging in market manipulation, fake accounts, insider trading schemes, or fraudulent activities. These threats not only jeopardize individual investors but also threaten the platform’s reputation and regulatory compliance.
Timely reporting helps prevent potential losses from scams or manipulative practices. It also assists the platform’s security teams in identifying vulnerabilities early on. For users committed to responsible investing and maintaining a secure environment for all participants, understanding how to report suspicious activity is an essential part of their digital safety toolkit.
How Does Investing.com Handle Reports of Suspicious Activities?
Investing.com typically offers dedicated channels or features designed specifically for reporting concerns about suspicious behavior. These mechanisms are often accessible directly through user account settings or via prominent "Report" buttons integrated into various sections of the website.
Once a user identifies unusual activity—such as abnormal trading patterns, fake profiles impersonating legitimate accounts, or signs of potential fraud—they can submit detailed reports through these channels. The process usually involves filling out an online form that captures critical information like:
- The nature of the suspicious activity
- Details about involved accounts
- Relevant evidence (screenshots or transaction records)
- Any additional comments that may assist investigators
This structured approach ensures that reports contain sufficient context for security teams to evaluate threats effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide: Reporting Suspicious Activity on Investing.com
To ensure your report is comprehensive and actionable:
- Log into Your Account: Access your Investing.com account securely.
- Locate the Reporting Feature: Look for options such as "Report Issue," "Security Concern," or similar links within account settings or footer menus.
- Fill Out the Report Form: Provide detailed descriptions including:
- Specific behaviors observed (e.g., unusual trades)
- Account details involved
- Evidence supporting your claim (attachments if possible)
- Submit Your Report: Confirm all information is accurate before submitting.
- Follow Up if Necessary: Some platforms may offer confirmation emails; keep track of any case numbers provided.
By following this process carefully—ensuring clarity and detail—you help facilitate swift action from security teams who investigate reported issues promptly.
Security Measures Supporting Fraud Prevention
Investing.com's commitment to cybersecurity includes deploying advanced monitoring systems capable of detecting anomalies in real time—such as irregular trading volumes or login attempts from suspicious IP addresses—which could indicate malicious intent.
Furthermore, they implement strict verification procedures during account creation and ongoing user authentication processes to prevent fake profiles from proliferating on their platform. These measures work together with user-reported concerns to create a layered defense system against fraudsters.
Recent Developments & Ongoing Improvements
While there have been no major recent announcements specifically related to changes in investing.com's reporting mechanisms as of October 2023, continuous updates are common across reputable platforms aiming at enhancing security protocols further.
The company's ongoing efforts include integrating AI-driven threat detection tools and refining their incident response strategies based on emerging cyber threats within global financial markets—a reflection of their commitment toward regulatory compliance under authorities like FINRA and SEC standards.
Risks Associated With Not Reporting Suspicious Activities
Failing to report suspected misconduct can have serious consequences:
- Users might suffer significant financial losses due to unaddressed scams
- Malicious actors could manipulate markets undetected
- The overall trustworthiness of the platform diminishes
- Regulatory bodies may impose penalties if platforms are found negligent regarding fraud prevention measures
Conversely, active participation by informed users greatly enhances collective security—helping maintain fair trading environments where everyone’s investments are protected under law enforcement oversight when necessary.
Key Takeaways:
Always stay vigilant when noticing unusual behavior such as unexpected trades or profile impersonations.
Use official channels provided by Investing.com—like dedicated forms—to report suspicions accurately.
Include detailed evidence whenever possible; this accelerates investigations.
Remember that timely reporting supports both personal safety and broader market integrity.
By understanding these steps thoroughly—and remaining proactive—you contribute significantly toward creating safer online investment spaces while protecting your assets effectively.
Keywords: reporting suspicious activity investing.com | how to report scam | online fraud prevention | secure investing practices | investment platform safety
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
KYC Steps for TradingView Broker Integration: A Complete Guide
Understanding the Know Your Customer (KYC) process is essential for traders and investors who want to connect their accounts with TradingView brokers. As a leading platform for market analysis and trading, TradingView’s integration with brokers streamlines the trading experience but also introduces regulatory compliance requirements. This article provides a detailed overview of the KYC steps involved in this process, ensuring users are well-informed about what to expect and how to navigate these procedures effectively.
What Is KYC and Why Is It Important?
KYC, or Know Your Customer, refers to the set of procedures financial institutions implement to verify their clients' identities. Its primary purpose is to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing. For platforms like TradingView that facilitate trading through integrated brokers, adhering to KYC regulations ensures that all transactions are legitimate and compliant with international standards.
In practice, KYC involves collecting personal information from users—such as identification documents—and verifying their authenticity before granting access to trading features. This process not only helps maintain platform integrity but also protects users from potential fraud or identity theft.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Shaping KYC Procedures
Global regulatory agencies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) have established comprehensive guidelines aimed at standardizing anti-money laundering (AML) measures worldwide. These guidelines influence how brokerages linked with TradingView implement their own KYC protocols.
Regulatory compliance varies across jurisdictions; some countries enforce strict verification processes requiring extensive documentation, while others may have more lenient standards. Nonetheless, international cooperation has led many platforms to adopt robust verification methods that meet or exceed global expectations.
Typical User Onboarding Process for Broker Integration on TradingView
When a user attempts to link a broker account within TradingView:
Account Creation: The user begins by creating an account on either TradingView or directly through the broker’s platform.
Initiating Verification: During onboarding—or sometimes after initial login—the system prompts users for identity verification.
Providing Personal Details: Users submit necessary personal information such as full name, date of birth, address, contact details.
Uploading Identification Documents: To verify identity accurately:
- Passports
- Driver’s licenses
- National ID cards
- Proofs of address like utility bills or bank statements
Verification Checks: The platform reviews submitted documents against databases or uses automated tools for validation.
Approval & Access Granting: Once verified successfully—either instantly via AI algorithms or after manual review—the user gains full access to trading functionalities through integrated brokers on TradingView.
This structured approach ensures both security and compliance while providing a seamless onboarding experience when executed efficiently.
Common Methods Used in KYC Verification
Different platforms employ various techniques during the verification phase:
- Document Uploads: Users scan and upload copies of official IDs which are then checked manually or automatically.
- Biometric Verification: Facial recognition technology compares live images captured via webcam or mobile camera against ID photos.
- Phone & Email Confirmation: Sending codes via SMS/email helps confirm contact details’ validity.
- Third-party Data Checks: Cross-referencing data against global watchlists and databases enhances accuracy further.
Employing multiple methods increases security levels but can also impact user convenience; hence many platforms aim for an optimal balance between thoroughness and simplicity.
Ongoing Monitoring After Initial Verification
Verification isn’t a one-time event; continuous monitoring plays an essential role in maintaining compliance over time:
- Detecting suspicious activity patterns
- Updating customer information periodically
- Conducting enhanced due diligence if unusual transactions occur
This ongoing oversight helps prevent illicit activities post-integration while safeguarding both traders’ interests and regulatory adherence.
Data Security & Privacy Considerations
Handling sensitive personal data requires strict adherence to data protection laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Platforms must ensure:
- Secure storage using encryption technologies
- Limited access only authorized personnel
- Clear privacy policies informing users about data usage
Transparency builds trust among users who share highly confidential information during the verification process.
Recent Trends & Developments in KYC Processes
The landscape of financial regulation continues evolving rapidly due mainly to technological advancements:
Enhanced Regulations Post-Cryptocurrency Boom
The surge in cryptocurrency exchanges has prompted regulators worldwide — including FATF —to tighten AML/KYC rules further across digital asset markets which now extend into traditional brokerage services connected via platforms like TradingView.
Technological Innovations
Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning algorithms, blockchain-based solutions are increasingly used:
- To automate document validation efficiently
- To detect fraudulent activity proactively
These innovations aim at reducing manual effort while increasing accuracy—a win-win situation balancing security with user experience improvements.
Improving User Experience Without Compromising Security
While rigorous checks are necessary legally—and often ethically—they can be cumbersome for end-users:
Platforms strive — including those integrated with TradingView—to streamline processes by implementing intuitive interfaces,reducing document submission times,and enabling instant verifications where possible without sacrificing compliance standards.
International Cooperation Enhances Global Compliance
Organizations such as FATF promote harmonized standards across borders—making it easier for multinational firms operating globally within different legal frameworks—to adhere uniformly without gaps that could be exploited by bad actors.
Risks Associated With Non-compliance
Failure by brokers—or associated platforms—to meet these stringent requirements can lead not only to hefty fines but also legal actions that damage reputation long-term efforts toward transparency.
Navigating Your Broker's KYC Requirements Effectively
For traders integrating their accounts into TradingView:
- Prepare valid identification documents ahead of time.
- Follow instructions carefully during submission—ensure clarity when uploading files.
- Be patient if manual review is needed; response times may vary based on workload.4.. Keep your profile updated regularly especially if your details change over time.
Final Thoughts on Ensuring Smooth Broker Integration Under Regulatory Standards
Meeting KYC requirements might seem tedious initially—but it plays a vital role in fostering secure trading environments aligned with global regulations! By understanding each step—from document submission through ongoing monitoring—you can ensure smoother onboarding experiences while contributing positively toward combating financial crimes worldwide.


kai
2025-05-26 23:27
What KYC steps are required for TradingView broker integration?
KYC Steps for TradingView Broker Integration: A Complete Guide
Understanding the Know Your Customer (KYC) process is essential for traders and investors who want to connect their accounts with TradingView brokers. As a leading platform for market analysis and trading, TradingView’s integration with brokers streamlines the trading experience but also introduces regulatory compliance requirements. This article provides a detailed overview of the KYC steps involved in this process, ensuring users are well-informed about what to expect and how to navigate these procedures effectively.
What Is KYC and Why Is It Important?
KYC, or Know Your Customer, refers to the set of procedures financial institutions implement to verify their clients' identities. Its primary purpose is to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing. For platforms like TradingView that facilitate trading through integrated brokers, adhering to KYC regulations ensures that all transactions are legitimate and compliant with international standards.
In practice, KYC involves collecting personal information from users—such as identification documents—and verifying their authenticity before granting access to trading features. This process not only helps maintain platform integrity but also protects users from potential fraud or identity theft.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Shaping KYC Procedures
Global regulatory agencies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) have established comprehensive guidelines aimed at standardizing anti-money laundering (AML) measures worldwide. These guidelines influence how brokerages linked with TradingView implement their own KYC protocols.
Regulatory compliance varies across jurisdictions; some countries enforce strict verification processes requiring extensive documentation, while others may have more lenient standards. Nonetheless, international cooperation has led many platforms to adopt robust verification methods that meet or exceed global expectations.
Typical User Onboarding Process for Broker Integration on TradingView
When a user attempts to link a broker account within TradingView:
Account Creation: The user begins by creating an account on either TradingView or directly through the broker’s platform.
Initiating Verification: During onboarding—or sometimes after initial login—the system prompts users for identity verification.
Providing Personal Details: Users submit necessary personal information such as full name, date of birth, address, contact details.
Uploading Identification Documents: To verify identity accurately:
- Passports
- Driver’s licenses
- National ID cards
- Proofs of address like utility bills or bank statements
Verification Checks: The platform reviews submitted documents against databases or uses automated tools for validation.
Approval & Access Granting: Once verified successfully—either instantly via AI algorithms or after manual review—the user gains full access to trading functionalities through integrated brokers on TradingView.
This structured approach ensures both security and compliance while providing a seamless onboarding experience when executed efficiently.
Common Methods Used in KYC Verification
Different platforms employ various techniques during the verification phase:
- Document Uploads: Users scan and upload copies of official IDs which are then checked manually or automatically.
- Biometric Verification: Facial recognition technology compares live images captured via webcam or mobile camera against ID photos.
- Phone & Email Confirmation: Sending codes via SMS/email helps confirm contact details’ validity.
- Third-party Data Checks: Cross-referencing data against global watchlists and databases enhances accuracy further.
Employing multiple methods increases security levels but can also impact user convenience; hence many platforms aim for an optimal balance between thoroughness and simplicity.
Ongoing Monitoring After Initial Verification
Verification isn’t a one-time event; continuous monitoring plays an essential role in maintaining compliance over time:
- Detecting suspicious activity patterns
- Updating customer information periodically
- Conducting enhanced due diligence if unusual transactions occur
This ongoing oversight helps prevent illicit activities post-integration while safeguarding both traders’ interests and regulatory adherence.
Data Security & Privacy Considerations
Handling sensitive personal data requires strict adherence to data protection laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Platforms must ensure:
- Secure storage using encryption technologies
- Limited access only authorized personnel
- Clear privacy policies informing users about data usage
Transparency builds trust among users who share highly confidential information during the verification process.
Recent Trends & Developments in KYC Processes
The landscape of financial regulation continues evolving rapidly due mainly to technological advancements:
Enhanced Regulations Post-Cryptocurrency Boom
The surge in cryptocurrency exchanges has prompted regulators worldwide — including FATF —to tighten AML/KYC rules further across digital asset markets which now extend into traditional brokerage services connected via platforms like TradingView.
Technological Innovations
Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning algorithms, blockchain-based solutions are increasingly used:
- To automate document validation efficiently
- To detect fraudulent activity proactively
These innovations aim at reducing manual effort while increasing accuracy—a win-win situation balancing security with user experience improvements.
Improving User Experience Without Compromising Security
While rigorous checks are necessary legally—and often ethically—they can be cumbersome for end-users:
Platforms strive — including those integrated with TradingView—to streamline processes by implementing intuitive interfaces,reducing document submission times,and enabling instant verifications where possible without sacrificing compliance standards.
International Cooperation Enhances Global Compliance
Organizations such as FATF promote harmonized standards across borders—making it easier for multinational firms operating globally within different legal frameworks—to adhere uniformly without gaps that could be exploited by bad actors.
Risks Associated With Non-compliance
Failure by brokers—or associated platforms—to meet these stringent requirements can lead not only to hefty fines but also legal actions that damage reputation long-term efforts toward transparency.
Navigating Your Broker's KYC Requirements Effectively
For traders integrating their accounts into TradingView:
- Prepare valid identification documents ahead of time.
- Follow instructions carefully during submission—ensure clarity when uploading files.
- Be patient if manual review is needed; response times may vary based on workload.4.. Keep your profile updated regularly especially if your details change over time.
Final Thoughts on Ensuring Smooth Broker Integration Under Regulatory Standards
Meeting KYC requirements might seem tedious initially—but it plays a vital role in fostering secure trading environments aligned with global regulations! By understanding each step—from document submission through ongoing monitoring—you can ensure smoother onboarding experiences while contributing positively toward combating financial crimes worldwide.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Protocols for Connecting Wallets to dApps Without Sharing Private Keys
In the rapidly evolving blockchain ecosystem, the seamless and secure connection between digital wallets and decentralized applications (dApps) is essential. As DeFi, NFTs, and other blockchain-based services grow in popularity, users demand solutions that protect their private keys while enabling easy interaction with dApps. This article explores the key protocols designed to facilitate this secure connection without exposing sensitive information.
Why Secure Wallet-dApp Connections Matter
Private keys are the cornerstone of cryptocurrency security—they grant access to funds and control over digital assets. Sharing these keys with third-party applications or during transactions can lead to theft or unauthorized access. Therefore, protocols that enable wallet-dApp interactions without sharing private keys are critical for maintaining user trust and security.
The challenge lies in balancing ease of use with robust security measures. Users want frictionless experiences similar to traditional banking apps but require cryptographic safeguards inherent in blockchain technology.
Main Protocols Enabling Secure Wallet-DApp Interactions
Several protocols have been developed over recent years to address this need. Each offers unique features tailored toward enhancing security while maintaining usability across various platforms.
Web3.js and Ethers.js: Developer Tools for Blockchain Interaction
Web3.js and Ethers.js are JavaScript libraries widely used by developers building Ethereum-based dApps. They provide APIs that interact with blockchain nodes via JSON-RPC endpoints—allowing web applications to read data from or send transactions to the Ethereum network securely.
These libraries do not handle private keys directly; instead, they interface with wallet providers like MetaMask or hardware wallets through standardized methods such as injected providers or external signers. This approach ensures that private keys remain within user-controlled environments while enabling transaction signing through secure prompts.
MetaMask: User-Friendly Browser Wallet Extension
MetaMask is arguably the most popular wallet extension for browsers like Chrome and Firefox, as well as mobile versions. It acts as a bridge between users’ private keys stored locally on their devices and dApps running within browsers.
MetaMask employs cryptographic techniques such as local encryption storage combined with secure prompts when signing transactions or messages—meaning users never share their private keys directly with websites or dApps. Instead, they approve actions via cryptographic signatures managed internally by MetaMask’s secure environment.
WalletConnect: Cross-Platform Secure Communication Protocol
WalletConnect stands out due to its open-source nature designed explicitly for cross-wallet compatibility across multiple platforms—including mobile wallets like Trust Wallet, Rainbow, Argent—and desktop environments via QR codes or deep links.
This protocol creates an encrypted session between a user's wallet app and a dApp by generating a temporary pairing code (QR code). All sensitive data remains encrypted during transmission; only transaction requests are signed locally on the user's device before being sent back securely—never exposing private keys outside trusted environments.
Cosmos SDK & Polkadot's Substrate: Modular Frameworks for Custom Solutions
For developers building bespoke blockchain solutions beyond Ethereum’s scope, frameworks like Cosmos SDK and Polkadot's Substrate offer modular architectures emphasizing privacy-preserving interactions:
- Cosmos SDK provides tools allowing custom modules that can implement advanced cryptography ensuring user privacy.
- Substrate enables tailored blockchains where developers can embed specific cryptographic protocols into wallet interactions—enhancing security at every step of communication between wallets and decentralized apps built on these frameworks.
Both frameworks support integration strategies focused on safeguarding user secrets while facilitating flexible application development suited for enterprise-grade solutions.
Recent Innovations Enhancing Security & Usability
The landscape of wallet-dApp connection protocols continues evolving rapidly—with recent updates focusing heavily on improving both security standards and user experience:
WalletConnect 2.0, launched in 2023, introduces stronger encryption algorithms alongside streamlined onboarding processes such as simplified QR code scanning workflows—making it easier than ever for users across different devices.
Ethereum's EIP-4337, proposed recently within Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), aims at creating "smart accounts" capable of executing complex transactions without revealing private key details upfront—a significant step toward fully trustless interactions.
MetaMask’s latest updates include multi-account management features introduced in 2024 which allow users greater control over different identities within one interface—all secured through enhanced encryption techniques ensuring funds remain protected even if one account is compromised.
Challenges Facing Future Adoption
Despite technological advancements making wallet-dApp connections more secure than ever before, several hurdles still exist:
Complexity: The sophisticated nature of some protocols may intimidate new users unfamiliar with crypto concepts—potentially limiting mainstream adoption.
Interoperability: Different standards may not always work seamlessly together; fragmented ecosystems could hinder smooth cross-platform experiences.
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely worldwide, new regulations could impose restrictions affecting how these protocols operate—or even restrict certain functionalities altogether.
Moving Toward a Safer Decentralized Future
Ensuring safe yet accessible connections between wallets and dApps remains central to fostering broader adoption of blockchain technologies—from DeFi platforms offering financial services without intermediaries to NFT marketplaces revolutionizing digital ownership rights.
By leveraging established standards like Web3.js/Ethers.js integrated seamlessly into trusted wallets such as MetaMask—and adopting innovative solutions like WalletConnect 2.x—the industry continues progressing toward more resilient systems capable of protecting user assets against emerging threats while providing frictionless experiences suitable for mass markets.
This overview underscores how diverse protocol options cater specifically to different needs—from developer-centric tools enabling custom integrations—to end-user-focused solutions prioritizing ease-of-use alongside robust security measures—all vital components shaping the future landscape of decentralized finance infrastructure worldwide.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 22:14
What protocols exist to connect wallets to dApps without sharing keys?
Protocols for Connecting Wallets to dApps Without Sharing Private Keys
In the rapidly evolving blockchain ecosystem, the seamless and secure connection between digital wallets and decentralized applications (dApps) is essential. As DeFi, NFTs, and other blockchain-based services grow in popularity, users demand solutions that protect their private keys while enabling easy interaction with dApps. This article explores the key protocols designed to facilitate this secure connection without exposing sensitive information.
Why Secure Wallet-dApp Connections Matter
Private keys are the cornerstone of cryptocurrency security—they grant access to funds and control over digital assets. Sharing these keys with third-party applications or during transactions can lead to theft or unauthorized access. Therefore, protocols that enable wallet-dApp interactions without sharing private keys are critical for maintaining user trust and security.
The challenge lies in balancing ease of use with robust security measures. Users want frictionless experiences similar to traditional banking apps but require cryptographic safeguards inherent in blockchain technology.
Main Protocols Enabling Secure Wallet-DApp Interactions
Several protocols have been developed over recent years to address this need. Each offers unique features tailored toward enhancing security while maintaining usability across various platforms.
Web3.js and Ethers.js: Developer Tools for Blockchain Interaction
Web3.js and Ethers.js are JavaScript libraries widely used by developers building Ethereum-based dApps. They provide APIs that interact with blockchain nodes via JSON-RPC endpoints—allowing web applications to read data from or send transactions to the Ethereum network securely.
These libraries do not handle private keys directly; instead, they interface with wallet providers like MetaMask or hardware wallets through standardized methods such as injected providers or external signers. This approach ensures that private keys remain within user-controlled environments while enabling transaction signing through secure prompts.
MetaMask: User-Friendly Browser Wallet Extension
MetaMask is arguably the most popular wallet extension for browsers like Chrome and Firefox, as well as mobile versions. It acts as a bridge between users’ private keys stored locally on their devices and dApps running within browsers.
MetaMask employs cryptographic techniques such as local encryption storage combined with secure prompts when signing transactions or messages—meaning users never share their private keys directly with websites or dApps. Instead, they approve actions via cryptographic signatures managed internally by MetaMask’s secure environment.
WalletConnect: Cross-Platform Secure Communication Protocol
WalletConnect stands out due to its open-source nature designed explicitly for cross-wallet compatibility across multiple platforms—including mobile wallets like Trust Wallet, Rainbow, Argent—and desktop environments via QR codes or deep links.
This protocol creates an encrypted session between a user's wallet app and a dApp by generating a temporary pairing code (QR code). All sensitive data remains encrypted during transmission; only transaction requests are signed locally on the user's device before being sent back securely—never exposing private keys outside trusted environments.
Cosmos SDK & Polkadot's Substrate: Modular Frameworks for Custom Solutions
For developers building bespoke blockchain solutions beyond Ethereum’s scope, frameworks like Cosmos SDK and Polkadot's Substrate offer modular architectures emphasizing privacy-preserving interactions:
- Cosmos SDK provides tools allowing custom modules that can implement advanced cryptography ensuring user privacy.
- Substrate enables tailored blockchains where developers can embed specific cryptographic protocols into wallet interactions—enhancing security at every step of communication between wallets and decentralized apps built on these frameworks.
Both frameworks support integration strategies focused on safeguarding user secrets while facilitating flexible application development suited for enterprise-grade solutions.
Recent Innovations Enhancing Security & Usability
The landscape of wallet-dApp connection protocols continues evolving rapidly—with recent updates focusing heavily on improving both security standards and user experience:
WalletConnect 2.0, launched in 2023, introduces stronger encryption algorithms alongside streamlined onboarding processes such as simplified QR code scanning workflows—making it easier than ever for users across different devices.
Ethereum's EIP-4337, proposed recently within Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), aims at creating "smart accounts" capable of executing complex transactions without revealing private key details upfront—a significant step toward fully trustless interactions.
MetaMask’s latest updates include multi-account management features introduced in 2024 which allow users greater control over different identities within one interface—all secured through enhanced encryption techniques ensuring funds remain protected even if one account is compromised.
Challenges Facing Future Adoption
Despite technological advancements making wallet-dApp connections more secure than ever before, several hurdles still exist:
Complexity: The sophisticated nature of some protocols may intimidate new users unfamiliar with crypto concepts—potentially limiting mainstream adoption.
Interoperability: Different standards may not always work seamlessly together; fragmented ecosystems could hinder smooth cross-platform experiences.
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely worldwide, new regulations could impose restrictions affecting how these protocols operate—or even restrict certain functionalities altogether.
Moving Toward a Safer Decentralized Future
Ensuring safe yet accessible connections between wallets and dApps remains central to fostering broader adoption of blockchain technologies—from DeFi platforms offering financial services without intermediaries to NFT marketplaces revolutionizing digital ownership rights.
By leveraging established standards like Web3.js/Ethers.js integrated seamlessly into trusted wallets such as MetaMask—and adopting innovative solutions like WalletConnect 2.x—the industry continues progressing toward more resilient systems capable of protecting user assets against emerging threats while providing frictionless experiences suitable for mass markets.
This overview underscores how diverse protocol options cater specifically to different needs—from developer-centric tools enabling custom integrations—to end-user-focused solutions prioritizing ease-of-use alongside robust security measures—all vital components shaping the future landscape of decentralized finance infrastructure worldwide.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Assessing an exchange’s security practices and reputation is a critical step for anyone involved in cryptocurrency trading or investment. With the increasing popularity of digital assets, the landscape has become more complex, making it essential to evaluate how well an exchange protects user funds and maintains trust within the community. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of key factors to consider when assessing an exchange’s security measures and overall reputation.
Understanding the Importance of Security Practices in Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges act as gateways to digital asset markets, handling large volumes of transactions and sensitive user data. Their security protocols directly impact user confidence and financial safety. A breach or failure can lead to significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and regulatory repercussions. Therefore, scrutinizing their security infrastructure is vital before depositing funds or engaging in trading activities.
Good security practices include multiple layers of protection such as two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage solutions, regular audits, and insurance policies for stored assets. These measures help mitigate risks associated with hacking attempts or internal vulnerabilities.
Key Security Measures That Indicate a Reputable Exchange
When evaluating an exchange's security posture, look for specific features that demonstrate proactive risk management:
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Most reputable platforms require 2FA during login processes to add an extra layer of account protection beyond just passwords.
Cold Storage: A significant portion of user funds should be stored offline in cold wallets disconnected from internet access—this minimizes exposure to online threats.
Regular Security Audits: Independent audits conducted periodically help identify potential vulnerabilities within the platform's infrastructure.
Insurance Coverage: Some exchanges offer insurance policies that protect users’ assets against thefts or system failures—adding reassurance about asset safety.
These elements collectively contribute toward building a secure environment where users can trade with confidence.
Factors Influencing Exchange Reputation
An exchange’s reputation extends beyond its technical safeguards; it encompasses transparency, compliance with regulations, community feedback, and industry recognition:
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to local laws ensures operational legitimacy and reduces legal risks. Exchanges compliant with regulations like AML (Anti-Money Laundering) standards tend to be more trustworthy.
Transparency: Clear communication regarding fee structures, operational procedures, data handling policies—and openly sharing information about their security protocols—builds trust among users.
User Reviews & Community Feedback: Platforms with positive reviews on forums like Reddit or Trustpilot often reflect reliable service quality; however, always cross-reference multiple sources for accuracy.
Industry Awards & Recognition: External accolades from reputable organizations serve as indicators that an exchange maintains high standards within the industry.
Building a good reputation requires consistent effort across these areas over time.
Recent Incidents Highlighting Security Challenges
Recent events underscore why continuous vigilance is necessary when choosing an exchange:
In May 2023, Binance experienced a major hack resulting in approximately $100 million worth of cryptocurrencies stolen by malicious actors. Although Binance responded swiftly by suspending withdrawals temporarily while investigating the breach—and claimed they had sufficient reserves—the incident emphasized vulnerabilities even among leading platforms known for robust defenses.
The collapse of FTX in November 2022 further shook investor confidence worldwide. The fallout revealed issues related not only to liquidity but also raised questions about internal controls and transparency practices at some exchanges—highlighting how poor governance can undermine perceived safety even if technical measures are adequate initially.
Regulatory actions have also increased globally; authorities are scrutinizing exchanges more closely than ever before. Non-compliance penalties—including fines or shutdowns—can severely damage reputations overnight if violations are uncovered post-factum.
How Investors Can Protect Themselves When Choosing Exchanges
Given these complexities—and recognizing that no platform is entirely immune from risks—it becomes crucial for investors themselves to conduct due diligence:
Verify whether the platform employs strong security features such as 2FA and cold storage solutions.
Check if they comply with relevant regulatory frameworks applicable in your jurisdiction.
Review recent news reports on any breaches or legal issues involving the platform.
Read independent reviews from trusted sources like industry reports by Chainalysis or CipherTrace which analyze compliance levels and risk profiles across various exchanges.
Engage with community forums where real users share experiences—though always approach anecdotal feedback critically alongside official disclosures.
By combining technical evaluation with community insights—and staying informed through reliable resources—you can make smarter decisions aligned with your risk appetite.
Additional Resources
For further reading on this topic:
- Visit regulatory bodies’ websites such as SEC.gov for updates on enforcement actions affecting crypto platforms
- Explore detailed industry reports from firms like Chainalysis which provide insights into global compliance trends
- Participate actively in online communities like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency where firsthand experiences are shared regularly
Staying informed enables you not only to select safer exchanges but also helps you adapt strategies over time amid evolving threats within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Final Thoughts
Assessing an exchange's security practices involves examining both technological safeguards—including encryption methods—and broader factors such as regulatory adherence and community trustworthiness. While incidents like Binance’s hack highlight ongoing challenges faced by all platforms—even those considered top-tier—the key lies in diligent research combined with personal vigilance when managing digital assets securely within this dynamic environment.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 10:40
How do you assess an exchange’s security practices and reputation?
Assessing an exchange’s security practices and reputation is a critical step for anyone involved in cryptocurrency trading or investment. With the increasing popularity of digital assets, the landscape has become more complex, making it essential to evaluate how well an exchange protects user funds and maintains trust within the community. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of key factors to consider when assessing an exchange’s security measures and overall reputation.
Understanding the Importance of Security Practices in Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges act as gateways to digital asset markets, handling large volumes of transactions and sensitive user data. Their security protocols directly impact user confidence and financial safety. A breach or failure can lead to significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and regulatory repercussions. Therefore, scrutinizing their security infrastructure is vital before depositing funds or engaging in trading activities.
Good security practices include multiple layers of protection such as two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage solutions, regular audits, and insurance policies for stored assets. These measures help mitigate risks associated with hacking attempts or internal vulnerabilities.
Key Security Measures That Indicate a Reputable Exchange
When evaluating an exchange's security posture, look for specific features that demonstrate proactive risk management:
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Most reputable platforms require 2FA during login processes to add an extra layer of account protection beyond just passwords.
Cold Storage: A significant portion of user funds should be stored offline in cold wallets disconnected from internet access—this minimizes exposure to online threats.
Regular Security Audits: Independent audits conducted periodically help identify potential vulnerabilities within the platform's infrastructure.
Insurance Coverage: Some exchanges offer insurance policies that protect users’ assets against thefts or system failures—adding reassurance about asset safety.
These elements collectively contribute toward building a secure environment where users can trade with confidence.
Factors Influencing Exchange Reputation
An exchange’s reputation extends beyond its technical safeguards; it encompasses transparency, compliance with regulations, community feedback, and industry recognition:
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to local laws ensures operational legitimacy and reduces legal risks. Exchanges compliant with regulations like AML (Anti-Money Laundering) standards tend to be more trustworthy.
Transparency: Clear communication regarding fee structures, operational procedures, data handling policies—and openly sharing information about their security protocols—builds trust among users.
User Reviews & Community Feedback: Platforms with positive reviews on forums like Reddit or Trustpilot often reflect reliable service quality; however, always cross-reference multiple sources for accuracy.
Industry Awards & Recognition: External accolades from reputable organizations serve as indicators that an exchange maintains high standards within the industry.
Building a good reputation requires consistent effort across these areas over time.
Recent Incidents Highlighting Security Challenges
Recent events underscore why continuous vigilance is necessary when choosing an exchange:
In May 2023, Binance experienced a major hack resulting in approximately $100 million worth of cryptocurrencies stolen by malicious actors. Although Binance responded swiftly by suspending withdrawals temporarily while investigating the breach—and claimed they had sufficient reserves—the incident emphasized vulnerabilities even among leading platforms known for robust defenses.
The collapse of FTX in November 2022 further shook investor confidence worldwide. The fallout revealed issues related not only to liquidity but also raised questions about internal controls and transparency practices at some exchanges—highlighting how poor governance can undermine perceived safety even if technical measures are adequate initially.
Regulatory actions have also increased globally; authorities are scrutinizing exchanges more closely than ever before. Non-compliance penalties—including fines or shutdowns—can severely damage reputations overnight if violations are uncovered post-factum.
How Investors Can Protect Themselves When Choosing Exchanges
Given these complexities—and recognizing that no platform is entirely immune from risks—it becomes crucial for investors themselves to conduct due diligence:
Verify whether the platform employs strong security features such as 2FA and cold storage solutions.
Check if they comply with relevant regulatory frameworks applicable in your jurisdiction.
Review recent news reports on any breaches or legal issues involving the platform.
Read independent reviews from trusted sources like industry reports by Chainalysis or CipherTrace which analyze compliance levels and risk profiles across various exchanges.
Engage with community forums where real users share experiences—though always approach anecdotal feedback critically alongside official disclosures.
By combining technical evaluation with community insights—and staying informed through reliable resources—you can make smarter decisions aligned with your risk appetite.
Additional Resources
For further reading on this topic:
- Visit regulatory bodies’ websites such as SEC.gov for updates on enforcement actions affecting crypto platforms
- Explore detailed industry reports from firms like Chainalysis which provide insights into global compliance trends
- Participate actively in online communities like Reddit’s r/CryptoCurrency where firsthand experiences are shared regularly
Staying informed enables you not only to select safer exchanges but also helps you adapt strategies over time amid evolving threats within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Final Thoughts
Assessing an exchange's security practices involves examining both technological safeguards—including encryption methods—and broader factors such as regulatory adherence and community trustworthiness. While incidents like Binance’s hack highlight ongoing challenges faced by all platforms—even those considered top-tier—the key lies in diligent research combined with personal vigilance when managing digital assets securely within this dynamic environment.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Paper Wallet and Is It Still a Recommended Storage Method?
Understanding Paper Wallets in Cryptocurrency Security
A paper wallet is a physical document that contains the public and private keys needed to manage cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others. Unlike digital wallets stored on devices or online platforms, paper wallets are entirely offline, making them an attractive option for long-term storage of crypto assets. They typically include QR codes for easy scanning during transactions and are designed to provide a secure way to hold cryptocurrencies away from potential cyber threats.
Historically, paper wallets emerged during the early days of Bitcoin around 2010-2011 when users sought safer alternatives to storing private keys on computers or mobile devices vulnerable to hacking. The concept was simple: generate cryptographic key pairs using reputable tools, print them out securely, and store the physical copy in a safe location like a safe deposit box or fireproof safe. This method aimed to mitigate risks associated with online theft while offering full control over one's assets.
How Do Paper Wallets Work?
The process of using a paper wallet involves three main steps:
Key Generation: Users utilize specialized software or online tools—preferably reputable ones—to generate a pair of cryptographic keys: one public (used as an address for receiving funds) and one private (used for spending).
Printing: These keys are then printed onto paper—often in QR code format—to facilitate quick scanning during transactions.
Storage: The printed wallet is stored securely offline in protected locations such as safes or safety deposit boxes to prevent unauthorized access or damage.
This straightforward approach allows users complete control over their cryptocurrency holdings without relying on third-party services.
Security Considerations When Using Paper Wallets
While paper wallets offer certain security advantages due to their offline nature, they also come with notable risks that users must carefully consider:
Physical Security Risks: Since the wallet exists physically outside digital environments, safeguarding it from theft, loss, fire damage, water exposure, or deterioration is critical. A compromised physical copy can lead directly to asset loss.
Human Error: Mistakes during generation—such as printing errors—or mishandling can result in losing access permanently if backups aren’t properly created beforehand.
Counterfeit Concerns: There have been instances where counterfeit or maliciously generated paper wallets were distributed; therefore, verifying the authenticity of tools used is essential for security assurance.
Despite these challenges, many still view paper wallets as secure when generated with trusted tools and stored properly; however, they require diligent handling.
The Rise of Hardware and Digital Wallets
Over recent years since their inception around 2010–2011—and especially after significant advancements between 2014–2015—the landscape of cryptocurrency storage has shifted dramatically toward hardware solutions like Ledger Nano S/X and Trezor devices. These hardware wallets combine offline security with user-friendly interfaces featuring PIN protection and multi-signature capabilities that significantly reduce human error risks associated with manual handling of private keys.
Simultaneously evolving digital wallets such as MetaMask or Coinbase offer enhanced security features including two-factor authentication (2FA), biometric verification options—and some even provide insurance against certain types of losses—making them more accessible yet still secure options suitable for everyday use by most investors.
Regulatory developments have also played an influential role; stricter regulations introduced around 2017–2018 have encouraged adoption toward more compliant storage solutions that meet legal standards across jurisdictions worldwide.
Are Paper Wallets Still Recommended Today?
Given technological progressions over the past decade—including improvements in hardware security devices—and increased regulatory oversight—the popularity of traditional paper wallets has declined considerably among both casual users and professional investors alike. While they remain technically viable if generated securely under trusted conditions—they are generally considered less practical today due to several inherent limitations:
- Vulnerability to human error during creation
- Risky physical handling leading potentially to loss
- Susceptibility to counterfeiting if not verified properly
- Environmental concerns related to printing materials
Most experts now recommend alternative methods such as hardware cold storage solutions which provide higher levels of protection combined with ease-of-use suitable even for beginners.
Environmental Impact & Future Trends
Beyond security considerations lies environmental impact: producing printed copies consumes resources like paper—a concern given global sustainability efforts—and storing large quantities physically requires space management strategies not necessary with digital counterparts. As blockchain technology evolves—with innovations like multi-signature schemes becoming more common—the reliance on physical media diminishes further.
Staying Informed About Cryptocurrency Storage Options
For anyone involved in cryptocurrency investment today—from newcomers seeking basic safety measures—to seasoned traders managing substantial portfolios—it’s vital always stay informed about emerging best practices within cybersecurity frameworks tailored specifically for blockchain assets. This includes understanding how new hardware innovations compare against older methods like paper-based solutions while considering factors such as convenience versus risk mitigation strategies.
Summary: Should You Use a Paper Wallet Today?
While historically significant within crypto's development timeline—as an early method designed primarily for maximum offline security—paper wallets now occupy a niche role rather than mainstream practice due mainly to their vulnerabilities concerning human error and environmental factors. Modern alternatives like hardware cold storages offer superior protection combined with user-friendly features suited both novices’ needs and professional requirements alike.
Key Takeaways at-a-glance:
- Introduced early in Bitcoin’s history (~2010–2011) as an offline storage solution.
- Offer strong resistance against hacking since they’re disconnected from internet networks.
- Pose risks related mainly through mishandling — including damage/loss/counterfeiting.
- Have seen declining popularity owing largely due to advances in hardware/software wallet technology.
- Remain relevant only under strict conditions involving careful generation/storage practices.
By understanding these aspects thoroughly—from historical context through current best practices—you can make informed decisions about securing your cryptocurrencies effectively today while preparing yourself better against future developments within this rapidly evolving field.
Keywords: cryptocurrency storage methods; cold storage options; crypto wallet types; secure crypto management; blockchain asset safety


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 05:50
What is a paper wallet, and is it still a recommended option?
What Is a Paper Wallet and Is It Still a Recommended Storage Method?
Understanding Paper Wallets in Cryptocurrency Security
A paper wallet is a physical document that contains the public and private keys needed to manage cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others. Unlike digital wallets stored on devices or online platforms, paper wallets are entirely offline, making them an attractive option for long-term storage of crypto assets. They typically include QR codes for easy scanning during transactions and are designed to provide a secure way to hold cryptocurrencies away from potential cyber threats.
Historically, paper wallets emerged during the early days of Bitcoin around 2010-2011 when users sought safer alternatives to storing private keys on computers or mobile devices vulnerable to hacking. The concept was simple: generate cryptographic key pairs using reputable tools, print them out securely, and store the physical copy in a safe location like a safe deposit box or fireproof safe. This method aimed to mitigate risks associated with online theft while offering full control over one's assets.
How Do Paper Wallets Work?
The process of using a paper wallet involves three main steps:
Key Generation: Users utilize specialized software or online tools—preferably reputable ones—to generate a pair of cryptographic keys: one public (used as an address for receiving funds) and one private (used for spending).
Printing: These keys are then printed onto paper—often in QR code format—to facilitate quick scanning during transactions.
Storage: The printed wallet is stored securely offline in protected locations such as safes or safety deposit boxes to prevent unauthorized access or damage.
This straightforward approach allows users complete control over their cryptocurrency holdings without relying on third-party services.
Security Considerations When Using Paper Wallets
While paper wallets offer certain security advantages due to their offline nature, they also come with notable risks that users must carefully consider:
Physical Security Risks: Since the wallet exists physically outside digital environments, safeguarding it from theft, loss, fire damage, water exposure, or deterioration is critical. A compromised physical copy can lead directly to asset loss.
Human Error: Mistakes during generation—such as printing errors—or mishandling can result in losing access permanently if backups aren’t properly created beforehand.
Counterfeit Concerns: There have been instances where counterfeit or maliciously generated paper wallets were distributed; therefore, verifying the authenticity of tools used is essential for security assurance.
Despite these challenges, many still view paper wallets as secure when generated with trusted tools and stored properly; however, they require diligent handling.
The Rise of Hardware and Digital Wallets
Over recent years since their inception around 2010–2011—and especially after significant advancements between 2014–2015—the landscape of cryptocurrency storage has shifted dramatically toward hardware solutions like Ledger Nano S/X and Trezor devices. These hardware wallets combine offline security with user-friendly interfaces featuring PIN protection and multi-signature capabilities that significantly reduce human error risks associated with manual handling of private keys.
Simultaneously evolving digital wallets such as MetaMask or Coinbase offer enhanced security features including two-factor authentication (2FA), biometric verification options—and some even provide insurance against certain types of losses—making them more accessible yet still secure options suitable for everyday use by most investors.
Regulatory developments have also played an influential role; stricter regulations introduced around 2017–2018 have encouraged adoption toward more compliant storage solutions that meet legal standards across jurisdictions worldwide.
Are Paper Wallets Still Recommended Today?
Given technological progressions over the past decade—including improvements in hardware security devices—and increased regulatory oversight—the popularity of traditional paper wallets has declined considerably among both casual users and professional investors alike. While they remain technically viable if generated securely under trusted conditions—they are generally considered less practical today due to several inherent limitations:
- Vulnerability to human error during creation
- Risky physical handling leading potentially to loss
- Susceptibility to counterfeiting if not verified properly
- Environmental concerns related to printing materials
Most experts now recommend alternative methods such as hardware cold storage solutions which provide higher levels of protection combined with ease-of-use suitable even for beginners.
Environmental Impact & Future Trends
Beyond security considerations lies environmental impact: producing printed copies consumes resources like paper—a concern given global sustainability efforts—and storing large quantities physically requires space management strategies not necessary with digital counterparts. As blockchain technology evolves—with innovations like multi-signature schemes becoming more common—the reliance on physical media diminishes further.
Staying Informed About Cryptocurrency Storage Options
For anyone involved in cryptocurrency investment today—from newcomers seeking basic safety measures—to seasoned traders managing substantial portfolios—it’s vital always stay informed about emerging best practices within cybersecurity frameworks tailored specifically for blockchain assets. This includes understanding how new hardware innovations compare against older methods like paper-based solutions while considering factors such as convenience versus risk mitigation strategies.
Summary: Should You Use a Paper Wallet Today?
While historically significant within crypto's development timeline—as an early method designed primarily for maximum offline security—paper wallets now occupy a niche role rather than mainstream practice due mainly to their vulnerabilities concerning human error and environmental factors. Modern alternatives like hardware cold storages offer superior protection combined with user-friendly features suited both novices’ needs and professional requirements alike.
Key Takeaways at-a-glance:
- Introduced early in Bitcoin’s history (~2010–2011) as an offline storage solution.
- Offer strong resistance against hacking since they’re disconnected from internet networks.
- Pose risks related mainly through mishandling — including damage/loss/counterfeiting.
- Have seen declining popularity owing largely due to advances in hardware/software wallet technology.
- Remain relevant only under strict conditions involving careful generation/storage practices.
By understanding these aspects thoroughly—from historical context through current best practices—you can make informed decisions about securing your cryptocurrencies effectively today while preparing yourself better against future developments within this rapidly evolving field.
Keywords: cryptocurrency storage methods; cold storage options; crypto wallet types; secure crypto management; blockchain asset safety
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Advance-Decline Line (A/D Line)?
The Advance-Decline Line, often abbreviated as the A/D Line, is a vital technical indicator used by traders and investors to assess the overall health of the stock market. Unlike price-based indicators that focus solely on individual stocks or indices, the A/D Line provides insight into market breadth—how many stocks are participating in upward or downward movements. This makes it a powerful tool for understanding whether a rally is broad-based or driven by a few large-cap stocks.
The calculation of the A/D Line involves tracking the number of advancing stocks versus declining stocks over a specific period, such as daily or weekly intervals. When more stocks are advancing than declining, the line tends to rise, signaling strong participation and momentum across various sectors. Conversely, if more stocks are declining than advancing, it indicates waning participation and potential weakness in market sentiment.
Understanding this indicator helps investors identify underlying trends that may not be immediately apparent from price movements alone. For example, during bullish phases where major indices hit new highs but fewer individual stocks participate in these gains (a phenomenon known as divergence), traders can use the A/D Line to detect early signs of potential reversals.
How Does The Advance-Decline Line Work?
The core principle behind the A/D Line is straightforward: it measures market breadth by comparing how many securities are moving higher versus those moving lower within an index or sector. Its calculation typically involves:
- Counting advancing stocks—those closing higher than their previous close.
- Counting declining stocks—those closing lower than their previous close.
- Subtracting declines from advances for each period.
- Cumulatively adding these differences over time to generate a line chart.
This cumulative approach smooths out short-term fluctuations and reveals longer-term trends in market participation. When plotted alongside price charts of major indices like S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), analysts can observe how breadth correlates with overall market direction.
Interpreting changes in this line offers valuable insights:
Rising A/D Line: Indicates increasing participation across multiple sectors; generally considered bullish.
Falling A/D Line: Suggests weakening participation; often signals bearish sentiment.
Furthermore, divergences between price action and the A/D Line serve as early warning signals for potential trend reversals—a rising index accompanied by a falling A/D line could warn of underlying weakness despite apparent strength.
Significance Of The Advance–Decline Indicator
Market breadth indicators like the A/D Line provide context beyond simple index levels—they reveal how widespread buying or selling activity truly is. This broader perspective helps differentiate between sustainable rallies and those driven by limited segments of markets.
For example:
- Bullish Market Confirmation: When both prices and breadth indicators like the A/D Lines are rising together, it confirms broad investor confidence across sectors.
- Bearish Divergence Signals: If stock prices reach new highs while Breadth declines (A/D falls), it suggests that only select large-cap companies might be driving gains while most others lag behind—a warning sign for potential correction.
- Trend Validation: Consistent movement in both price charts and Breadth indicators strengthens confidence in ongoing trends; discrepancies warrant caution.
Investors also use divergence analysis with other technical tools such as moving averages or Relative Strength Index (RSI) to refine their outlooks further—adding layers of confirmation before making trading decisions.
Recent Trends And Sector-Specific Insights
In recent years, especially amid volatile economic conditions caused by geopolitical tensions and technological shifts, analyzing sector-specific advance-decline data has gained importance. For instance:
In technology sectors like Chinese chipmakers affected by international restrictions on advanced manufacturing technology—which led to share declines—the corresponding sector-specific A/D Lines reflected reduced participation levels[1].
During periods when certain industries face headwinds due to regulatory changes or supply chain disruptions—for example automotive manufacturers during semiconductor shortages—their sector's Breadth metrics tend to weaken even if broader indices remain resilient[2].
Such insights enable investors focusing on specific industries to gauge internal health beyond headline index movements effectively.
Using The Advance–Decline Data With Other Indicators
While valuable independently, combining The A / D lines with other technical tools enhances predictive accuracy:
• Moving averages help smooth out short-term noise
• Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicates overbought/oversold conditions
• Volume analysis confirms conviction behind moves
For instance: If an index hits new highs but its associated Breadth indicator shows divergence—declining while prices rise—it could signal weakening momentum ahead[3]. Similarly, cross-referencing with volume spikes can validate whether broad participation supports current trends.
Practical Applications:
Detecting early signs of trend reversals
Confirming strength during sustained rallies
Identifying sector rotation patterns
Managing risk through divergence signals
By integrating these tools into your analysis process — especially considering recent developments — you gain deeper insights into underlying market dynamics rather than relying solely on headline figures.
Risks And Limitations Of Relying On The Advance–Decline Indicator
Despite its usefulness, there are limitations worth noting:
Lagging Nature: Like most technical indicators based on historical data—they reflect past activity rather than predicting future moves directly.
Market Anomalies: During highly volatile periods such as flash crashes or sudden geopolitical shocks—the relationship between Breadth measures and actual price action may become distorted temporarily[4].
Sector Biases & Market Cap Influence: Large-cap dominance can skew results; some sectors might show strong internal health even if overall breadth appears weak due to smaller companies' struggles.
Divergences Can Persist Longer Than Expected: Divergences between Price & Breadth do not always lead immediately to reversals—they require careful interpretation within broader context.
Best Practices:
Use alongside other technical analyses
Monitor multiple timeframes for confirmation
Be cautious during extreme volatility
Understanding these limitations ensures better risk management when incorporating advance-decline data into your trading strategy.
How To Incorporate The Advanced Decline Data Into Your Investment Strategy
To leverage what you learn from analyzing The Advance–Decline Lines effectively:
- Combine with Price Action Analysis: Look at whether rising/breakout markets align with positive breadth signals
2.Integrate With Sector Analysis: Use sector-specific Breadth data for targeted investments
3.Monitor Divergences Regularly: Watch for discrepancies indicating possible trend shifts
4.Use Multiple Timeframes: Short-term divergences may differ from long-term trends
5.Stay Updated On Market News & Economic Indicators: External factors influence both broad markets and individual sectors
By systematically applying these principles within your investment framework—and staying informed about recent developments—you improve decision-making quality significantly.
Final Thoughts
The advance-decline line remains one of the most insightful tools available for assessing overall market health through its focus on breadth rather than just prices alone.[5] Its ability to reveal hidden weaknesses via divergences makes it invaluable for seasoned traders seeking confirmation before entering positions—or alerting them about impending risks.[6] As markets continue evolving amid global uncertainties—from technological disruptions affecting industry fundamentals—to geopolitical tensions influencing investor sentiment—the importance of comprehensive analysis using tools like this cannot be overstated.
References
1. [Recent tech sector divergence reports]
2. [Impact assessments on Chinese chipmakers]
3. [Technical analysis case studies involving Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company]
4. [Market volatility studies related to divergence signals]
5. [Overview articles on Market Breadth Indicators]
6. [Expert commentary on advanced decline lines]


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 05:30
What is Advance–Decline Line (A/D Line)?
What Is the Advance-Decline Line (A/D Line)?
The Advance-Decline Line, often abbreviated as the A/D Line, is a vital technical indicator used by traders and investors to assess the overall health of the stock market. Unlike price-based indicators that focus solely on individual stocks or indices, the A/D Line provides insight into market breadth—how many stocks are participating in upward or downward movements. This makes it a powerful tool for understanding whether a rally is broad-based or driven by a few large-cap stocks.
The calculation of the A/D Line involves tracking the number of advancing stocks versus declining stocks over a specific period, such as daily or weekly intervals. When more stocks are advancing than declining, the line tends to rise, signaling strong participation and momentum across various sectors. Conversely, if more stocks are declining than advancing, it indicates waning participation and potential weakness in market sentiment.
Understanding this indicator helps investors identify underlying trends that may not be immediately apparent from price movements alone. For example, during bullish phases where major indices hit new highs but fewer individual stocks participate in these gains (a phenomenon known as divergence), traders can use the A/D Line to detect early signs of potential reversals.
How Does The Advance-Decline Line Work?
The core principle behind the A/D Line is straightforward: it measures market breadth by comparing how many securities are moving higher versus those moving lower within an index or sector. Its calculation typically involves:
- Counting advancing stocks—those closing higher than their previous close.
- Counting declining stocks—those closing lower than their previous close.
- Subtracting declines from advances for each period.
- Cumulatively adding these differences over time to generate a line chart.
This cumulative approach smooths out short-term fluctuations and reveals longer-term trends in market participation. When plotted alongside price charts of major indices like S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), analysts can observe how breadth correlates with overall market direction.
Interpreting changes in this line offers valuable insights:
Rising A/D Line: Indicates increasing participation across multiple sectors; generally considered bullish.
Falling A/D Line: Suggests weakening participation; often signals bearish sentiment.
Furthermore, divergences between price action and the A/D Line serve as early warning signals for potential trend reversals—a rising index accompanied by a falling A/D line could warn of underlying weakness despite apparent strength.
Significance Of The Advance–Decline Indicator
Market breadth indicators like the A/D Line provide context beyond simple index levels—they reveal how widespread buying or selling activity truly is. This broader perspective helps differentiate between sustainable rallies and those driven by limited segments of markets.
For example:
- Bullish Market Confirmation: When both prices and breadth indicators like the A/D Lines are rising together, it confirms broad investor confidence across sectors.
- Bearish Divergence Signals: If stock prices reach new highs while Breadth declines (A/D falls), it suggests that only select large-cap companies might be driving gains while most others lag behind—a warning sign for potential correction.
- Trend Validation: Consistent movement in both price charts and Breadth indicators strengthens confidence in ongoing trends; discrepancies warrant caution.
Investors also use divergence analysis with other technical tools such as moving averages or Relative Strength Index (RSI) to refine their outlooks further—adding layers of confirmation before making trading decisions.
Recent Trends And Sector-Specific Insights
In recent years, especially amid volatile economic conditions caused by geopolitical tensions and technological shifts, analyzing sector-specific advance-decline data has gained importance. For instance:
In technology sectors like Chinese chipmakers affected by international restrictions on advanced manufacturing technology—which led to share declines—the corresponding sector-specific A/D Lines reflected reduced participation levels[1].
During periods when certain industries face headwinds due to regulatory changes or supply chain disruptions—for example automotive manufacturers during semiconductor shortages—their sector's Breadth metrics tend to weaken even if broader indices remain resilient[2].
Such insights enable investors focusing on specific industries to gauge internal health beyond headline index movements effectively.
Using The Advance–Decline Data With Other Indicators
While valuable independently, combining The A / D lines with other technical tools enhances predictive accuracy:
• Moving averages help smooth out short-term noise
• Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicates overbought/oversold conditions
• Volume analysis confirms conviction behind moves
For instance: If an index hits new highs but its associated Breadth indicator shows divergence—declining while prices rise—it could signal weakening momentum ahead[3]. Similarly, cross-referencing with volume spikes can validate whether broad participation supports current trends.
Practical Applications:
Detecting early signs of trend reversals
Confirming strength during sustained rallies
Identifying sector rotation patterns
Managing risk through divergence signals
By integrating these tools into your analysis process — especially considering recent developments — you gain deeper insights into underlying market dynamics rather than relying solely on headline figures.
Risks And Limitations Of Relying On The Advance–Decline Indicator
Despite its usefulness, there are limitations worth noting:
Lagging Nature: Like most technical indicators based on historical data—they reflect past activity rather than predicting future moves directly.
Market Anomalies: During highly volatile periods such as flash crashes or sudden geopolitical shocks—the relationship between Breadth measures and actual price action may become distorted temporarily[4].
Sector Biases & Market Cap Influence: Large-cap dominance can skew results; some sectors might show strong internal health even if overall breadth appears weak due to smaller companies' struggles.
Divergences Can Persist Longer Than Expected: Divergences between Price & Breadth do not always lead immediately to reversals—they require careful interpretation within broader context.
Best Practices:
Use alongside other technical analyses
Monitor multiple timeframes for confirmation
Be cautious during extreme volatility
Understanding these limitations ensures better risk management when incorporating advance-decline data into your trading strategy.
How To Incorporate The Advanced Decline Data Into Your Investment Strategy
To leverage what you learn from analyzing The Advance–Decline Lines effectively:
- Combine with Price Action Analysis: Look at whether rising/breakout markets align with positive breadth signals
2.Integrate With Sector Analysis: Use sector-specific Breadth data for targeted investments
3.Monitor Divergences Regularly: Watch for discrepancies indicating possible trend shifts
4.Use Multiple Timeframes: Short-term divergences may differ from long-term trends
5.Stay Updated On Market News & Economic Indicators: External factors influence both broad markets and individual sectors
By systematically applying these principles within your investment framework—and staying informed about recent developments—you improve decision-making quality significantly.
Final Thoughts
The advance-decline line remains one of the most insightful tools available for assessing overall market health through its focus on breadth rather than just prices alone.[5] Its ability to reveal hidden weaknesses via divergences makes it invaluable for seasoned traders seeking confirmation before entering positions—or alerting them about impending risks.[6] As markets continue evolving amid global uncertainties—from technological disruptions affecting industry fundamentals—to geopolitical tensions influencing investor sentiment—the importance of comprehensive analysis using tools like this cannot be overstated.
References
1. [Recent tech sector divergence reports]
2. [Impact assessments on Chinese chipmakers]
3. [Technical analysis case studies involving Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company]
4. [Market volatility studies related to divergence signals]
5. [Overview articles on Market Breadth Indicators]
6. [Expert commentary on advanced decline lines]
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is TRON (TRX)?
TRON (TRX) is a blockchain-based platform designed to facilitate decentralized digital entertainment and content sharing. Launched in 2017 by Justin Sun, a prominent Chinese entrepreneur, TRON aims to revolutionize how digital content is created, distributed, and monetized. Unlike traditional centralized platforms that control content distribution and revenue sharing, TRON offers a decentralized alternative where creators can directly connect with their audiences.
The native cryptocurrency of the TRON network is TRX, which serves as the primary medium for transactions within the ecosystem. The platform leverages blockchain technology to ensure transparency, security, and censorship resistance—key features that appeal to both developers and users seeking more control over their digital assets.
Primary Focus of TRON: Decentralizing Digital Entertainment
At its core, TRON's main goal is to create a decentralized internet—sometimes referred to as Web3—that empowers content creators by removing intermediaries such as YouTube or Spotify. This decentralization allows artists, musicians, video producers, and other creators to monetize their work directly through smart contracts on the blockchain without relying on third-party platforms that often take significant commissions.
This focus aligns with broader trends in the cryptocurrency space advocating for decentralization—reducing reliance on centralized authorities like governments or corporations—and promoting user sovereignty over data and digital assets. By enabling direct peer-to-peer transactions and transparent royalty payments via smart contracts, TRON seeks to foster an ecosystem where creativity can thrive without censorship or unfair revenue cuts.
How Does Blockchain Technology Support TRON’s Mission?
TRON utilizes advanced blockchain technology tailored for high scalability and efficiency. Its network supports storing digital content securely while facilitating rapid transaction processing—a critical feature given the volume of data involved in entertainment applications.
One notable aspect of TRON’s architecture is its compatibility with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This means developers familiar with Ethereum can easily deploy existing smart contracts or dApps (decentralized applications) onto the TRON network without extensive modifications. Such compatibility accelerates innovation within its ecosystem by attracting developers from other blockchain communities.
Furthermore, features like sharding—a method of partitioning data across multiple nodes—and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus algorithms enhance scalability while maintaining security standards necessary for handling large-scale operations typical in entertainment platforms.
Key Features That Define TRON
- Decentralization: Removing middlemen ensures fairer revenue distribution for creators.
- High Scalability: Capable of processing thousands of transactions per second due to technological optimizations.
- Smart Contract Support: Enables complex programmable agreements essential for monetization models.
- Partnerships & Ecosystem Growth: Collaborations with companies like BitTorrent expand its reach into peer-to-peer file sharing.
- User Control & Censorship Resistance: Content hosted on a decentralized network reduces risks associated with censorship or shutdowns by authorities or corporations.
These features position TRON as an attractive platform not only for entertainment but also for developing diverse decentralized applications across various industries beyond media sharing.
Recent Developments Enhancing Its Ecosystem
Since its inception, several strategic initiatives have strengthened what TRON offers:
BitTorrent Acquisition (2018)
Acquiring BitTorrent—the popular peer-to-peer file-sharing protocol—was pivotal in integrating file-sharing capabilities into the broader Tron ecosystem. This move aimed at creating a seamless environment where users could share large files efficiently while earning rewards through tokens integrated into this system.MainNet Launch (2018)
Transitioning from testnet environments to MainNet marked a significant milestone allowing real-world usage at scale. It provided stability needed for widespread adoption among developers and consumers alike.Tron Virtual Machine (TVM) Introduction (2019)
The TVM supports deploying smart contracts compatible with EVM standards but optimized specifically for Tron’s infrastructure—making it easier for Ethereum-based dApps developers to migrate or build new projects within Tron’s ecosystem.Tron DAO Reserve System (2022)
To address price volatility issues common among cryptocurrencies like TRX itself—a reserve system was introduced using fiat currencies alongside cryptocurrencies aimed at stabilizing token value during market fluctuations.
These developments demonstrate ongoing efforts toward building a robust infrastructure capable of supporting diverse use cases—from entertainment streaming services to enterprise-level solutions—all rooted in decentralization principles.
Challenges Facing Tron's Ecosystem
Despite impressive progressions over recent years; however,
- Regulatory hurdles remain significant since governments worldwide are scrutinizing crypto projects more closely regarding compliance issues related especially to securities laws,
- Competition from other scalable blockchains such as Polkadot or Solana poses challenges requiring continuous innovation,
- Security concerns are paramount; any vulnerabilities could undermine trustworthiness leading users away from adopting new functionalities confidently,
Addressing these challenges requires proactive engagement with regulators alongside ongoing technical improvements ensuring safety measures against potential breaches.
Summary
TRX stands out as an innovative project dedicated primarily toward transforming how digital entertainment operates through decentralization powered by blockchain technology. Its strategic partnerships—including BitTorrent—and technological advancements position it well within this rapidly evolving industry landscape; however long-term success depends heavily on navigating regulatory environments effectively while maintaining high-security standards amidst fierce competition globally.
Keywords:
Blockchain technology | Decentralized internet | Smart contracts | Cryptocurrency | Digital content monetization | Peer-to-peer sharing | Scalability solutions | Cryptocurrency regulation


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-15 00:29
What is TRON (TRX) and what is its primary focus?
What Is TRON (TRX)?
TRON (TRX) is a blockchain-based platform designed to facilitate decentralized digital entertainment and content sharing. Launched in 2017 by Justin Sun, a prominent Chinese entrepreneur, TRON aims to revolutionize how digital content is created, distributed, and monetized. Unlike traditional centralized platforms that control content distribution and revenue sharing, TRON offers a decentralized alternative where creators can directly connect with their audiences.
The native cryptocurrency of the TRON network is TRX, which serves as the primary medium for transactions within the ecosystem. The platform leverages blockchain technology to ensure transparency, security, and censorship resistance—key features that appeal to both developers and users seeking more control over their digital assets.
Primary Focus of TRON: Decentralizing Digital Entertainment
At its core, TRON's main goal is to create a decentralized internet—sometimes referred to as Web3—that empowers content creators by removing intermediaries such as YouTube or Spotify. This decentralization allows artists, musicians, video producers, and other creators to monetize their work directly through smart contracts on the blockchain without relying on third-party platforms that often take significant commissions.
This focus aligns with broader trends in the cryptocurrency space advocating for decentralization—reducing reliance on centralized authorities like governments or corporations—and promoting user sovereignty over data and digital assets. By enabling direct peer-to-peer transactions and transparent royalty payments via smart contracts, TRON seeks to foster an ecosystem where creativity can thrive without censorship or unfair revenue cuts.
How Does Blockchain Technology Support TRON’s Mission?
TRON utilizes advanced blockchain technology tailored for high scalability and efficiency. Its network supports storing digital content securely while facilitating rapid transaction processing—a critical feature given the volume of data involved in entertainment applications.
One notable aspect of TRON’s architecture is its compatibility with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This means developers familiar with Ethereum can easily deploy existing smart contracts or dApps (decentralized applications) onto the TRON network without extensive modifications. Such compatibility accelerates innovation within its ecosystem by attracting developers from other blockchain communities.
Furthermore, features like sharding—a method of partitioning data across multiple nodes—and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus algorithms enhance scalability while maintaining security standards necessary for handling large-scale operations typical in entertainment platforms.
Key Features That Define TRON
- Decentralization: Removing middlemen ensures fairer revenue distribution for creators.
- High Scalability: Capable of processing thousands of transactions per second due to technological optimizations.
- Smart Contract Support: Enables complex programmable agreements essential for monetization models.
- Partnerships & Ecosystem Growth: Collaborations with companies like BitTorrent expand its reach into peer-to-peer file sharing.
- User Control & Censorship Resistance: Content hosted on a decentralized network reduces risks associated with censorship or shutdowns by authorities or corporations.
These features position TRON as an attractive platform not only for entertainment but also for developing diverse decentralized applications across various industries beyond media sharing.
Recent Developments Enhancing Its Ecosystem
Since its inception, several strategic initiatives have strengthened what TRON offers:
BitTorrent Acquisition (2018)
Acquiring BitTorrent—the popular peer-to-peer file-sharing protocol—was pivotal in integrating file-sharing capabilities into the broader Tron ecosystem. This move aimed at creating a seamless environment where users could share large files efficiently while earning rewards through tokens integrated into this system.MainNet Launch (2018)
Transitioning from testnet environments to MainNet marked a significant milestone allowing real-world usage at scale. It provided stability needed for widespread adoption among developers and consumers alike.Tron Virtual Machine (TVM) Introduction (2019)
The TVM supports deploying smart contracts compatible with EVM standards but optimized specifically for Tron’s infrastructure—making it easier for Ethereum-based dApps developers to migrate or build new projects within Tron’s ecosystem.Tron DAO Reserve System (2022)
To address price volatility issues common among cryptocurrencies like TRX itself—a reserve system was introduced using fiat currencies alongside cryptocurrencies aimed at stabilizing token value during market fluctuations.
These developments demonstrate ongoing efforts toward building a robust infrastructure capable of supporting diverse use cases—from entertainment streaming services to enterprise-level solutions—all rooted in decentralization principles.
Challenges Facing Tron's Ecosystem
Despite impressive progressions over recent years; however,
- Regulatory hurdles remain significant since governments worldwide are scrutinizing crypto projects more closely regarding compliance issues related especially to securities laws,
- Competition from other scalable blockchains such as Polkadot or Solana poses challenges requiring continuous innovation,
- Security concerns are paramount; any vulnerabilities could undermine trustworthiness leading users away from adopting new functionalities confidently,
Addressing these challenges requires proactive engagement with regulators alongside ongoing technical improvements ensuring safety measures against potential breaches.
Summary
TRX stands out as an innovative project dedicated primarily toward transforming how digital entertainment operates through decentralization powered by blockchain technology. Its strategic partnerships—including BitTorrent—and technological advancements position it well within this rapidly evolving industry landscape; however long-term success depends heavily on navigating regulatory environments effectively while maintaining high-security standards amidst fierce competition globally.
Keywords:
Blockchain technology | Decentralized internet | Smart contracts | Cryptocurrency | Digital content monetization | Peer-to-peer sharing | Scalability solutions | Cryptocurrency regulation
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Are Smart Contract Upgrades Managed for Tether USDt (USDT)?
Tether USDt (USDT) is one of the most widely used stablecoins in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, providing a digital dollar equivalent that facilitates trading, remittances, and hedging. As a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, its stability depends heavily on secure and reliable smart contracts operating across multiple blockchain platforms such as Ethereum, Tron, and Binance Smart Chain. Understanding how these smart contracts are governed—particularly regarding upgrades—is essential for users seeking transparency and security in their digital assets.
Centralized Governance Model of Tether USDt
Unlike many decentralized projects that rely on community voting or autonomous organizations to manage protocol changes, Tether Limited maintains centralized control over its USDT smart contracts. This means that decisions related to contract updates—including bug fixes, security enhancements, or performance improvements—are made solely by Tether Limited’s team. This centralized approach allows for rapid decision-making when urgent issues arise but also introduces certain risks associated with lack of community oversight.
Tether Limited’s authority extends to implementing modifications directly into the smart contract code deployed on various blockchains. These modifications can include deploying new versions or patches designed to improve functionality or address vulnerabilities. While this model streamlines operations and ensures quick responses during emergencies, it raises questions about transparency and potential conflicts of interest.
Transparency Measures and Audits
To mitigate concerns about centralization risks and maintain user trust, Tether Limited has adopted several transparency measures. The company conducts regular third-party audits aimed at verifying reserves backing USDT tokens—an essential aspect given regulatory scrutiny around stablecoins’ backing mechanisms. These audits help reassure users that each USDT token is indeed backed by an equivalent amount of fiat currency held in reserve.
Additionally, periodic updates regarding smart contract changes are published publicly on Tether’s official website or communication channels. Although these disclosures do not involve community voting processes typical in decentralized governance models, they serve as vital information sources for stakeholders monitoring potential upgrades or modifications affecting their holdings.
Recent Developments in Smart Contract Management
2023 Smart Contract Upgrade on Ethereum
In 2023, Tether announced a major upgrade targeting its Ethereum-based USDT smart contracts aimed at bolstering security features while optimizing transaction efficiency. The upgrade involved deploying new security protocols designed to prevent exploits and reduce transaction costs—a critical factor considering Ethereum's network congestion issues at times.
This upgrade was executed through a carefully planned process involving deploying new contract versions rather than altering existing ones directly—a best practice known as "upgradeability." Such practices allow developers to introduce improvements without compromising existing token balances or disrupting ongoing transactions.
2024 Blockchain Migration Plans
Looking ahead into early 2024, Tether revealed plans to migrate some USDT tokens from Ethereum onto alternative blockchain platforms like Tron or Binance Smart Chain (BSC). The primary motivation behind this move is reducing transaction fees while enhancing scalability—a common challenge faced by high-volume stablecoins operating on congested networks like Ethereum.
However, migrating tokens between blockchains involves complex technical procedures such as token wrapping or bridging mechanisms which require meticulous planning to avoid market disruptions or loss of funds during transition periods. Ensuring transparent communication with users throughout this process remains paramount for maintaining confidence among holders.
Risks Associated with Centralized Control Over Upgrades
While centralized governance enables swift action during emergencies—such as fixing critical bugs—it also introduces notable risks:
Regulatory Scrutiny: Authorities may scrutinize the lack of decentralization within governance structures; regulators often favor transparent processes involving stakeholder participation.
Market Impact: Major upgrades can influence market perceptions; unexpected changes might cause temporary volatility if not communicated properly.
Security Concerns: Concentrated control could potentially lead to malicious actions if safeguards are insufficient; hence rigorous audits become even more crucial under centralized models.
Furthermore, critics argue that absence of community involvement diminishes overall trustworthiness since stakeholders have limited say over decisions impacting their assets’ stability.
Community Perspectives & Future Considerations
The debate around governance models continues within the crypto space: Should stablecoins like USDT adopt more decentralized approaches? Many advocates believe increased stakeholder participation could enhance transparency and resilience against malicious attacks—or regulatory crackdowns—by distributing decision-making power across multiple parties instead of relying solely on corporate entities like Tether Limited.
As regulatory environments evolve globally—with agencies paying closer attention toward issuer accountability—the future management strategies for stablecoin upgrades may shift toward hybrid models combining centralized oversight with elements of decentralization such as multi-signature wallets or governance councils involving trusted industry players.
Key Takeaways:
- Centralized Control: Managed primarily by Tether Limited who oversees all smart contract updates.
- Upgrade Processes: Typically involve deploying new contract versions rather than modifying existing ones directly.
- Transparency Efforts: Include regular audits and public disclosures about changes made.
- Recent Initiatives: Focused on improving security via upgrades (2023) and expanding blockchain compatibility through migration plans (2024).
- Risks & Challenges: Include regulatory scrutiny due to centralization concerns alongside market volatility from major protocol changes.
Understanding how these mechanisms operate helps investors assess risk levels associated with holding USDT—and highlights ongoing discussions about balancing efficiency with transparency within crypto asset management frameworks.


Lo
2025-05-14 20:11
What governance mechanisms control smart contract upgrades for Tether USDt (USDT)?
How Are Smart Contract Upgrades Managed for Tether USDt (USDT)?
Tether USDt (USDT) is one of the most widely used stablecoins in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, providing a digital dollar equivalent that facilitates trading, remittances, and hedging. As a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, its stability depends heavily on secure and reliable smart contracts operating across multiple blockchain platforms such as Ethereum, Tron, and Binance Smart Chain. Understanding how these smart contracts are governed—particularly regarding upgrades—is essential for users seeking transparency and security in their digital assets.
Centralized Governance Model of Tether USDt
Unlike many decentralized projects that rely on community voting or autonomous organizations to manage protocol changes, Tether Limited maintains centralized control over its USDT smart contracts. This means that decisions related to contract updates—including bug fixes, security enhancements, or performance improvements—are made solely by Tether Limited’s team. This centralized approach allows for rapid decision-making when urgent issues arise but also introduces certain risks associated with lack of community oversight.
Tether Limited’s authority extends to implementing modifications directly into the smart contract code deployed on various blockchains. These modifications can include deploying new versions or patches designed to improve functionality or address vulnerabilities. While this model streamlines operations and ensures quick responses during emergencies, it raises questions about transparency and potential conflicts of interest.
Transparency Measures and Audits
To mitigate concerns about centralization risks and maintain user trust, Tether Limited has adopted several transparency measures. The company conducts regular third-party audits aimed at verifying reserves backing USDT tokens—an essential aspect given regulatory scrutiny around stablecoins’ backing mechanisms. These audits help reassure users that each USDT token is indeed backed by an equivalent amount of fiat currency held in reserve.
Additionally, periodic updates regarding smart contract changes are published publicly on Tether’s official website or communication channels. Although these disclosures do not involve community voting processes typical in decentralized governance models, they serve as vital information sources for stakeholders monitoring potential upgrades or modifications affecting their holdings.
Recent Developments in Smart Contract Management
2023 Smart Contract Upgrade on Ethereum
In 2023, Tether announced a major upgrade targeting its Ethereum-based USDT smart contracts aimed at bolstering security features while optimizing transaction efficiency. The upgrade involved deploying new security protocols designed to prevent exploits and reduce transaction costs—a critical factor considering Ethereum's network congestion issues at times.
This upgrade was executed through a carefully planned process involving deploying new contract versions rather than altering existing ones directly—a best practice known as "upgradeability." Such practices allow developers to introduce improvements without compromising existing token balances or disrupting ongoing transactions.
2024 Blockchain Migration Plans
Looking ahead into early 2024, Tether revealed plans to migrate some USDT tokens from Ethereum onto alternative blockchain platforms like Tron or Binance Smart Chain (BSC). The primary motivation behind this move is reducing transaction fees while enhancing scalability—a common challenge faced by high-volume stablecoins operating on congested networks like Ethereum.
However, migrating tokens between blockchains involves complex technical procedures such as token wrapping or bridging mechanisms which require meticulous planning to avoid market disruptions or loss of funds during transition periods. Ensuring transparent communication with users throughout this process remains paramount for maintaining confidence among holders.
Risks Associated with Centralized Control Over Upgrades
While centralized governance enables swift action during emergencies—such as fixing critical bugs—it also introduces notable risks:
Regulatory Scrutiny: Authorities may scrutinize the lack of decentralization within governance structures; regulators often favor transparent processes involving stakeholder participation.
Market Impact: Major upgrades can influence market perceptions; unexpected changes might cause temporary volatility if not communicated properly.
Security Concerns: Concentrated control could potentially lead to malicious actions if safeguards are insufficient; hence rigorous audits become even more crucial under centralized models.
Furthermore, critics argue that absence of community involvement diminishes overall trustworthiness since stakeholders have limited say over decisions impacting their assets’ stability.
Community Perspectives & Future Considerations
The debate around governance models continues within the crypto space: Should stablecoins like USDT adopt more decentralized approaches? Many advocates believe increased stakeholder participation could enhance transparency and resilience against malicious attacks—or regulatory crackdowns—by distributing decision-making power across multiple parties instead of relying solely on corporate entities like Tether Limited.
As regulatory environments evolve globally—with agencies paying closer attention toward issuer accountability—the future management strategies for stablecoin upgrades may shift toward hybrid models combining centralized oversight with elements of decentralization such as multi-signature wallets or governance councils involving trusted industry players.
Key Takeaways:
- Centralized Control: Managed primarily by Tether Limited who oversees all smart contract updates.
- Upgrade Processes: Typically involve deploying new contract versions rather than modifying existing ones directly.
- Transparency Efforts: Include regular audits and public disclosures about changes made.
- Recent Initiatives: Focused on improving security via upgrades (2023) and expanding blockchain compatibility through migration plans (2024).
- Risks & Challenges: Include regulatory scrutiny due to centralization concerns alongside market volatility from major protocol changes.
Understanding how these mechanisms operate helps investors assess risk levels associated with holding USDT—and highlights ongoing discussions about balancing efficiency with transparency within crypto asset management frameworks.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Copulas Model Dependency Structures Between Asset Returns?
Understanding how different assets move in relation to each other is fundamental in financial modeling, risk management, and portfolio optimization. Traditional correlation measures often fall short when capturing complex dependencies, especially during extreme market events. This is where copulas come into play—powerful mathematical tools that provide a more nuanced view of the dependency structures between asset returns.
What Are Copulas and Why Are They Important in Finance?
Copulas are functions that link univariate marginal distributions to form a multivariate joint distribution. Unlike simple correlation coefficients, copulas allow analysts to model complex dependencies beyond linear relationships. They effectively separate the individual behavior of each asset (marginal distributions) from their joint dependence structure, offering flexibility and precision.
In finance, this separation is crucial because assets rarely follow normal distributions or exhibit purely linear correlations. Market crashes or booms often involve tail dependencies—simultaneous extreme movements—that traditional models may underestimate or overlook. Copulas enable capturing these tail dependencies accurately, making them invaluable for risk assessment and derivative pricing.
Types of Copulas Used in Financial Modeling
Different types of copulas are suited for various dependency patterns observed in financial data:
- Gaussian (Normal) Copula: Assumes symmetric dependence similar to the Gaussian distribution; widely used but limited in modeling tail dependence.
- Clayton Copula: Captures lower tail dependence well; useful when joint extreme lows are common.
- Gumbel Copula: Focuses on upper tail dependence; suitable for modeling joint extreme highs.
- Frank Copula: Handles moderate dependencies without strong tail emphasis; flexible across various scenarios.
Choosing the appropriate copula depends on understanding the specific dependency characteristics of your assets or portfolio.
How Do Copulas Model Asset Return Dependencies?
Traditional methods like Pearson’s correlation measure linear relationships but fail during periods of market stress when asset returns tend to move together more strongly than usual—a phenomenon known as tail dependence.
Copulas address this by modeling the entire distributional relationship between assets rather than just their average co-movement. For example:
- By applying a Gumbel copula, analysts can quantify how likely two stocks are to experience simultaneous large gains.
- Using Clayton copulas helps assess risks associated with concurrent downturns during crises.
This detailed depiction allows investors and risk managers to better understand potential vulnerabilities within portfolios under different market conditions.
Recent Advances Enhancing Dependency Modeling
The field has seen significant progress through integrating machine learning techniques with traditional copula theory:
- Machine Learning Integration: Algorithms now help select optimal copula types based on data patterns and improve parameter estimation accuracy.
- Non-Parametric Methods: These approaches do not assume specific distribution forms, increasing model robustness especially with high-dimensional data or non-standard distributions common in real-world markets.
- Quantile Regression Coupled with Copulas: Focuses on modeling specific quantiles (e.g., worst-case losses), which enhances risk management strategies by providing insights into potential extreme outcomes.
These innovations have expanded the applicability of copula models across diverse financial contexts—from cryptocurrencies’ volatile markets to systemic risk analysis involving interconnected financial institutions.
Practical Applications of Copulas in Finance
Copula-based models serve multiple purposes within finance:
Risk Management
By accurately capturing dependency structures—including rare but impactful events—copulas improve Value-at-Risk (VaR) calculations and stress testing procedures essential for regulatory compliance and internal controls.
Portfolio Optimization
Investors leverage copolas' ability to model complex relationships among assets for constructing diversified portfolios that minimize downside risks while maximizing returns under various market scenarios.
Derivative Pricing
Pricing multi-asset options benefits from detailed dependency modeling provided by copulsas since payoffs depend heavily on how underlying assets behave jointly during different states of the world.
Systemic Risk Analysis
Regulators use these models to identify vulnerabilities within interconnected financial systems by analyzing how distress can propagate through dependent institutions under adverse conditions.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Using Copolas
Despite their advantages, deploying copola models involves certain challenges:
Data Quality & Availability: Reliable high-frequency data is necessary for precise parameter estimation; poor quality can lead to misleading results.
Model Selection & Complexity: Choosing an inappropriate type or misestimating parameters may result in inaccurate depencency assessments—potentially leading decision-makers astray.
Regulatory Considerations: As these models become more sophisticated, regulators need frameworks ensuring transparency and proper validation standards are met before widespread adoption occurs.
Cybersecurity Concerns: The integration of machine learning algorithms increases vulnerability points where cyber threats could compromise sensitive financial information.
The Future Role Of Covariance Structures In Financial Markets
As technological advances continue shaping finance—with increased computational power and richer datasets—the role of advanced dependency models like those based on coplas will grow even more prominent. Their ability to adaptively capture evolving relationships makes them vital tools amid increasingly complex markets influenced by ESG factors, geopolitical shifts, cryptocurrencies—and beyond.
Final Thoughts
Modeling dependency structures between asset returns using coplas offers a comprehensive approach far superior to traditional correlation metrics alone. By embracing these tools—especially as recent innovations make them more accessible—they empower investors and risk managers alike with deeper insights into potential vulnerabilities—and opportunities—in dynamic financial landscapes.


kai
2025-05-14 17:23
How can copulas model dependency structures between asset returns?
How Do Copulas Model Dependency Structures Between Asset Returns?
Understanding how different assets move in relation to each other is fundamental in financial modeling, risk management, and portfolio optimization. Traditional correlation measures often fall short when capturing complex dependencies, especially during extreme market events. This is where copulas come into play—powerful mathematical tools that provide a more nuanced view of the dependency structures between asset returns.
What Are Copulas and Why Are They Important in Finance?
Copulas are functions that link univariate marginal distributions to form a multivariate joint distribution. Unlike simple correlation coefficients, copulas allow analysts to model complex dependencies beyond linear relationships. They effectively separate the individual behavior of each asset (marginal distributions) from their joint dependence structure, offering flexibility and precision.
In finance, this separation is crucial because assets rarely follow normal distributions or exhibit purely linear correlations. Market crashes or booms often involve tail dependencies—simultaneous extreme movements—that traditional models may underestimate or overlook. Copulas enable capturing these tail dependencies accurately, making them invaluable for risk assessment and derivative pricing.
Types of Copulas Used in Financial Modeling
Different types of copulas are suited for various dependency patterns observed in financial data:
- Gaussian (Normal) Copula: Assumes symmetric dependence similar to the Gaussian distribution; widely used but limited in modeling tail dependence.
- Clayton Copula: Captures lower tail dependence well; useful when joint extreme lows are common.
- Gumbel Copula: Focuses on upper tail dependence; suitable for modeling joint extreme highs.
- Frank Copula: Handles moderate dependencies without strong tail emphasis; flexible across various scenarios.
Choosing the appropriate copula depends on understanding the specific dependency characteristics of your assets or portfolio.
How Do Copulas Model Asset Return Dependencies?
Traditional methods like Pearson’s correlation measure linear relationships but fail during periods of market stress when asset returns tend to move together more strongly than usual—a phenomenon known as tail dependence.
Copulas address this by modeling the entire distributional relationship between assets rather than just their average co-movement. For example:
- By applying a Gumbel copula, analysts can quantify how likely two stocks are to experience simultaneous large gains.
- Using Clayton copulas helps assess risks associated with concurrent downturns during crises.
This detailed depiction allows investors and risk managers to better understand potential vulnerabilities within portfolios under different market conditions.
Recent Advances Enhancing Dependency Modeling
The field has seen significant progress through integrating machine learning techniques with traditional copula theory:
- Machine Learning Integration: Algorithms now help select optimal copula types based on data patterns and improve parameter estimation accuracy.
- Non-Parametric Methods: These approaches do not assume specific distribution forms, increasing model robustness especially with high-dimensional data or non-standard distributions common in real-world markets.
- Quantile Regression Coupled with Copulas: Focuses on modeling specific quantiles (e.g., worst-case losses), which enhances risk management strategies by providing insights into potential extreme outcomes.
These innovations have expanded the applicability of copula models across diverse financial contexts—from cryptocurrencies’ volatile markets to systemic risk analysis involving interconnected financial institutions.
Practical Applications of Copulas in Finance
Copula-based models serve multiple purposes within finance:
Risk Management
By accurately capturing dependency structures—including rare but impactful events—copulas improve Value-at-Risk (VaR) calculations and stress testing procedures essential for regulatory compliance and internal controls.
Portfolio Optimization
Investors leverage copolas' ability to model complex relationships among assets for constructing diversified portfolios that minimize downside risks while maximizing returns under various market scenarios.
Derivative Pricing
Pricing multi-asset options benefits from detailed dependency modeling provided by copulsas since payoffs depend heavily on how underlying assets behave jointly during different states of the world.
Systemic Risk Analysis
Regulators use these models to identify vulnerabilities within interconnected financial systems by analyzing how distress can propagate through dependent institutions under adverse conditions.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Using Copolas
Despite their advantages, deploying copola models involves certain challenges:
Data Quality & Availability: Reliable high-frequency data is necessary for precise parameter estimation; poor quality can lead to misleading results.
Model Selection & Complexity: Choosing an inappropriate type or misestimating parameters may result in inaccurate depencency assessments—potentially leading decision-makers astray.
Regulatory Considerations: As these models become more sophisticated, regulators need frameworks ensuring transparency and proper validation standards are met before widespread adoption occurs.
Cybersecurity Concerns: The integration of machine learning algorithms increases vulnerability points where cyber threats could compromise sensitive financial information.
The Future Role Of Covariance Structures In Financial Markets
As technological advances continue shaping finance—with increased computational power and richer datasets—the role of advanced dependency models like those based on coplas will grow even more prominent. Their ability to adaptively capture evolving relationships makes them vital tools amid increasingly complex markets influenced by ESG factors, geopolitical shifts, cryptocurrencies—and beyond.
Final Thoughts
Modeling dependency structures between asset returns using coplas offers a comprehensive approach far superior to traditional correlation metrics alone. By embracing these tools—especially as recent innovations make them more accessible—they empower investors and risk managers alike with deeper insights into potential vulnerabilities—and opportunities—in dynamic financial landscapes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does the Hilbert Transform Detect Cycles in Price Series?
Understanding how financial markets, especially cryptocurrencies, exhibit recurring patterns or cycles is crucial for traders and analysts aiming to make informed decisions. One advanced mathematical tool that has gained prominence in this area is the Hilbert Transform. This technique allows analysts to identify underlying cyclical behaviors within price data that might not be visible through traditional methods. In this article, we explore how the Hilbert Transform works in detecting these cycles and why it has become a valuable asset in modern financial analysis.
What Is the Hilbert Transform?
The Hilbert Transform is a fundamental concept from signal processing, designed to analyze signals by transforming real-valued functions into complex representations. Essentially, it takes a real-valued time series—such as cryptocurrency prices—and produces an analytic signal comprising both amplitude and phase information. Mathematically, it involves an integral operation that shifts the phase of each frequency component of the original signal by 90 degrees.
This transformation results in a complex function where the original data forms the real part, and its transformed counterpart forms the imaginary part. The combined analytic signal provides richer information about oscillations within data sets—specifically their instantaneous frequency and amplitude—which are key indicators of cyclical behavior.
Applying the Hilbert Transform to Financial Data
In financial markets like cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum), price series often contain hidden periodicities or cycles driven by various factors such as investor sentiment, macroeconomic events, or technological developments. Traditional tools like moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index) can sometimes miss these subtle patterns because they focus on smoothing or momentum rather than frequency analysis.
By applying the Hilbert Transform to price data:
- Instantaneous Frequency: It reveals how quickly prices are oscillating at any given moment.
- Instantaneous Amplitude: It indicates how strong these oscillations are at specific points in time.
These two components help traders understand whether a market is entering a bullish or bearish phase based on cycle peaks and troughs detected through phase shifts derived from analytical signals.
How Does It Detect Cycles?
The core idea behind cycle detection using the Hilbert Transform lies in analyzing changes in phase angles over time. Once you obtain an analytic signal from your price series:
- Calculate its phase angle (( \phi(t) )), which describes where you are within a cycle.
- Derive instantaneous frequency (( \omega(t) = d\phi(t)/dt )) — essentially measuring how fast phases change.
- Identify recurring patterns when phases repeat or align over specific periods.
When certain frequencies persist across different segments of data—indicating regular oscillations—the method highlights potential cyclical behavior within market prices.
For example:
- A rising instantaneous frequency may suggest increasing volatility.
- Repeating phase patterns can point toward predictable cycles that traders could exploit for timing entries/exits.
Why Is Cycle Detection Important for Cryptocurrency Markets?
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility and complex dynamics compared to traditional assets like stocks or bonds. Identifying underlying cycles helps traders anticipate potential turning points before they occur—a significant advantage given crypto's rapid movements.
Using techniques like the Hilbert Transform enables:
- Better understanding of short-term versus long-term trends
- Detection of emerging bullish/bearish phases
- Validation of other technical indicators with more precise timing
Moreover, recent advancements have integrated machine learning with signal processing outputs from methods like this one—further improving accuracy and predictive power when analyzing noisy crypto data streams.
Limitations & Challenges
Despite its strengths, applying The Hilbert Transform isn't without challenges:
Noise Sensitivity: Crypto markets generate noisy signals; excessive noise can distort phase calculations leading to false cycle detections.
Overfitting Risks: Without proper validation techniques such as cross-validation on historical datasets, there's potential for overfitting models based on spurious signals.
Complex Interpretation: Understanding instantaneous frequency/amplitude requires advanced mathematical knowledge; misinterpretation could lead traders astray if not handled carefully.
To mitigate these issues:
- Use filtering techniques prior to applying transformations
- Combine results with other technical analysis tools
- Validate findings across multiple datasets
Recent Trends & Research Developments
Since around 2015–2016 when applications began gaining traction among quantitative analysts—and particularly since 2018–2019 with increased interest specifically targeting cryptocurrencies—the use of spectral analysis methods has expanded significantly.
Recent research published between 2022 and 2023 emphasizes:
- Enhanced algorithms integrating machine learning with spectral features derived via Fourier-based methods alongside wavelet transforms
- Improved robustness against noise through adaptive filtering techniques
These developments aim at refining cycle detection accuracy while reducing false positives—a critical factor given crypto's unpredictable nature.
Practical Steps for Using The Hilbert Transform in Trading Strategies
If you're considering incorporating this technique into your trading toolkit:
- Collect high-quality historical price data relevant to your asset class.2.. Apply preprocessing steps such as detrending or filtering out noise components.3.. Use software packages (e.g., MATLAB, Python libraries like SciPy) capable of performing analytical signal computations via Fourier transforms combined with empirical mode decomposition if needed.4.. Analyze resulting instantaneous frequencies/phases alongside traditional indicators for confirmation signals.5.. Backtest strategies rigorously before deploying them live.
Final Thoughts: Harnessing Advanced Signal Processing Techniques
The application of sophisticated mathematical tools such as The Hilbert Transform marks an evolution toward more scientific approaches within financial analysis—particularly suited for volatile assets like cryptocurrencies where traditional methods may fall short alone. By providing insights into hidden cyclicality through detailed frequency-phase analysis, investors gain another layer of understanding about market dynamics—not just looking at past prices but also anticipating future movements based on underlying rhythms embedded deep within price series data.
Note: As always when employing advanced analytical techniques involving complex mathematics—including spectral analyses—it’s essential to combine multiple sources of information along with sound risk management practices for optimal decision-making outcomes.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-14 15:09
How does the Hilbert Transform detect cycles in price series?
How Does the Hilbert Transform Detect Cycles in Price Series?
Understanding how financial markets, especially cryptocurrencies, exhibit recurring patterns or cycles is crucial for traders and analysts aiming to make informed decisions. One advanced mathematical tool that has gained prominence in this area is the Hilbert Transform. This technique allows analysts to identify underlying cyclical behaviors within price data that might not be visible through traditional methods. In this article, we explore how the Hilbert Transform works in detecting these cycles and why it has become a valuable asset in modern financial analysis.
What Is the Hilbert Transform?
The Hilbert Transform is a fundamental concept from signal processing, designed to analyze signals by transforming real-valued functions into complex representations. Essentially, it takes a real-valued time series—such as cryptocurrency prices—and produces an analytic signal comprising both amplitude and phase information. Mathematically, it involves an integral operation that shifts the phase of each frequency component of the original signal by 90 degrees.
This transformation results in a complex function where the original data forms the real part, and its transformed counterpart forms the imaginary part. The combined analytic signal provides richer information about oscillations within data sets—specifically their instantaneous frequency and amplitude—which are key indicators of cyclical behavior.
Applying the Hilbert Transform to Financial Data
In financial markets like cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum), price series often contain hidden periodicities or cycles driven by various factors such as investor sentiment, macroeconomic events, or technological developments. Traditional tools like moving averages or RSI (Relative Strength Index) can sometimes miss these subtle patterns because they focus on smoothing or momentum rather than frequency analysis.
By applying the Hilbert Transform to price data:
- Instantaneous Frequency: It reveals how quickly prices are oscillating at any given moment.
- Instantaneous Amplitude: It indicates how strong these oscillations are at specific points in time.
These two components help traders understand whether a market is entering a bullish or bearish phase based on cycle peaks and troughs detected through phase shifts derived from analytical signals.
How Does It Detect Cycles?
The core idea behind cycle detection using the Hilbert Transform lies in analyzing changes in phase angles over time. Once you obtain an analytic signal from your price series:
- Calculate its phase angle (( \phi(t) )), which describes where you are within a cycle.
- Derive instantaneous frequency (( \omega(t) = d\phi(t)/dt )) — essentially measuring how fast phases change.
- Identify recurring patterns when phases repeat or align over specific periods.
When certain frequencies persist across different segments of data—indicating regular oscillations—the method highlights potential cyclical behavior within market prices.
For example:
- A rising instantaneous frequency may suggest increasing volatility.
- Repeating phase patterns can point toward predictable cycles that traders could exploit for timing entries/exits.
Why Is Cycle Detection Important for Cryptocurrency Markets?
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility and complex dynamics compared to traditional assets like stocks or bonds. Identifying underlying cycles helps traders anticipate potential turning points before they occur—a significant advantage given crypto's rapid movements.
Using techniques like the Hilbert Transform enables:
- Better understanding of short-term versus long-term trends
- Detection of emerging bullish/bearish phases
- Validation of other technical indicators with more precise timing
Moreover, recent advancements have integrated machine learning with signal processing outputs from methods like this one—further improving accuracy and predictive power when analyzing noisy crypto data streams.
Limitations & Challenges
Despite its strengths, applying The Hilbert Transform isn't without challenges:
Noise Sensitivity: Crypto markets generate noisy signals; excessive noise can distort phase calculations leading to false cycle detections.
Overfitting Risks: Without proper validation techniques such as cross-validation on historical datasets, there's potential for overfitting models based on spurious signals.
Complex Interpretation: Understanding instantaneous frequency/amplitude requires advanced mathematical knowledge; misinterpretation could lead traders astray if not handled carefully.
To mitigate these issues:
- Use filtering techniques prior to applying transformations
- Combine results with other technical analysis tools
- Validate findings across multiple datasets
Recent Trends & Research Developments
Since around 2015–2016 when applications began gaining traction among quantitative analysts—and particularly since 2018–2019 with increased interest specifically targeting cryptocurrencies—the use of spectral analysis methods has expanded significantly.
Recent research published between 2022 and 2023 emphasizes:
- Enhanced algorithms integrating machine learning with spectral features derived via Fourier-based methods alongside wavelet transforms
- Improved robustness against noise through adaptive filtering techniques
These developments aim at refining cycle detection accuracy while reducing false positives—a critical factor given crypto's unpredictable nature.
Practical Steps for Using The Hilbert Transform in Trading Strategies
If you're considering incorporating this technique into your trading toolkit:
- Collect high-quality historical price data relevant to your asset class.2.. Apply preprocessing steps such as detrending or filtering out noise components.3.. Use software packages (e.g., MATLAB, Python libraries like SciPy) capable of performing analytical signal computations via Fourier transforms combined with empirical mode decomposition if needed.4.. Analyze resulting instantaneous frequencies/phases alongside traditional indicators for confirmation signals.5.. Backtest strategies rigorously before deploying them live.
Final Thoughts: Harnessing Advanced Signal Processing Techniques
The application of sophisticated mathematical tools such as The Hilbert Transform marks an evolution toward more scientific approaches within financial analysis—particularly suited for volatile assets like cryptocurrencies where traditional methods may fall short alone. By providing insights into hidden cyclicality through detailed frequency-phase analysis, investors gain another layer of understanding about market dynamics—not just looking at past prices but also anticipating future movements based on underlying rhythms embedded deep within price series data.
Note: As always when employing advanced analytical techniques involving complex mathematics—including spectral analyses—it’s essential to combine multiple sources of information along with sound risk management practices for optimal decision-making outcomes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
Decentralized exchanges, commonly known as DEXs, are transforming the landscape of cryptocurrency trading. Unlike traditional centralized platforms, DEXs operate without a single controlling authority, offering users greater control over their assets and transactions. This shift aligns with the core principles of blockchain technology—transparency, security, and decentralization—making DEXs an integral part of the rapidly expanding decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
How Do Decentralized Exchanges Work?
At their core, DEXs leverage smart contracts—self-executing contracts with coded rules—to facilitate trades directly between users. These smart contracts are deployed on blockchain networks such as Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. When traders initiate a swap or trade on a DEX, they interact with these smart contracts rather than relying on an intermediary like a bank or traditional exchange.
This mechanism ensures that transactions are transparent and tamper-proof since all activities are recorded immutably on the blockchain. Users retain control over their private keys and funds throughout the process, reducing risks associated with hacking or mismanagement often seen in centralized exchanges.
Types of Decentralized Exchanges
There are several main types of DEXs distinguished by how they facilitate trading:
Liquidity Pool-Based Platforms: These utilize pools of tokens locked into smart contracts to provide liquidity for various trading pairs. Users can contribute to these pools and earn fees in return.
Order Book-Based Platforms: Similar to traditional exchanges but operating in a decentralized manner. They maintain an order book where buy and sell orders are matched automatically through smart contract algorithms.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs): These use mathematical formulas to set prices based on available liquidity pools rather than order books. Popular AMMs include Uniswap and SushiSwap.
Each type offers different advantages concerning user experience, liquidity management, and scalability.
Benefits of Using a DEX
Decentralized exchanges offer several compelling benefits that appeal to both individual traders and institutional participants:
Enhanced Security: Since transactions occur directly on the blockchain via immutable records, there's less risk of fraud or hacking compared to centralized platforms which hold user funds.
Greater Transparency: All transaction data is publicly accessible on the blockchain network; this openness fosters trust among users.
Increased Accessibility: Anyone with internet access can participate without needing approval from intermediaries or undergoing extensive KYC procedures.
Censorship Resistance: No single entity controls the platform; thus it’s resistant to censorship attempts by governments or other authorities.
These features align well with DeFi's goal: creating open financial systems accessible worldwide without intermediaries.
Challenges Facing Decentralized Exchanges
Despite their advantages, DEXs face notable hurdles that could impact widespread adoption:
Scalability Issues
Many popular blockchains like Ethereum suffer from high gas fees during peak times due to network congestion. This makes small trades expensive and discourages casual users from engaging actively in DeFi markets hosted via DEXs.
Liquidity Constraints
For smaller or newer platforms especially those still establishing user bases, maintaining sufficient liquidity remains challenging. Low liquidity can lead to slippage—where traders receive less favorable prices—and reduced overall usability for large trades.
Regulatory Environment
The legal landscape surrounding DeFi is still evolving globally. Some jurisdictions consider certain aspects of decentralized trading platforms as unregulated securities markets—which could lead regulators like SEC imposing restrictions—or even bans in extreme cases.
Navigating this uncertain regulatory terrain requires ongoing compliance efforts from platform operators while educating users about potential risks involved in unregulated environments.
Recent Trends & Innovations in the Space
The growth trajectory for DEXs continues upward amid technological advancements:
Rise Within DeFi Ecosystem
Platforms such as Uniswap have become household names within crypto communities due to their ease-of-use interfaces combined with robust features like yield farming integrations—all contributing significantly toward mainstream acceptance of decentralized trading solutions.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
To address scalability issues inherent in base layer chains like Ethereum mainnet — characterized by high transaction costs — developers have turned toward layer 2 solutions such as Polygon (formerly Matic), Optimism, Arbitrum etc., which enable faster transactions at lower fees while maintaining security guarantees provided by underlying blockchains.
Alternative Blockchain Networks
Newer ecosystems including Solana and Polkadot offer faster transaction speeds coupled with lower costs compared to older chains; many projects now deploy cross-chain bridges enabling seamless asset transfers across multiple networks—a key step towards interoperability within DeFi space.
Security Enhancements & Risks
While blockchain technology inherently provides security benefits through cryptography and decentralization mechanisms—hack incidents targeting specific protocols highlight ongoing vulnerabilities requiring continuous improvement through audits—including multi-signature wallets—and advanced threat detection systems.
The Future Outlook for Decentralized Exchanges
As regulatory clarity improves globally alongside technological innovations addressing current limitations such as scalability concerns—the outlook for DEX adoption appears promising yet cautious. Continued development around layer 2 scaling solutions will likely make decentralized trading more affordable for everyday users while fostering increased trust through enhanced security measures.
However—as regulatory scrutiny intensifies—the industry must balance innovation with compliance standards ensuring consumer protection without compromising decentralization principles that underpin these platforms’ ethos.
By staying informed about emerging trends—including new protocols adopting cross-chain functionalities—and practicing best security practices when interacting within DeFi environments—users can maximize benefits while minimizing risks associated with this rapidly evolving sector.
This comprehensive overview aims at providing clarity around what decentralized exchanges are—from operational mechanics through recent innovations—and helps readers understand both opportunities offered by these platforms along with existing challenges they face today within broader financial landscapes driven increasingly by decentralization principles.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-11 12:41
What is a decentralized exchange (DEX)?
What Is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
Decentralized exchanges, commonly known as DEXs, are transforming the landscape of cryptocurrency trading. Unlike traditional centralized platforms, DEXs operate without a single controlling authority, offering users greater control over their assets and transactions. This shift aligns with the core principles of blockchain technology—transparency, security, and decentralization—making DEXs an integral part of the rapidly expanding decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
How Do Decentralized Exchanges Work?
At their core, DEXs leverage smart contracts—self-executing contracts with coded rules—to facilitate trades directly between users. These smart contracts are deployed on blockchain networks such as Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. When traders initiate a swap or trade on a DEX, they interact with these smart contracts rather than relying on an intermediary like a bank or traditional exchange.
This mechanism ensures that transactions are transparent and tamper-proof since all activities are recorded immutably on the blockchain. Users retain control over their private keys and funds throughout the process, reducing risks associated with hacking or mismanagement often seen in centralized exchanges.
Types of Decentralized Exchanges
There are several main types of DEXs distinguished by how they facilitate trading:
Liquidity Pool-Based Platforms: These utilize pools of tokens locked into smart contracts to provide liquidity for various trading pairs. Users can contribute to these pools and earn fees in return.
Order Book-Based Platforms: Similar to traditional exchanges but operating in a decentralized manner. They maintain an order book where buy and sell orders are matched automatically through smart contract algorithms.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs): These use mathematical formulas to set prices based on available liquidity pools rather than order books. Popular AMMs include Uniswap and SushiSwap.
Each type offers different advantages concerning user experience, liquidity management, and scalability.
Benefits of Using a DEX
Decentralized exchanges offer several compelling benefits that appeal to both individual traders and institutional participants:
Enhanced Security: Since transactions occur directly on the blockchain via immutable records, there's less risk of fraud or hacking compared to centralized platforms which hold user funds.
Greater Transparency: All transaction data is publicly accessible on the blockchain network; this openness fosters trust among users.
Increased Accessibility: Anyone with internet access can participate without needing approval from intermediaries or undergoing extensive KYC procedures.
Censorship Resistance: No single entity controls the platform; thus it’s resistant to censorship attempts by governments or other authorities.
These features align well with DeFi's goal: creating open financial systems accessible worldwide without intermediaries.
Challenges Facing Decentralized Exchanges
Despite their advantages, DEXs face notable hurdles that could impact widespread adoption:
Scalability Issues
Many popular blockchains like Ethereum suffer from high gas fees during peak times due to network congestion. This makes small trades expensive and discourages casual users from engaging actively in DeFi markets hosted via DEXs.
Liquidity Constraints
For smaller or newer platforms especially those still establishing user bases, maintaining sufficient liquidity remains challenging. Low liquidity can lead to slippage—where traders receive less favorable prices—and reduced overall usability for large trades.
Regulatory Environment
The legal landscape surrounding DeFi is still evolving globally. Some jurisdictions consider certain aspects of decentralized trading platforms as unregulated securities markets—which could lead regulators like SEC imposing restrictions—or even bans in extreme cases.
Navigating this uncertain regulatory terrain requires ongoing compliance efforts from platform operators while educating users about potential risks involved in unregulated environments.
Recent Trends & Innovations in the Space
The growth trajectory for DEXs continues upward amid technological advancements:
Rise Within DeFi Ecosystem
Platforms such as Uniswap have become household names within crypto communities due to their ease-of-use interfaces combined with robust features like yield farming integrations—all contributing significantly toward mainstream acceptance of decentralized trading solutions.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
To address scalability issues inherent in base layer chains like Ethereum mainnet — characterized by high transaction costs — developers have turned toward layer 2 solutions such as Polygon (formerly Matic), Optimism, Arbitrum etc., which enable faster transactions at lower fees while maintaining security guarantees provided by underlying blockchains.
Alternative Blockchain Networks
Newer ecosystems including Solana and Polkadot offer faster transaction speeds coupled with lower costs compared to older chains; many projects now deploy cross-chain bridges enabling seamless asset transfers across multiple networks—a key step towards interoperability within DeFi space.
Security Enhancements & Risks
While blockchain technology inherently provides security benefits through cryptography and decentralization mechanisms—hack incidents targeting specific protocols highlight ongoing vulnerabilities requiring continuous improvement through audits—including multi-signature wallets—and advanced threat detection systems.
The Future Outlook for Decentralized Exchanges
As regulatory clarity improves globally alongside technological innovations addressing current limitations such as scalability concerns—the outlook for DEX adoption appears promising yet cautious. Continued development around layer 2 scaling solutions will likely make decentralized trading more affordable for everyday users while fostering increased trust through enhanced security measures.
However—as regulatory scrutiny intensifies—the industry must balance innovation with compliance standards ensuring consumer protection without compromising decentralization principles that underpin these platforms’ ethos.
By staying informed about emerging trends—including new protocols adopting cross-chain functionalities—and practicing best security practices when interacting within DeFi environments—users can maximize benefits while minimizing risks associated with this rapidly evolving sector.
This comprehensive overview aims at providing clarity around what decentralized exchanges are—from operational mechanics through recent innovations—and helps readers understand both opportunities offered by these platforms along with existing challenges they face today within broader financial landscapes driven increasingly by decentralization principles.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Revenue-Sharing Tokens Operate?
Revenue-sharing tokens have emerged as a notable innovation within the blockchain and cryptocurrency landscape, offering a unique way to align incentives between project creators and token holders. Understanding how these tokens operate requires examining their structure, revenue distribution mechanisms, trading dynamics, and the regulatory environment that influences their functionality.
What Are Revenue-Sharing Tokens?
At their core, revenue-sharing tokens are digital assets issued on blockchain platforms that entitle holders to a portion of the income generated by a specific project or platform. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies that primarily serve as stores of value or mediums of exchange, these tokens function more like profit-sharing instruments. They leverage smart contracts—self-executing code on blockchains—to automate the process of revenue distribution based on predefined rules.
The primary motivation behind issuing revenue-sharing tokens is to incentivize participation and investment in projects such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, NFT marketplaces, or gaming ecosystems. By providing a share of revenues directly to token holders, projects aim to foster loyalty and long-term engagement while attracting liquidity providers and users.
How Do Revenue-Sharing Tokens Generate Income?
Revenue generation for these tokens typically stems from the underlying project's activities. For example:
- DeFi Platforms: Fees collected from trading activities or lending operations are pooled into a treasury.
- NFT Marketplaces: Royalties from secondary sales can be allocated for distribution.
- Gaming Ecosystems: In-game transaction fees or royalties from digital asset sales contribute to revenue pools.
Once accumulated in a treasury or reserve fund managed via smart contracts, this income is systematically distributed among token holders according to their holdings. The distribution process often involves several key features:
- Vesting Schedules: To prevent immediate sell-offs post-distribution events, many tokens include vesting periods during which rewards are gradually unlocked.
- Lockup Periods: These restrict token transfers for specified durations after issuance or during certain phases to promote stability.
This structured approach ensures that investors remain committed over time while aligning their interests with ongoing project success.
Trading Dynamics and Fee Generation
A significant aspect of revenue-sharing tokens is their trading activity. Many such tokens generate substantial fees through transactions—buying and selling—that occur within exchanges or decentralized platforms where they are listed. These trading fees often constitute an important source of income for both platform operators and token holders.
For instance, recent reports highlight cases where millions in trading fees have been accumulated since early 2025 despite lockup mechanisms designed to restrict immediate liquidity movement. This indicates active market participation but also raises questions about market stability given high transaction volumes driven by speculative traders.
Regulatory Considerations
The legal landscape surrounding revenue-sharing tokens remains complex and evolving across jurisdictions worldwide. Some regulators express concern over whether these instruments resemble securities due to profit-sharing features akin to traditional financial assets. As such:
- Certain authorities may scrutinize these tokens under securities laws.
- There’s potential for regulatory crackdowns if misuse occurs—for example, if funds are misappropriated or if transparency issues arise.
Recent investigations into prominent examples like the Trump Meme Coin underscore this risk; despite its lockup mechanism intended for investor protection, substantial trading fee generation prompted regulatory probes focusing on compliance issues.
Recent Developments Impacting Operation
Innovations continue shaping how revenue-sharing tokens operate today:
- Emergence of New Models: Projects like Kaspa USD demonstrate alternative approaches by integrating stablecoin-like features with revenue sharing on emerging blockchains.
- Enhanced Transparency Measures: To address trust concerns amid regulatory scrutiny—and prevent insider manipulation—many projects now adopt transparent reporting practices regarding revenues collected and distributed.
- Smart Contract Security Improvements: Given past vulnerabilities leading to losses (as seen in some high-profile cases), developers increasingly prioritize security audits before deploying smart contracts managing distributions.
These developments aim not only at improving operational efficiency but also at ensuring compliance with evolving legal standards while maintaining user confidence.
Risks Associated With Revenue-Sharing Tokens
While promising attractive yields through passive income streams linked directly with project success,
several risks must be considered:
Market Volatility: High transaction volumes driven by speculation can cause price swings that undermine investor confidence.
Regulatory Risks: Future legislation might classify certain types of revenue sharing as securities requiring registration—a costly process potentially limiting issuance options.
Security Vulnerabilities: Flaws in smart contract code could lead to significant financial losses if exploited by malicious actors—a risk highlighted by past incidents involving compromised distributions.
Trustworthiness & Transparency Issues: If projects lack clear disclosure about revenues generated versus distributed amounts—or engage in insider dealings—their credibility diminishes among users.
Understanding these risks helps investors make informed decisions when engaging with such financial instruments within crypto ecosystems.
Summary: The Future Outlook for Revenue-Sharing Tokens
Revenue-sharing tokens represent an innovative intersection between blockchain technology's transparency capabilities and traditional profit-distribution models found in conventional finance sectors like equities dividends or mutual funds managements—but adapted for decentralized environments. Their operation hinges upon secure smart contract execution combined with transparent reporting practices aimed at fostering trust among participants.
However,
their future depends heavily on navigating complex regulatory landscapes while maintaining market stability amidst volatile trading behaviors fueled partly by speculative interest rather than fundamental value growth.. As blockchain technology matures alongside evolving legal frameworks,
projects adopting this model will need robust security measures,clear communication strategies,and proactive compliance effortsto sustain long-term viability—and ultimately realize their potential as sustainable tools for democratized wealth sharing within decentralized economies


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-09 19:37
How do revenue-sharing tokens operate?
How Do Revenue-Sharing Tokens Operate?
Revenue-sharing tokens have emerged as a notable innovation within the blockchain and cryptocurrency landscape, offering a unique way to align incentives between project creators and token holders. Understanding how these tokens operate requires examining their structure, revenue distribution mechanisms, trading dynamics, and the regulatory environment that influences their functionality.
What Are Revenue-Sharing Tokens?
At their core, revenue-sharing tokens are digital assets issued on blockchain platforms that entitle holders to a portion of the income generated by a specific project or platform. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies that primarily serve as stores of value or mediums of exchange, these tokens function more like profit-sharing instruments. They leverage smart contracts—self-executing code on blockchains—to automate the process of revenue distribution based on predefined rules.
The primary motivation behind issuing revenue-sharing tokens is to incentivize participation and investment in projects such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, NFT marketplaces, or gaming ecosystems. By providing a share of revenues directly to token holders, projects aim to foster loyalty and long-term engagement while attracting liquidity providers and users.
How Do Revenue-Sharing Tokens Generate Income?
Revenue generation for these tokens typically stems from the underlying project's activities. For example:
- DeFi Platforms: Fees collected from trading activities or lending operations are pooled into a treasury.
- NFT Marketplaces: Royalties from secondary sales can be allocated for distribution.
- Gaming Ecosystems: In-game transaction fees or royalties from digital asset sales contribute to revenue pools.
Once accumulated in a treasury or reserve fund managed via smart contracts, this income is systematically distributed among token holders according to their holdings. The distribution process often involves several key features:
- Vesting Schedules: To prevent immediate sell-offs post-distribution events, many tokens include vesting periods during which rewards are gradually unlocked.
- Lockup Periods: These restrict token transfers for specified durations after issuance or during certain phases to promote stability.
This structured approach ensures that investors remain committed over time while aligning their interests with ongoing project success.
Trading Dynamics and Fee Generation
A significant aspect of revenue-sharing tokens is their trading activity. Many such tokens generate substantial fees through transactions—buying and selling—that occur within exchanges or decentralized platforms where they are listed. These trading fees often constitute an important source of income for both platform operators and token holders.
For instance, recent reports highlight cases where millions in trading fees have been accumulated since early 2025 despite lockup mechanisms designed to restrict immediate liquidity movement. This indicates active market participation but also raises questions about market stability given high transaction volumes driven by speculative traders.
Regulatory Considerations
The legal landscape surrounding revenue-sharing tokens remains complex and evolving across jurisdictions worldwide. Some regulators express concern over whether these instruments resemble securities due to profit-sharing features akin to traditional financial assets. As such:
- Certain authorities may scrutinize these tokens under securities laws.
- There’s potential for regulatory crackdowns if misuse occurs—for example, if funds are misappropriated or if transparency issues arise.
Recent investigations into prominent examples like the Trump Meme Coin underscore this risk; despite its lockup mechanism intended for investor protection, substantial trading fee generation prompted regulatory probes focusing on compliance issues.
Recent Developments Impacting Operation
Innovations continue shaping how revenue-sharing tokens operate today:
- Emergence of New Models: Projects like Kaspa USD demonstrate alternative approaches by integrating stablecoin-like features with revenue sharing on emerging blockchains.
- Enhanced Transparency Measures: To address trust concerns amid regulatory scrutiny—and prevent insider manipulation—many projects now adopt transparent reporting practices regarding revenues collected and distributed.
- Smart Contract Security Improvements: Given past vulnerabilities leading to losses (as seen in some high-profile cases), developers increasingly prioritize security audits before deploying smart contracts managing distributions.
These developments aim not only at improving operational efficiency but also at ensuring compliance with evolving legal standards while maintaining user confidence.
Risks Associated With Revenue-Sharing Tokens
While promising attractive yields through passive income streams linked directly with project success,
several risks must be considered:
Market Volatility: High transaction volumes driven by speculation can cause price swings that undermine investor confidence.
Regulatory Risks: Future legislation might classify certain types of revenue sharing as securities requiring registration—a costly process potentially limiting issuance options.
Security Vulnerabilities: Flaws in smart contract code could lead to significant financial losses if exploited by malicious actors—a risk highlighted by past incidents involving compromised distributions.
Trustworthiness & Transparency Issues: If projects lack clear disclosure about revenues generated versus distributed amounts—or engage in insider dealings—their credibility diminishes among users.
Understanding these risks helps investors make informed decisions when engaging with such financial instruments within crypto ecosystems.
Summary: The Future Outlook for Revenue-Sharing Tokens
Revenue-sharing tokens represent an innovative intersection between blockchain technology's transparency capabilities and traditional profit-distribution models found in conventional finance sectors like equities dividends or mutual funds managements—but adapted for decentralized environments. Their operation hinges upon secure smart contract execution combined with transparent reporting practices aimed at fostering trust among participants.
However,
their future depends heavily on navigating complex regulatory landscapes while maintaining market stability amidst volatile trading behaviors fueled partly by speculative interest rather than fundamental value growth.. As blockchain technology matures alongside evolving legal frameworks,
projects adopting this model will need robust security measures,clear communication strategies,and proactive compliance effortsto sustain long-term viability—and ultimately realize their potential as sustainable tools for democratized wealth sharing within decentralized economies
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Slashing Conditions in Staking: A Complete Guide
What Are Slashing Conditions in Blockchain Staking?
Slashing conditions are predefined rules embedded within blockchain protocols that penalize validators or stakers who act maliciously or negligently. In proof-of-stake (PoS) and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) systems, validators are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks. To ensure the network's security and integrity, these systems implement slashing mechanisms that automatically penalize misbehavior.
Typically, slashing involves confiscating a portion of the validator’s staked tokens as a penalty. This process not only discourages malicious activities but also aligns validators’ incentives with the health of the network. By enforcing strict penalties for misconduct such as double-signing or failing to validate correctly, slashing helps maintain trustworthiness within decentralized networks.
Why Are Slashing Conditions Important?
In blockchain ecosystems where security is paramount, maintaining honest validator behavior is critical. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single authority enforces rules, decentralized networks rely on economic incentives to promote good conduct among participants.
Slashing conditions serve multiple purposes:
- Deterring Malicious Actions: The threat of losing staked tokens discourages validators from attempting double-signing or submitting invalid transactions.
- Ensuring Network Security: By penalizing dishonest behavior swiftly and automatically, slashing reduces vulnerabilities like double-spending attacks.
- Aligning Incentives: Validators have skin in the game; their financial stake motivates them to act honestly because misconduct can lead to significant financial loss.
This mechanism fosters a trustworthy environment essential for applications like DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and other blockchain-based services that depend on secure validation processes.
Common Types of Misbehavior That Lead to Slashing
Validators can engage in various forms of misbehavior that trigger penalties under slashing conditions:
- Double-Signing: Signing two different blocks at the same height undermines consensus by creating conflicting versions of transaction history.
- Failing to Sign Blocks: Consistently missing block validations can slow down network performance and compromise reliability.
- Signing Invalid Blocks: Submitting fraudulent data or invalid signatures intentionally damages network integrity.
These violations threaten decentralization by potentially enabling malicious actors to manipulate transaction histories or disrupt consensus mechanisms.
How Do Slashing Penalties Work?
Slashing is typically implemented through smart contracts integrated into the blockchain protocol. When misbehavior occurs—detected either automatically via protocol rules or through community reporting—the system enforces penalties without human intervention.
The severity of penalties varies depending on factors such as:
- The type of misconduct
- The frequency or severity
- Protocol-specific parameters set by developers
Common consequences include:
- Confiscation of a specific percentage (often 5–50%) of staked tokens
- Temporary suspension from validating duties
- Permanent removal from validator pools
In some cases, repeated offenses may lead to complete exclusion from participation in validation activities altogether.
Recent Developments in Slashing Mechanisms
Blockchain projects continually refine their slashing protocols to enhance security while minimizing false positives that could unfairly punish honest validators.
Cardano (ADA)
Cardano’s Ouroboros protocol incorporates sophisticated slashing mechanisms aimed at preventing double-signing and other forms of misbehavior. In 2023, Cardano introduced an upgraded slasher system with increased penalties designed specifically for malicious activity detection[1]. These enhancements aim at deterring bad actors more effectively while preserving validator participation levels.
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot’s Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) system relies heavily on staking pools managed by nominators who select trustworthy validators. In 2022, Polkadot updated its protocol rules with stricter slashing conditions targeting non-participation issues like missed block signing[2]. These changes bolster overall network resilience against both accidental failures and intentional attacks.
Solana (SOL)
Solana employs its unique Proof-of-History consensus algorithm combined with staking mechanisms requiring high uptime standards from validators[3]. In 2024, Solana rolled out enhanced slasher features focused on preventing manipulative behaviors related to historical data tampering—an emerging concern given its fast-paced ecosystem[3].
These updates reflect ongoing efforts across leading networks worldwide toward balancing robust security measures with fair treatment for honest participants.
Impact on Validator Behavior & Network Security
The presence—and continuous improvement—of slashing conditions significantly influence how validators behave within these ecosystems:
- They promote responsible participation by making malicious acts costly.
- They help prevent attacks such as chain reorganization attempts or censorship strategies.
However, overly harsh penalties might discourage new entrants due to perceived risks; thus many protocols strive for balanced enforcement policies that protect security without deterring decentralization efforts altogether.
Furthermore, effective implementation ensures rapid response times when misbehavior occurs—minimizing potential damage during attack scenarios—and sustains user confidence crucial for mainstream adoption.
Challenges & Considerations When Implementing Slashes
While essential for maintaining trustworthiness in PoS/DPoS networks,
validators' risk management becomes complex due to factors like:
- False positives: Mistakenly penalizing honest nodes due to bugs or network latency
- Penalty calibration: Setting appropriate slash amounts so they’re punitive yet fair
- Community governance: Deciding how updates should modify existing slash policies
Developers must carefully design these parameters based on empirical data and community feedback while ensuring transparency around enforcement procedures.
Future Trends & Evolving Standards
As blockchain technology advances rapidly,
we expect further innovations around slashings including:
- Adaptive penalty models tailored dynamically based on network health metrics
- Cross-chain compatibility allowing shared standards between different ecosystems
- Enhanced dispute resolution processes involving community oversight
Moreover,regulatory considerations may influence how transparent slash enforcement remains over time — especially if token confiscations impact investor rights significantly.
Understanding what constitutes proper implementation alongside ongoing improvements will be vital as decentralized finance grows more complex and widespread across industries worldwide.
References
Cardano. (2023). Ouroboros Protocol Update: Enhanced Slaying Mechanism. Retrieved from https://www.cardano.org/en/blog/2023/02/ouroboros-protocol-update-enhanced-slashings/
Polkadot Network Blog. (2022). NPoS Protocol Update: Strengthened Slashings. Retrieved from https://polkadot.network/blog/npos-protocol-update-strengthened-slashings/
Solana Official Blog. (2024). Proof-of-History Update: Enhanced Slashings. Retrieved from https://solana.com/blog/proof-of-history-update-enhanced-slashings/


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 14:38
What are slashing conditions in staking?
Slashing Conditions in Staking: A Complete Guide
What Are Slashing Conditions in Blockchain Staking?
Slashing conditions are predefined rules embedded within blockchain protocols that penalize validators or stakers who act maliciously or negligently. In proof-of-stake (PoS) and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) systems, validators are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks. To ensure the network's security and integrity, these systems implement slashing mechanisms that automatically penalize misbehavior.
Typically, slashing involves confiscating a portion of the validator’s staked tokens as a penalty. This process not only discourages malicious activities but also aligns validators’ incentives with the health of the network. By enforcing strict penalties for misconduct such as double-signing or failing to validate correctly, slashing helps maintain trustworthiness within decentralized networks.
Why Are Slashing Conditions Important?
In blockchain ecosystems where security is paramount, maintaining honest validator behavior is critical. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single authority enforces rules, decentralized networks rely on economic incentives to promote good conduct among participants.
Slashing conditions serve multiple purposes:
- Deterring Malicious Actions: The threat of losing staked tokens discourages validators from attempting double-signing or submitting invalid transactions.
- Ensuring Network Security: By penalizing dishonest behavior swiftly and automatically, slashing reduces vulnerabilities like double-spending attacks.
- Aligning Incentives: Validators have skin in the game; their financial stake motivates them to act honestly because misconduct can lead to significant financial loss.
This mechanism fosters a trustworthy environment essential for applications like DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and other blockchain-based services that depend on secure validation processes.
Common Types of Misbehavior That Lead to Slashing
Validators can engage in various forms of misbehavior that trigger penalties under slashing conditions:
- Double-Signing: Signing two different blocks at the same height undermines consensus by creating conflicting versions of transaction history.
- Failing to Sign Blocks: Consistently missing block validations can slow down network performance and compromise reliability.
- Signing Invalid Blocks: Submitting fraudulent data or invalid signatures intentionally damages network integrity.
These violations threaten decentralization by potentially enabling malicious actors to manipulate transaction histories or disrupt consensus mechanisms.
How Do Slashing Penalties Work?
Slashing is typically implemented through smart contracts integrated into the blockchain protocol. When misbehavior occurs—detected either automatically via protocol rules or through community reporting—the system enforces penalties without human intervention.
The severity of penalties varies depending on factors such as:
- The type of misconduct
- The frequency or severity
- Protocol-specific parameters set by developers
Common consequences include:
- Confiscation of a specific percentage (often 5–50%) of staked tokens
- Temporary suspension from validating duties
- Permanent removal from validator pools
In some cases, repeated offenses may lead to complete exclusion from participation in validation activities altogether.
Recent Developments in Slashing Mechanisms
Blockchain projects continually refine their slashing protocols to enhance security while minimizing false positives that could unfairly punish honest validators.
Cardano (ADA)
Cardano’s Ouroboros protocol incorporates sophisticated slashing mechanisms aimed at preventing double-signing and other forms of misbehavior. In 2023, Cardano introduced an upgraded slasher system with increased penalties designed specifically for malicious activity detection[1]. These enhancements aim at deterring bad actors more effectively while preserving validator participation levels.
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot’s Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) system relies heavily on staking pools managed by nominators who select trustworthy validators. In 2022, Polkadot updated its protocol rules with stricter slashing conditions targeting non-participation issues like missed block signing[2]. These changes bolster overall network resilience against both accidental failures and intentional attacks.
Solana (SOL)
Solana employs its unique Proof-of-History consensus algorithm combined with staking mechanisms requiring high uptime standards from validators[3]. In 2024, Solana rolled out enhanced slasher features focused on preventing manipulative behaviors related to historical data tampering—an emerging concern given its fast-paced ecosystem[3].
These updates reflect ongoing efforts across leading networks worldwide toward balancing robust security measures with fair treatment for honest participants.
Impact on Validator Behavior & Network Security
The presence—and continuous improvement—of slashing conditions significantly influence how validators behave within these ecosystems:
- They promote responsible participation by making malicious acts costly.
- They help prevent attacks such as chain reorganization attempts or censorship strategies.
However, overly harsh penalties might discourage new entrants due to perceived risks; thus many protocols strive for balanced enforcement policies that protect security without deterring decentralization efforts altogether.
Furthermore, effective implementation ensures rapid response times when misbehavior occurs—minimizing potential damage during attack scenarios—and sustains user confidence crucial for mainstream adoption.
Challenges & Considerations When Implementing Slashes
While essential for maintaining trustworthiness in PoS/DPoS networks,
validators' risk management becomes complex due to factors like:
- False positives: Mistakenly penalizing honest nodes due to bugs or network latency
- Penalty calibration: Setting appropriate slash amounts so they’re punitive yet fair
- Community governance: Deciding how updates should modify existing slash policies
Developers must carefully design these parameters based on empirical data and community feedback while ensuring transparency around enforcement procedures.
Future Trends & Evolving Standards
As blockchain technology advances rapidly,
we expect further innovations around slashings including:
- Adaptive penalty models tailored dynamically based on network health metrics
- Cross-chain compatibility allowing shared standards between different ecosystems
- Enhanced dispute resolution processes involving community oversight
Moreover,regulatory considerations may influence how transparent slash enforcement remains over time — especially if token confiscations impact investor rights significantly.
Understanding what constitutes proper implementation alongside ongoing improvements will be vital as decentralized finance grows more complex and widespread across industries worldwide.
References
Cardano. (2023). Ouroboros Protocol Update: Enhanced Slaying Mechanism. Retrieved from https://www.cardano.org/en/blog/2023/02/ouroboros-protocol-update-enhanced-slashings/
Polkadot Network Blog. (2022). NPoS Protocol Update: Strengthened Slashings. Retrieved from https://polkadot.network/blog/npos-protocol-update-strengthened-slashings/
Solana Official Blog. (2024). Proof-of-History Update: Enhanced Slashings. Retrieved from https://solana.com/blog/proof-of-history-update-enhanced-slashings/
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding the Role of Volume Divergence in Confirming Breakouts
When analyzing financial markets, especially in technical analysis, traders seek reliable signals to predict future price movements. One such signal is volume divergence, a phenomenon that can provide critical confirmation—or warning—regarding potential breakouts. Recognizing how volume divergence works and its implications can significantly improve trading decisions across various asset classes, including stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
What Is Volume Divergence?
Volume divergence occurs when the trading volume does not align with the price action on a chart. In essence, it indicates a disconnect between how much trading activity is happening and the direction of price movement. This discrepancy often hints at underlying market strength or weakness that might not be immediately visible through price alone.
There are two primary types of volume divergence:
- Bullish Divergence: This happens when prices make lower lows while trading volumes increase. It suggests that buyers are becoming more aggressive despite falling prices, hinting at a possible trend reversal upward.
- Bearish Divergence: Conversely, this occurs when prices reach higher highs but accompanied by declining volumes. It indicates waning buying interest or increasing selling pressure at higher levels—potentially signaling an upcoming reversal downward.
Understanding these divergences helps traders gauge whether current trends are sustainable or if they might soon reverse.
How Volume Divergence Confirms Breakouts
Breakouts happen when an asset's price moves beyond established support or resistance levels with increased momentum. However, not all breakouts are genuine; some may be false signals caused by temporary volatility or market manipulation.
This is where volume divergence plays a crucial role:
Confirmation of Strength: A breakout accompanied by rising volume confirms strong participation from traders and investors. High-volume breakouts suggest conviction behind the move and increase the likelihood that the trend will continue.
Weakness Indication: Conversely, if a breakout occurs but trading volumes remain low or decline during the move, it raises suspicion about its sustainability. Low-volume breakouts often lack sufficient market commitment and may quickly reverse—a classic false signal scenario.
By analyzing whether volume supports or contradicts price movements during breakouts, traders can better assess their validity before entering trades.
Practical Applications in Trading Strategies
Incorporating volume divergence into your technical analysis toolkit enhances decision-making accuracy:
Combining with Other Indicators: Traders often use moving averages (like 50-day or 200-day) alongside RSI (Relative Strength Index) to identify overbought/oversold conditions combined with divergence signals for more robust entries.
Spotting Reversal Opportunities: Bullish divergences during downtrends can signal potential reversals upward if confirmed by increasing volumes during subsequent candles.
Filtering False Breakouts: When encountering apparent breakouts on charts without supporting high-volume activity—especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies—it’s prudent to wait for confirmation before committing capital.
Crypto Market Considerations: Due to high volatility and liquidity fluctuations in digital assets like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Binance Coin (BNB), monitoring volume divergences becomes even more vital for timely trade entries and exits.
Recent Trends & Developments in Cryptocurrency Markets
The cryptocurrency landscape has seen notable instances where volume divergence played pivotal roles:
During Bitcoin’s surge amid COVID-19 pandemic fears in 2020–2021, increasing volumes confirmed strong bullish momentum leading to new highs.
In 2023’s turbulent crypto environment marked by regulatory crackdowns and macroeconomic shifts, traders relied heavily on observing divergences between declining prices yet rising volumes as signs of potential reversals or continuation patterns.
These developments underscore how understanding volume dynamics remains essential amid evolving market conditions.
Risks & Limitations of Relying on Volume Divergence
While valuable as part of comprehensive analysis strategies, relying solely on volume divergence carries risks:
False Signals: Sudden spikes due to news events or speculative activity can produce misleading divergences that do not result in sustained moves.
Market Manipulation: Large players may artificially inflate trading volumes through wash trades or spoofing tactics to create deceptive signals—particularly prevalent within less regulated crypto exchanges.
Therefore, it's crucial for traders to corroborate findings from volume analysis with other technical tools such as chart patterns and fundamental insights before making decisions.
By understanding what constitutes valid signs of diverging trade activity—and recognizing their implications—you enhance your ability to confirm genuine breakouts versus false alarms effectively. Incorporating this knowledge into your overall strategy allows for more informed trades rooted in sound technical principles rather than speculation alone.
Key Takeaways:
- Volume divergence highlights discrepancies between trade activity and price movement
- Confirmed breakouts typically feature high-volume increases
- Low-volume breaks may indicate weak moves prone to reversal
- Combining multiple indicators improves reliability
- Awareness of manipulation risks safeguards against false signals
Mastery over interpreting these subtle cues empowers you as a trader seeking consistent success across diverse markets—including volatile cryptocurrencies—and helps build confidence grounded in analytical rigor rather than guesswork alone.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 09:39
What is the role of volume divergence in confirming breakouts?
Understanding the Role of Volume Divergence in Confirming Breakouts
When analyzing financial markets, especially in technical analysis, traders seek reliable signals to predict future price movements. One such signal is volume divergence, a phenomenon that can provide critical confirmation—or warning—regarding potential breakouts. Recognizing how volume divergence works and its implications can significantly improve trading decisions across various asset classes, including stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
What Is Volume Divergence?
Volume divergence occurs when the trading volume does not align with the price action on a chart. In essence, it indicates a disconnect between how much trading activity is happening and the direction of price movement. This discrepancy often hints at underlying market strength or weakness that might not be immediately visible through price alone.
There are two primary types of volume divergence:
- Bullish Divergence: This happens when prices make lower lows while trading volumes increase. It suggests that buyers are becoming more aggressive despite falling prices, hinting at a possible trend reversal upward.
- Bearish Divergence: Conversely, this occurs when prices reach higher highs but accompanied by declining volumes. It indicates waning buying interest or increasing selling pressure at higher levels—potentially signaling an upcoming reversal downward.
Understanding these divergences helps traders gauge whether current trends are sustainable or if they might soon reverse.
How Volume Divergence Confirms Breakouts
Breakouts happen when an asset's price moves beyond established support or resistance levels with increased momentum. However, not all breakouts are genuine; some may be false signals caused by temporary volatility or market manipulation.
This is where volume divergence plays a crucial role:
Confirmation of Strength: A breakout accompanied by rising volume confirms strong participation from traders and investors. High-volume breakouts suggest conviction behind the move and increase the likelihood that the trend will continue.
Weakness Indication: Conversely, if a breakout occurs but trading volumes remain low or decline during the move, it raises suspicion about its sustainability. Low-volume breakouts often lack sufficient market commitment and may quickly reverse—a classic false signal scenario.
By analyzing whether volume supports or contradicts price movements during breakouts, traders can better assess their validity before entering trades.
Practical Applications in Trading Strategies
Incorporating volume divergence into your technical analysis toolkit enhances decision-making accuracy:
Combining with Other Indicators: Traders often use moving averages (like 50-day or 200-day) alongside RSI (Relative Strength Index) to identify overbought/oversold conditions combined with divergence signals for more robust entries.
Spotting Reversal Opportunities: Bullish divergences during downtrends can signal potential reversals upward if confirmed by increasing volumes during subsequent candles.
Filtering False Breakouts: When encountering apparent breakouts on charts without supporting high-volume activity—especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies—it’s prudent to wait for confirmation before committing capital.
Crypto Market Considerations: Due to high volatility and liquidity fluctuations in digital assets like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Binance Coin (BNB), monitoring volume divergences becomes even more vital for timely trade entries and exits.
Recent Trends & Developments in Cryptocurrency Markets
The cryptocurrency landscape has seen notable instances where volume divergence played pivotal roles:
During Bitcoin’s surge amid COVID-19 pandemic fears in 2020–2021, increasing volumes confirmed strong bullish momentum leading to new highs.
In 2023’s turbulent crypto environment marked by regulatory crackdowns and macroeconomic shifts, traders relied heavily on observing divergences between declining prices yet rising volumes as signs of potential reversals or continuation patterns.
These developments underscore how understanding volume dynamics remains essential amid evolving market conditions.
Risks & Limitations of Relying on Volume Divergence
While valuable as part of comprehensive analysis strategies, relying solely on volume divergence carries risks:
False Signals: Sudden spikes due to news events or speculative activity can produce misleading divergences that do not result in sustained moves.
Market Manipulation: Large players may artificially inflate trading volumes through wash trades or spoofing tactics to create deceptive signals—particularly prevalent within less regulated crypto exchanges.
Therefore, it's crucial for traders to corroborate findings from volume analysis with other technical tools such as chart patterns and fundamental insights before making decisions.
By understanding what constitutes valid signs of diverging trade activity—and recognizing their implications—you enhance your ability to confirm genuine breakouts versus false alarms effectively. Incorporating this knowledge into your overall strategy allows for more informed trades rooted in sound technical principles rather than speculation alone.
Key Takeaways:
- Volume divergence highlights discrepancies between trade activity and price movement
- Confirmed breakouts typically feature high-volume increases
- Low-volume breaks may indicate weak moves prone to reversal
- Combining multiple indicators improves reliability
- Awareness of manipulation risks safeguards against false signals
Mastery over interpreting these subtle cues empowers you as a trader seeking consistent success across diverse markets—including volatile cryptocurrencies—and helps build confidence grounded in analytical rigor rather than guesswork alone.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding the MACD Histogram as a Standalone Momentum Indicator
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) histogram is widely recognized in technical analysis for its ability to visualize momentum shifts in financial markets. While traditionally used alongside other indicators, recent discussions have explored its potential as an independent measure of market strength. This article delves into how traders and investors can leverage the MACD histogram alone to gauge momentum, interpret signals accurately, and enhance trading strategies.
What Is the MACD Histogram?
The MACD histogram is a graphical representation that illustrates the difference between the MACD line and its signal line. It provides a clear visual cue about whether bullish or bearish momentum is prevailing. The core components of this indicator include:
- MACD Line: Calculated by subtracting the 26-period exponential moving average (EMA) from the 12-period EMA.
- Signal Line: A 9-period EMA of the MACD line.
- Histogram: The difference between these two lines plotted over time.
When viewed on a chart, positive bars indicate upward momentum, while negative bars suggest downward pressure. The height and direction of these bars help traders identify potential trend reversals or continuations without needing additional overlays.
How Can You Use the MACD Histogram Independently?
Traditionally, traders combine multiple indicators for confirmation; however, focusing solely on the MACD histogram can still provide valuable insights into market dynamics. Here are practical ways to use it as an independent momentum measure:
Identifying Trend Strength
The size of the histogram bars reflects how strong current momentum is. Larger positive bars suggest increasing bullish strength, whereas larger negative bars indicate intensifying bearish pressure. When these bars start shrinking after reaching peaks or troughs, it may signal weakening momentum—potentially leading to reversals.
Spotting Divergences
One powerful technique involves observing divergences between price action and histograms:
- Bullish Divergence: Price makes lower lows while histograms form higher lows — indicating diminishing selling pressure despite falling prices.
- Bearish Divergence: Price reaches higher highs but histograms show lower highs — signaling waning buying interest even as prices rise.
These divergences often precede significant trend changes and can be used independently if confirmed with other analysis tools like volume or candlestick patterns.
Recognizing Overbought/Oversold Conditions
Extreme values in histogram readings—either very high positive or negative—may suggest overextended market conditions:
- High positive values could imply overbought scenarios where upward movement might pause or reverse.
- Conversely, deep negative readings might point toward oversold levels with potential for rebound.
While not definitive signals alone, monitoring these extremes helps gauge when markets are ripe for correction based solely on momentum shifts observed through histograms.
Timing Entry and Exit Points
By observing changes in bar color (if your platform supports it) or size trends within your chart setup—such as decreasing bullish candles—the histogram can guide timing decisions without relying heavily on other indicators. For example:
- A shift from increasing to decreasing positive bars could signal weakening bullishness before price declines.
- Conversely, rising negative bars may warn of accelerating downside before actual price drops occur.
This approach allows traders to act swiftly based purely on internal momentum cues derived from historical data represented by the histogram's behavior.
Advantages of Using Only The MACD Histogram
Focusing exclusively on this indicator offers several benefits:
- Simplicity: Reduces clutter by avoiding multiple overlays; ideal for quick decision-making.
- Clarity: Visualizes divergence patterns directly related to market strength without complex calculations.
- Real-Time Feedback: Provides immediate insight into changing sentiment through bar fluctuations.
- Versatility: Applicable across various asset classes including stocks, forex, commodities—and notably cryptocurrencies where rapid shifts occur frequently.
Moreover, since it's derived from moving averages—a lagging indicator—it inherently smooths out noise while highlighting genuine trend shifts when interpreted correctly as an independent tool rather than just part of a composite system.
Limitations & Risks When Using It Alone
Despite its usefulness as an independent measure of momentum,
it's crucial to recognize inherent limitations that necessitate cautious application:
False Signals: Like all lagging indicators rooted in past data points (moving averages), false positives are common during sideways markets or choppy conditions.
Market Noise Sensitivity: In highly volatile environments such as crypto markets during sudden news events or macroeconomic shocks,the histogram may produce conflicting signals that require careful interpretation beyond mere visual cues.
Lack of Contextual Confirmation: Relying solely on one indicator increases risk; combining with volume analysis or candlestick patterns enhances reliability but isn't always feasible if aiming for simplicity.
To mitigate these risks when using only this tool:
- Pay attention to divergence signals rather than isolated bar movements
- Watch for extreme readings indicating overbought/oversold states
- Confirm with broader market context before executing trades based solely on histogram cues
In essence, understanding that no single indicator guarantees success underscores prudent risk management practices alongside technical analysis strategies centered around the MACD histogram’s insights.
Enhancing Market Sentiment Analysis With The Histogram
Beyond individual trade setups,
the behavior of your Macd Histogram over time offers clues about overall market sentiment trends:
- Sustained high positive values often reflect strong bullish sentiment which could lead toward exhaustion phases
- Persistent negative readings might indicate entrenched bearishness approaching capitulation points
By tracking how quickly these values change—whether they accelerate rapidly indicating panic selling/buying—or stabilize at certain levels,
traders gain nuanced perspectives about underlying investor psychology without needing additional tools.
This makes it especially valuable in fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies where sentiment swings rapidly influence price trajectories.
Integrating Automated Trading Systems Using Only The Histogram
In recent years,
algorithmic trading platforms have incorporated standalone use cases for metrics like those provided by macd Histograms due to their real-time responsiveness:
- Algorithms monitor real-time bar changes
- Detect divergence formations automatically
- Trigger buy/sell orders upon predefined thresholds
Such automation leverages pure technical signals derived from internal data structures within charts,reducing human bias while enabling swift reaction times essential during volatile sessions.
However,
it’s vital that automated systems incorporate safeguards against false signals generated during unpredictable spikes—a challenge common across all technical metrics used independently.
Proper backtesting combined with adaptive parameters ensures robustness when deploying such systems relying primarily on macd Histograms.
Final Thoughts
Using only the MACD histogram as an independent measure provides a streamlined approach towards understanding market momentum dynamics effectively suited for experienced traders comfortable interpreting subtle divergence patterns and extreme value conditions alone.
While not infallible nor comprehensive enough to replace multi-faceted analysis frameworks entirely,
its simplicity combined with insightful divergence detection makes it a valuable component within any trader’s toolkit aimed at capturing early signs of trend reversals and assessing ongoing strength.
Always remember that integrating fundamental insights along with disciplined risk management enhances overall trading performance—even when relying heavily on tools like this powerful yet straightforward indicator.
Note: For best results,combine observations from your Macd Histogram with broader contextual factors such as volume trends,market news,and macroeconomic developments whenever possible—to ensure well-rounded decision-making grounded in both technical precision and fundamental awareness


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 08:44
How can the MACD histogram be used as an independent momentum measure?
Understanding the MACD Histogram as a Standalone Momentum Indicator
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) histogram is widely recognized in technical analysis for its ability to visualize momentum shifts in financial markets. While traditionally used alongside other indicators, recent discussions have explored its potential as an independent measure of market strength. This article delves into how traders and investors can leverage the MACD histogram alone to gauge momentum, interpret signals accurately, and enhance trading strategies.
What Is the MACD Histogram?
The MACD histogram is a graphical representation that illustrates the difference between the MACD line and its signal line. It provides a clear visual cue about whether bullish or bearish momentum is prevailing. The core components of this indicator include:
- MACD Line: Calculated by subtracting the 26-period exponential moving average (EMA) from the 12-period EMA.
- Signal Line: A 9-period EMA of the MACD line.
- Histogram: The difference between these two lines plotted over time.
When viewed on a chart, positive bars indicate upward momentum, while negative bars suggest downward pressure. The height and direction of these bars help traders identify potential trend reversals or continuations without needing additional overlays.
How Can You Use the MACD Histogram Independently?
Traditionally, traders combine multiple indicators for confirmation; however, focusing solely on the MACD histogram can still provide valuable insights into market dynamics. Here are practical ways to use it as an independent momentum measure:
Identifying Trend Strength
The size of the histogram bars reflects how strong current momentum is. Larger positive bars suggest increasing bullish strength, whereas larger negative bars indicate intensifying bearish pressure. When these bars start shrinking after reaching peaks or troughs, it may signal weakening momentum—potentially leading to reversals.
Spotting Divergences
One powerful technique involves observing divergences between price action and histograms:
- Bullish Divergence: Price makes lower lows while histograms form higher lows — indicating diminishing selling pressure despite falling prices.
- Bearish Divergence: Price reaches higher highs but histograms show lower highs — signaling waning buying interest even as prices rise.
These divergences often precede significant trend changes and can be used independently if confirmed with other analysis tools like volume or candlestick patterns.
Recognizing Overbought/Oversold Conditions
Extreme values in histogram readings—either very high positive or negative—may suggest overextended market conditions:
- High positive values could imply overbought scenarios where upward movement might pause or reverse.
- Conversely, deep negative readings might point toward oversold levels with potential for rebound.
While not definitive signals alone, monitoring these extremes helps gauge when markets are ripe for correction based solely on momentum shifts observed through histograms.
Timing Entry and Exit Points
By observing changes in bar color (if your platform supports it) or size trends within your chart setup—such as decreasing bullish candles—the histogram can guide timing decisions without relying heavily on other indicators. For example:
- A shift from increasing to decreasing positive bars could signal weakening bullishness before price declines.
- Conversely, rising negative bars may warn of accelerating downside before actual price drops occur.
This approach allows traders to act swiftly based purely on internal momentum cues derived from historical data represented by the histogram's behavior.
Advantages of Using Only The MACD Histogram
Focusing exclusively on this indicator offers several benefits:
- Simplicity: Reduces clutter by avoiding multiple overlays; ideal for quick decision-making.
- Clarity: Visualizes divergence patterns directly related to market strength without complex calculations.
- Real-Time Feedback: Provides immediate insight into changing sentiment through bar fluctuations.
- Versatility: Applicable across various asset classes including stocks, forex, commodities—and notably cryptocurrencies where rapid shifts occur frequently.
Moreover, since it's derived from moving averages—a lagging indicator—it inherently smooths out noise while highlighting genuine trend shifts when interpreted correctly as an independent tool rather than just part of a composite system.
Limitations & Risks When Using It Alone
Despite its usefulness as an independent measure of momentum,
it's crucial to recognize inherent limitations that necessitate cautious application:
False Signals: Like all lagging indicators rooted in past data points (moving averages), false positives are common during sideways markets or choppy conditions.
Market Noise Sensitivity: In highly volatile environments such as crypto markets during sudden news events or macroeconomic shocks,the histogram may produce conflicting signals that require careful interpretation beyond mere visual cues.
Lack of Contextual Confirmation: Relying solely on one indicator increases risk; combining with volume analysis or candlestick patterns enhances reliability but isn't always feasible if aiming for simplicity.
To mitigate these risks when using only this tool:
- Pay attention to divergence signals rather than isolated bar movements
- Watch for extreme readings indicating overbought/oversold states
- Confirm with broader market context before executing trades based solely on histogram cues
In essence, understanding that no single indicator guarantees success underscores prudent risk management practices alongside technical analysis strategies centered around the MACD histogram’s insights.
Enhancing Market Sentiment Analysis With The Histogram
Beyond individual trade setups,
the behavior of your Macd Histogram over time offers clues about overall market sentiment trends:
- Sustained high positive values often reflect strong bullish sentiment which could lead toward exhaustion phases
- Persistent negative readings might indicate entrenched bearishness approaching capitulation points
By tracking how quickly these values change—whether they accelerate rapidly indicating panic selling/buying—or stabilize at certain levels,
traders gain nuanced perspectives about underlying investor psychology without needing additional tools.
This makes it especially valuable in fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies where sentiment swings rapidly influence price trajectories.
Integrating Automated Trading Systems Using Only The Histogram
In recent years,
algorithmic trading platforms have incorporated standalone use cases for metrics like those provided by macd Histograms due to their real-time responsiveness:
- Algorithms monitor real-time bar changes
- Detect divergence formations automatically
- Trigger buy/sell orders upon predefined thresholds
Such automation leverages pure technical signals derived from internal data structures within charts,reducing human bias while enabling swift reaction times essential during volatile sessions.
However,
it’s vital that automated systems incorporate safeguards against false signals generated during unpredictable spikes—a challenge common across all technical metrics used independently.
Proper backtesting combined with adaptive parameters ensures robustness when deploying such systems relying primarily on macd Histograms.
Final Thoughts
Using only the MACD histogram as an independent measure provides a streamlined approach towards understanding market momentum dynamics effectively suited for experienced traders comfortable interpreting subtle divergence patterns and extreme value conditions alone.
While not infallible nor comprehensive enough to replace multi-faceted analysis frameworks entirely,
its simplicity combined with insightful divergence detection makes it a valuable component within any trader’s toolkit aimed at capturing early signs of trend reversals and assessing ongoing strength.
Always remember that integrating fundamental insights along with disciplined risk management enhances overall trading performance—even when relying heavily on tools like this powerful yet straightforward indicator.
Note: For best results,combine observations from your Macd Histogram with broader contextual factors such as volume trends,market news,and macroeconomic developments whenever possible—to ensure well-rounded decision-making grounded in both technical precision and fundamental awareness
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
#Render glisse sous sa structure en triangle et approche la zone de demande $3.05–$3.25.
📊 Scénarios à surveiller : ✅ Si ça tient → possible rebond court terme vers $4.00+ 🚀 ❌ Si ça casse → chute probable vers la zone $2.50–$2.70 ⚠️
👉 Selon vous, $RNDR prépare un rebond solide ou une plongée plus profonde ?
#RNDR #AI #CryptoMarkets
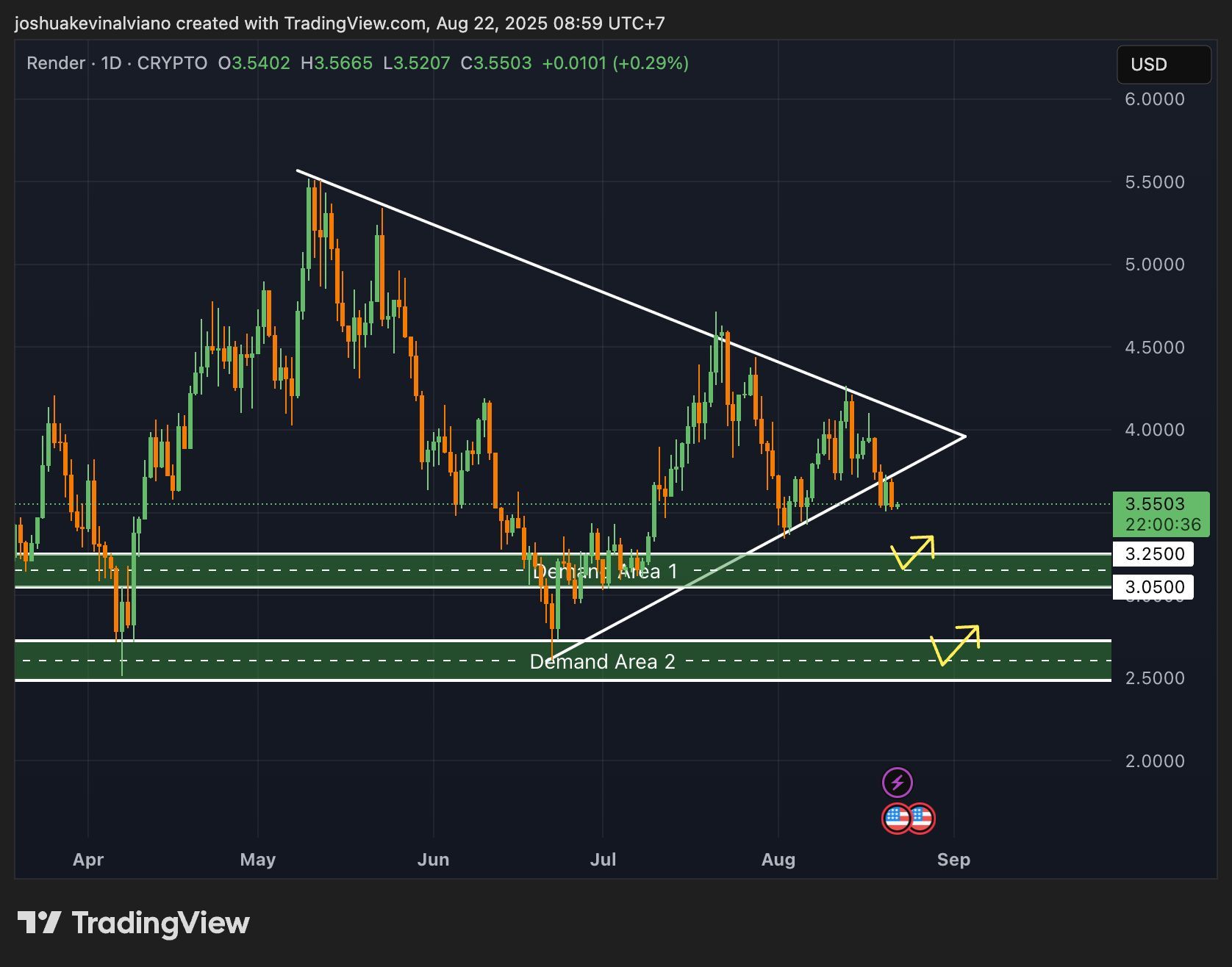


Carmelita
2025-08-22 11:50
$RNDR en zone critique : rebond ou cassure ?
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Can I Buy Chainlink (LINK)?
Buying Chainlink (LINK) is a straightforward process, but understanding the steps involved and the context behind this popular cryptocurrency can help you make informed decisions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to purchase Chainlink, including essential background information, practical steps, and key considerations for investors.
What Is Chainlink and Why Is It Valuable?
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that bridges real-world data with blockchain smart contracts. Founded in 2017 by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis, it has become an integral part of the blockchain ecosystem by enabling smart contracts to access external data securely and reliably. This capability unlocks numerous use cases across decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, supply chain management, and more.
The tokenomics of Chainlink involve a total supply of 1 billion LINK tokens. Its partnerships with major organizations like Google, Oracle, and SWIFT underscore its credibility as a trusted provider of real-world data feeds. As such, Chainlink plays a critical role in enhancing the functionality and security of blockchain applications.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Buy Chainlink
Choosing the Right Cryptocurrency Exchange
The first step in purchasing LINK involves selecting an appropriate cryptocurrency exchange. Popular platforms include Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, and Huobi—each offering user-friendly interfaces suitable for beginners as well as advanced traders. When choosing an exchange:
- Consider security features
- Review fee structures
- Check if they support your preferred payment methods
- Ensure they list LINK trading pairs
Creating Your Account
Once you've selected an exchange:
- Sign up by providing your email address or phone number.
- Create a strong password.
- Complete identity verification procedures if required—this may involve submitting personal identification documents due to KYC (Know Your Customer) regulations.
- Enable two-factor authentication for added security.
Funding Your Account
After account setup:
- Deposit funds using accepted payment methods such as bank transfers or credit/debit cards.
- Some exchanges also accept deposits in other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum if you already hold them elsewhere.
Funding options vary depending on your location; ensure you select secure transfer methods to protect your assets.
Purchasing Chainlink Tokens
With funds available:
- Navigate to the trading section on your chosen platform.
- Search for "LINK" or "Chainlink."
- Decide whether to place a market order (buy at current market price) or limit order (set your desired price).
- Enter the amount you'd like to purchase.
- Confirm the transaction details before executing.
Most exchanges provide real-time charts so you can monitor price movements during this process.
Securing Your Investment: Storage Options
Post-purchase storage is crucial for safeguarding your LINK tokens:
- Hot wallets: Digital wallets connected online; convenient but more vulnerable—examples include MetaMask or Trust Wallet.
- Hardware wallets: Physical devices like Ledger Nano S/X offer enhanced security against hacking attempts.
For long-term holding or significant investments, hardware wallets are recommended due to their increased protection against cyber threats.
Additional Tips for Buying Chainlink Safely
Investors should consider several best practices when buying cryptocurrencies like LINK:
- Always verify you're on official websites or trusted apps before entering sensitive information.
- Use strong passwords combined with two-factor authentication where possible.
- Be cautious about phishing scams targeting crypto users via emails or fake websites claiming partnership announcements or wallet updates.
Staying informed about recent developments related to regulatory changes can also help mitigate risks associated with legal uncertainties affecting cryptocurrencies globally.
Understanding Market Dynamics Before Investing
While buying Link offers potential benefits given its role within DeFi ecosystems—and its recent integrations such as Ethereum 2.o—the market remains volatile influenced by broader economic factors and regulatory scrutiny worldwide.
It’s advisable not only to research current trends but also consider diversification strategies within your portfolio rather than investing solely in one asset class like cryptocurrencies.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Risks & Opportunities
Investing in chains like Link requires balancing potential rewards against inherent risks such as market volatility driven by macroeconomic shifts or regulatory actions from authorities including SEC scrutiny in some jurisdictions—which could impact prices negatively if adverse rulings occur.
Furthermore,
- Competition from other oracle networks*—like Band Protocol—or emerging technologies might influence future adoption rates impacting value growth prospects over time.
By staying updated through reputable sources—including official project channels—and understanding both technical fundamentals plus macroeconomic influences—you position yourself better when deciding how much exposure makes sense based on personal risk tolerance levels.
Summary: Key Takeaways When Buying Chainlink
To summarize,
– Choose reputable exchanges supporting LINK trading pairs
– Complete necessary registration procedures securely
– Fund accounts via trusted payment methods
– Use secure storage solutions post-purchase
– Stay informed about industry news & regulatory developments
Following these steps ensures that you approach purchasing chain link responsibly while maximizing safety measures aligned with best practices within crypto investing communities.
Remember: Investing responsibly involves ongoing education about project fundamentals alongside awareness of broader market conditions—a vital aspect that enhances confidence whether you're new entrant into crypto markets or experienced investor seeking diversification opportunities through innovative projects like Chainlink


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-29 04:33
How can I buy Chainlink?
How Can I Buy Chainlink (LINK)?
Buying Chainlink (LINK) is a straightforward process, but understanding the steps involved and the context behind this popular cryptocurrency can help you make informed decisions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to purchase Chainlink, including essential background information, practical steps, and key considerations for investors.
What Is Chainlink and Why Is It Valuable?
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that bridges real-world data with blockchain smart contracts. Founded in 2017 by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis, it has become an integral part of the blockchain ecosystem by enabling smart contracts to access external data securely and reliably. This capability unlocks numerous use cases across decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, supply chain management, and more.
The tokenomics of Chainlink involve a total supply of 1 billion LINK tokens. Its partnerships with major organizations like Google, Oracle, and SWIFT underscore its credibility as a trusted provider of real-world data feeds. As such, Chainlink plays a critical role in enhancing the functionality and security of blockchain applications.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Buy Chainlink
Choosing the Right Cryptocurrency Exchange
The first step in purchasing LINK involves selecting an appropriate cryptocurrency exchange. Popular platforms include Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, and Huobi—each offering user-friendly interfaces suitable for beginners as well as advanced traders. When choosing an exchange:
- Consider security features
- Review fee structures
- Check if they support your preferred payment methods
- Ensure they list LINK trading pairs
Creating Your Account
Once you've selected an exchange:
- Sign up by providing your email address or phone number.
- Create a strong password.
- Complete identity verification procedures if required—this may involve submitting personal identification documents due to KYC (Know Your Customer) regulations.
- Enable two-factor authentication for added security.
Funding Your Account
After account setup:
- Deposit funds using accepted payment methods such as bank transfers or credit/debit cards.
- Some exchanges also accept deposits in other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum if you already hold them elsewhere.
Funding options vary depending on your location; ensure you select secure transfer methods to protect your assets.
Purchasing Chainlink Tokens
With funds available:
- Navigate to the trading section on your chosen platform.
- Search for "LINK" or "Chainlink."
- Decide whether to place a market order (buy at current market price) or limit order (set your desired price).
- Enter the amount you'd like to purchase.
- Confirm the transaction details before executing.
Most exchanges provide real-time charts so you can monitor price movements during this process.
Securing Your Investment: Storage Options
Post-purchase storage is crucial for safeguarding your LINK tokens:
- Hot wallets: Digital wallets connected online; convenient but more vulnerable—examples include MetaMask or Trust Wallet.
- Hardware wallets: Physical devices like Ledger Nano S/X offer enhanced security against hacking attempts.
For long-term holding or significant investments, hardware wallets are recommended due to their increased protection against cyber threats.
Additional Tips for Buying Chainlink Safely
Investors should consider several best practices when buying cryptocurrencies like LINK:
- Always verify you're on official websites or trusted apps before entering sensitive information.
- Use strong passwords combined with two-factor authentication where possible.
- Be cautious about phishing scams targeting crypto users via emails or fake websites claiming partnership announcements or wallet updates.
Staying informed about recent developments related to regulatory changes can also help mitigate risks associated with legal uncertainties affecting cryptocurrencies globally.
Understanding Market Dynamics Before Investing
While buying Link offers potential benefits given its role within DeFi ecosystems—and its recent integrations such as Ethereum 2.o—the market remains volatile influenced by broader economic factors and regulatory scrutiny worldwide.
It’s advisable not only to research current trends but also consider diversification strategies within your portfolio rather than investing solely in one asset class like cryptocurrencies.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Risks & Opportunities
Investing in chains like Link requires balancing potential rewards against inherent risks such as market volatility driven by macroeconomic shifts or regulatory actions from authorities including SEC scrutiny in some jurisdictions—which could impact prices negatively if adverse rulings occur.
Furthermore,
- Competition from other oracle networks*—like Band Protocol—or emerging technologies might influence future adoption rates impacting value growth prospects over time.
By staying updated through reputable sources—including official project channels—and understanding both technical fundamentals plus macroeconomic influences—you position yourself better when deciding how much exposure makes sense based on personal risk tolerance levels.
Summary: Key Takeaways When Buying Chainlink
To summarize,
– Choose reputable exchanges supporting LINK trading pairs
– Complete necessary registration procedures securely
– Fund accounts via trusted payment methods
– Use secure storage solutions post-purchase
– Stay informed about industry news & regulatory developments
Following these steps ensures that you approach purchasing chain link responsibly while maximizing safety measures aligned with best practices within crypto investing communities.
Remember: Investing responsibly involves ongoing education about project fundamentals alongside awareness of broader market conditions—a vital aspect that enhances confidence whether you're new entrant into crypto markets or experienced investor seeking diversification opportunities through innovative projects like Chainlink
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.